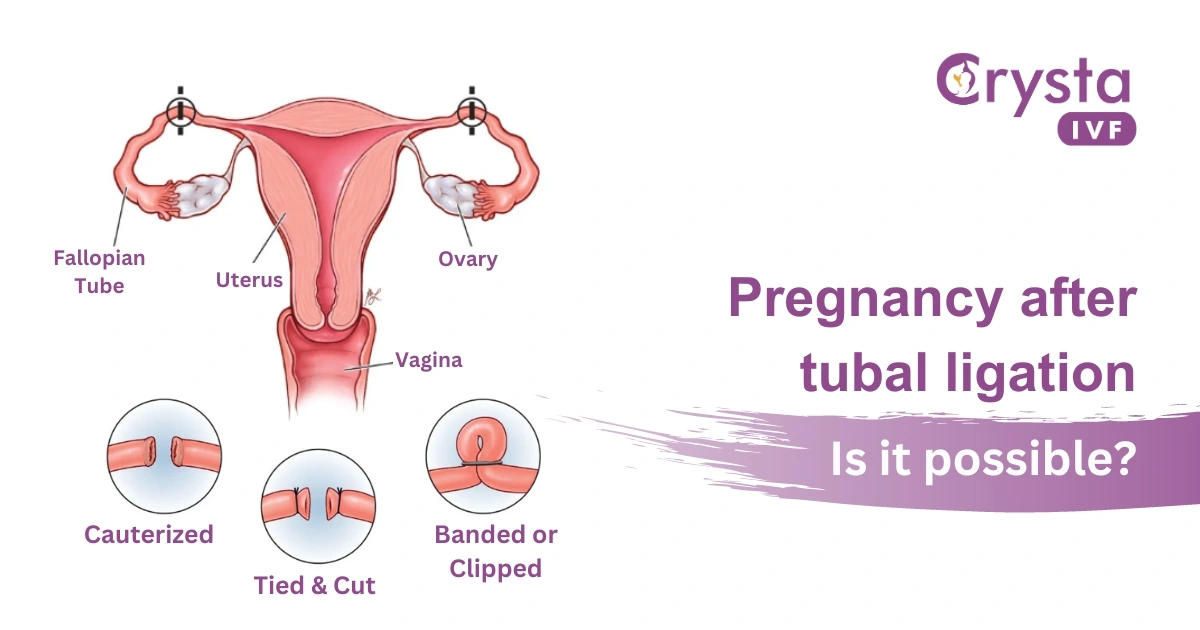
After the Chance: Pregnancy After Tubal Ligation
Tubal ligation, also known as "getting your tubes tied," is a surgical procedure that involves cutting, tying, or blocking the fallopian tubes to prevent pregnancy. It is a highly effective method of contraception, with a failure rate of less than 1%. However, in rare cases, women can become pregnant after tubal ligation. This is known as an after-chance pregnancy.
How Does an After-Chance Pregnancy Happen?
After-chance pregnancies can occur for several reasons:
- Tubal reanastomosis: The fallopian tubes can reconnect naturally after tubal ligation, allowing sperm to reach the eggs.
- Ectopic pregnancy: The fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, usually in the fallopian tube.
- Fistula formation: A small opening can develop between the uterus and the fallopian tube, allowing sperm to pass through.
- Surgical error: The fallopian tubes may not have been properly blocked or cut during the tubal ligation procedure.
Risk Factors for After-Chance Pregnancy
Certain factors can increase the risk of an after-chance pregnancy, including:
- Age: Women over 35 have a slightly higher risk of tubal reanastomosis.
- Type of tubal ligation: Certain methods, such as electrocoagulation, may be more likely to fail than others.
- Smoking: Smoking can damage the fallopian tubes and increase the risk of tubal reanastomosis.
- Hormonal factors: Women with high levels of estrogen may be more likely to experience tubal reanastomosis.
Symptoms of After-Chance Pregnancy
The symptoms of an after-chance pregnancy are similar to those of any other pregnancy, including:
- Missed period
- Nausea and vomiting
- Breast tenderness
- Fatigue
Diagnosis of After-Chance Pregnancy
An after-chance pregnancy can be diagnosed with a blood test to measure pregnancy hormones or an ultrasound to visualize the pregnancy.
Treatment Options for After-Chance Pregnancy
The treatment options for an after-chance pregnancy depend on the location of the pregnancy and the woman’s preferences.
- Ectopic pregnancy: An ectopic pregnancy is a medical emergency and requires immediate treatment. The fertilized egg must be removed to prevent life-threatening complications.
- Intrauterine pregnancy: If the pregnancy is located in the uterus, the woman can choose to continue the pregnancy or have an abortion.
Prevention of After-Chance Pregnancy
There is no surefire way to prevent an after-chance pregnancy, but there are steps women can take to reduce the risk:
- Choose a reliable tubal ligation method: Discuss the different methods with your doctor and choose one that has a low failure rate.
- Quit smoking: Smoking increases the risk of tubal reanastomosis.
- Monitor your menstrual cycle: If you experience any changes in your menstrual cycle, such as missed periods or irregular bleeding, consult your doctor.
- Consider additional contraception: If you are concerned about the risk of an after-chance pregnancy, you may want to consider using additional contraception, such as condoms or an intrauterine device (IUD).
Emotional Impact of After-Chance Pregnancy
An after-chance pregnancy can be a challenging experience emotionally. Women may feel a range of emotions, including shock, disappointment, and guilt. It is important to seek support from family, friends, or a therapist to process these emotions and make informed decisions about the pregnancy.
Conclusion
After-chance pregnancies are rare but possible. Understanding the risk factors, symptoms, and treatment options can help women make informed decisions about their reproductive health. By taking steps to reduce the risk of an after-chance pregnancy and seeking support if one occurs, women can navigate this unexpected event with confidence and compassion.