Abdominal Pain During Pregnancy
Abdominal pain is a common complaint during pregnancy, affecting up to 80% of women. While most abdominal pain is benign and resolves on its own, some types can indicate a more serious underlying condition. It is important to be aware of the different causes of abdominal pain during pregnancy and when to seek medical attention.
Causes of Abdominal Pain During Pregnancy
- Round ligament pain: This is a sharp, stabbing pain that occurs on one or both sides of the abdomen. It is caused by the stretching of the round ligaments, which support the uterus. Round ligament pain is usually mild and resolves on its own.
- Uterine contractions: Braxton Hicks contractions are practice contractions that occur throughout pregnancy. They are usually painless, but some women may experience mild abdominal discomfort. True labor contractions are more intense and regular, and they usually indicate that labor is imminent.
- Gas and bloating: Pregnancy hormones can slow down the digestive system, leading to gas and bloating. This can cause abdominal pain, discomfort, and flatulence.
- Constipation: Pregnancy hormones can also cause constipation, which can lead to abdominal pain and discomfort.
- Heartburn and indigestion: Pregnancy hormones can relax the valve between the stomach and esophagus, allowing stomach acid to reflux into the esophagus. This can cause heartburn and indigestion, which can lead to abdominal pain.
- Urinary tract infection (UTI): A UTI is a bacterial infection of the urinary tract. It can cause abdominal pain, burning with urination, and frequent urination.
- Ectopic pregnancy: An ectopic pregnancy occurs when the fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, usually in the fallopian tube. This can cause severe abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding, and other symptoms.
- Placental abruption: Placental abruption occurs when the placenta separates from the uterus before the baby is born. This can cause severe abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding, and other symptoms.
- Preeclampsia: Preeclampsia is a pregnancy-related condition characterized by high blood pressure and protein in the urine. It can cause abdominal pain, swelling, and other symptoms.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Most abdominal pain during pregnancy is benign and resolves on its own. However, it is important to seek medical attention if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- Severe abdominal pain that does not go away
- Abdominal pain accompanied by vaginal bleeding
- Abdominal pain accompanied by fever or chills
- Abdominal pain that is getting worse or more frequent
- Abdominal pain that is accompanied by other symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea
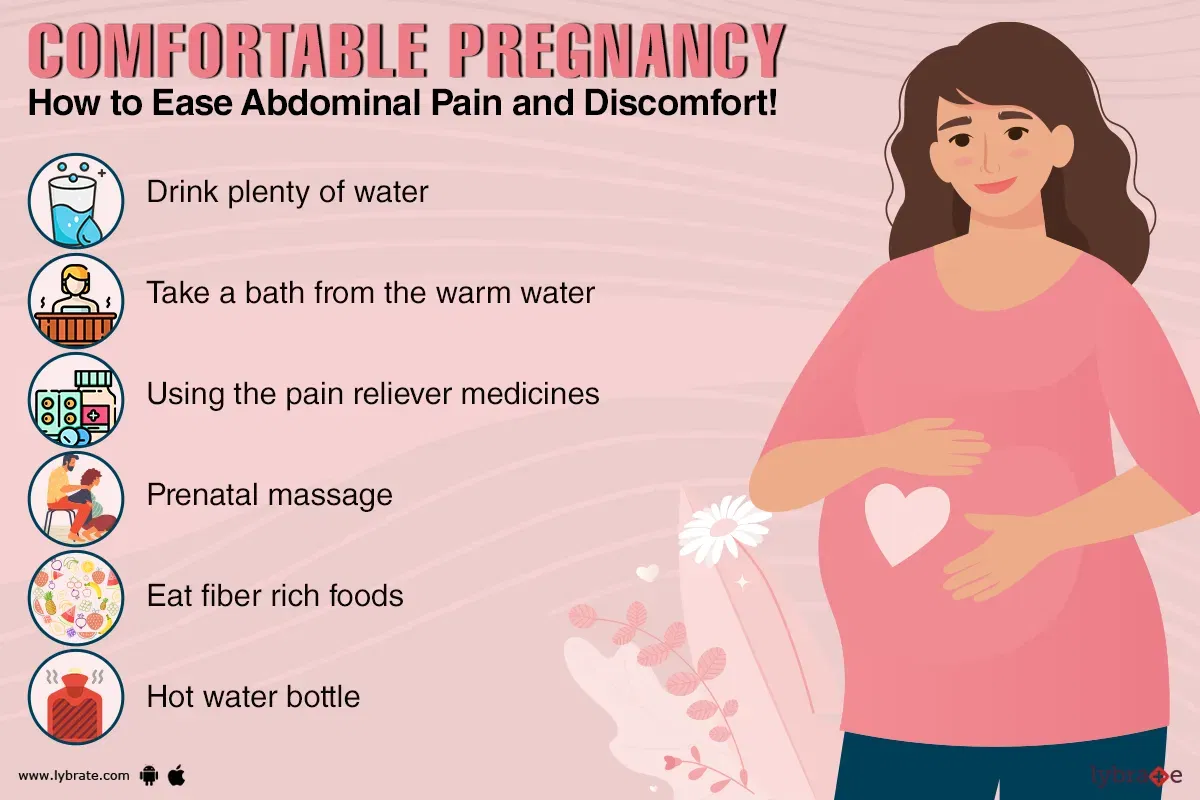
Treatment for Abdominal Pain During Pregnancy
The treatment for abdominal pain during pregnancy will depend on the underlying cause. For mild abdominal pain, home remedies such as rest, heat, and over-the-counter pain relievers may be helpful. For more severe abdominal pain, medical treatment may be necessary.
Prevention of Abdominal Pain During Pregnancy
There is no sure way to prevent abdominal pain during pregnancy, but there are some things you can do to reduce your risk:
- Get regular prenatal care
- Eat a healthy diet
- Exercise regularly
- Get enough rest
- Avoid smoking and alcohol
- Manage stress
Conclusion
Abdominal pain is a common complaint during pregnancy, but it is important to be aware of the different causes and when to seek medical attention. Most abdominal pain is benign and resolves on its own, but some types can indicate a more serious underlying condition. By following the tips above, you can reduce your risk of abdominal pain during pregnancy and ensure a healthy pregnancy.