Abortion Rates for Teen Pregnancy: A Comprehensive Analysis
Introduction
Teen pregnancy remains a significant public health concern in the United States, with far-reaching implications for both the young mothers and their children. Abortion is a common choice for pregnant teenagers, and understanding the factors that influence abortion rates is crucial for developing effective prevention and intervention strategies. This article delves into the complex landscape of abortion rates for teen pregnancy, examining the latest data, trends, and contributing factors.
National Trends
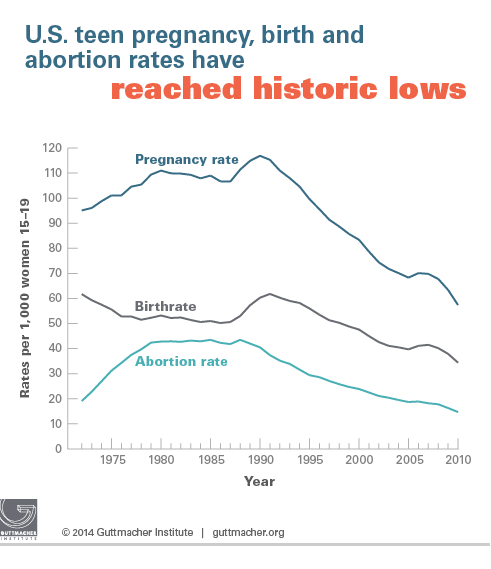
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the abortion rate for teenagers aged 15-19 in the United States has declined significantly over the past few decades. In 2020, the abortion rate was 10.8 abortions per 1,000 women in this age group, down from 39.6 abortions per 1,000 women in 1980. This decline is attributed to various factors, including increased access to contraception, improved sex education, and a shift in societal attitudes towards teen pregnancy.
Racial and Ethnic Disparities
Despite the overall decline in abortion rates, significant racial and ethnic disparities persist. Black and Hispanic teenagers have consistently higher abortion rates than their white counterparts. In 2020, the abortion rate for Black teenagers was 26.1 abortions per 1,000 women, while the rate for Hispanic teenagers was 15.8 abortions per 1,000 women. These disparities are likely due to a combination of factors, including socioeconomic status, access to healthcare, and cultural beliefs.
Geographic Variations
Abortion rates for teen pregnancy also vary significantly across different geographic regions of the United States. In 2020, the highest abortion rates were found in the South (12.8 abortions per 1,000 women), followed by the Midwest (11.4 abortions per 1,000 women), the West (9.8 abortions per 1,000 women), and the Northeast (7.9 abortions per 1,000 women). These variations may be influenced by factors such as state laws and policies, access to reproductive healthcare services, and cultural norms.
Contributing Factors
Numerous factors contribute to the decision of a teenager to have an abortion. These include:
- Unintended Pregnancy: The vast majority of teen pregnancies are unintended, resulting from unprotected sexual activity or contraceptive failure.
- Lack of Access to Contraception: Limited access to affordable and effective contraception can increase the risk of unintended pregnancy and subsequent abortion.
- Socioeconomic Status: Teenagers from low-income families are more likely to have an abortion due to limited access to healthcare, education, and support services.
- Parental Involvement: Parental support and guidance can play a significant role in reducing the likelihood of teen pregnancy and abortion.
- Cultural Beliefs: Cultural norms and beliefs about abortion can influence the decision-making process for teenagers.
Consequences of Abortion
Abortion has both short-term and long-term consequences for teenagers. Short-term consequences may include physical discomfort, emotional distress, and potential complications. Long-term consequences can include increased risk of future infertility, mental health issues, and substance abuse. However, it is important to note that these consequences are not universal, and many teenagers who have abortions experience positive outcomes.
Prevention and Intervention Strategies
Preventing teen pregnancy and reducing abortion rates requires a comprehensive approach that addresses the underlying factors contributing to these issues. Effective strategies include:
- Comprehensive Sex Education: Providing teenagers with accurate and age-appropriate information about sexual health, contraception, and pregnancy prevention is crucial.
- Increased Access to Contraception: Ensuring that teenagers have access to affordable and effective contraception can significantly reduce the risk of unintended pregnancy.
- Parental Involvement: Encouraging parental involvement in discussions about sexual health and providing support for teenagers can help prevent teen pregnancy and abortion.
- Social Support Programs: Providing social support programs for teenagers, such as mentoring, counseling, and after-school programs, can help address the underlying factors that contribute to teen pregnancy.
Conclusion
Abortion rates for teen pregnancy have declined significantly in the United States over the past few decades, but racial and ethnic disparities and geographic variations persist. Understanding the factors that contribute to teen pregnancy and abortion is essential for developing effective prevention and intervention strategies. By addressing the underlying causes, providing comprehensive sex education, increasing access to contraception, and fostering parental involvement, we can work towards reducing teen pregnancy and abortion rates and improving the health and well-being of young people.