Weight Gain During Pregnancy: A Week-by-Week Guide
Pregnancy is a transformative journey that brings about significant physical changes in a woman’s body. One of the most noticeable changes is weight gain, which is essential for the healthy development of the baby. Understanding the recommended weight gain during pregnancy can help ensure optimal fetal growth and maternal well-being.
Recommended Weight Gain
The amount of weight a woman should gain during pregnancy varies depending on her pre-pregnancy body mass index (BMI). The Institute of Medicine (IOM) provides the following guidelines:
- Underweight (BMI < 18.5): 28-40 pounds
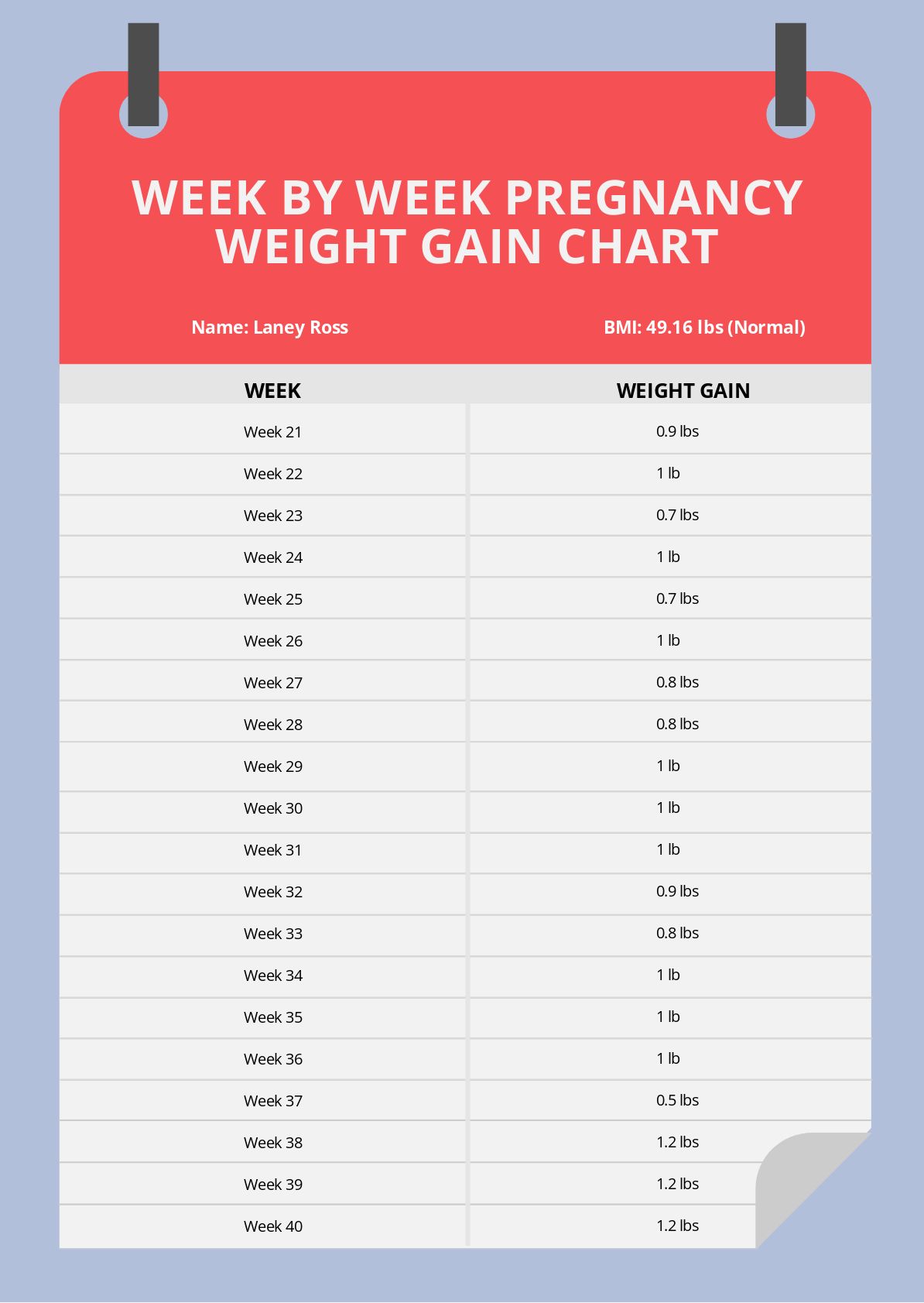
- Normal weight (BMI 18.5-24.9): 25-35 pounds
- Overweight (BMI 25-29.9): 15-25 pounds
- Obese (BMI ≥ 30): 11-20 pounds
Week-by-Week Weight Gain
Weight gain during pregnancy is not linear. It typically follows a gradual pattern, with most of the weight being gained in the second and third trimesters. Here is a week-by-week breakdown of recommended weight gain:
First Trimester (Weeks 1-12)
- Weeks 1-8: No significant weight gain expected
- Weeks 9-12: 1-2 pounds per week
Second Trimester (Weeks 13-28)
- Weeks 13-16: 1-2.5 pounds per week
- Weeks 17-20: 2-3 pounds per week
- Weeks 21-24: 2.5-3.5 pounds per week
- Weeks 25-28: 3-4 pounds per week
Third Trimester (Weeks 29-40)
- Weeks 29-32: 2.5-3.5 pounds per week
- Weeks 33-36: 2-3 pounds per week
- Weeks 37-40: 1-2 pounds per week
Factors Influencing Weight Gain
Several factors can influence weight gain during pregnancy, including:
- Pre-pregnancy weight: Women who are underweight or overweight before pregnancy may need to gain more or less weight, respectively.
- Multiple pregnancy: Carrying twins or triplets requires a higher weight gain.
- Activity level: Active women may gain less weight than sedentary women.
- Maternal age: Younger women tend to gain more weight than older women.
- Gestational diabetes: This condition can lead to excessive weight gain.
Consequences of Excessive or Insufficient Weight Gain
Both excessive and insufficient weight gain during pregnancy can have adverse consequences:
Excessive Weight Gain:
- Increased risk of gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, and cesarean delivery
- Difficulty losing weight after pregnancy
- Increased risk of obesity in the child
Insufficient Weight Gain:
- Low birth weight
- Premature birth
- Developmental problems in the child
Monitoring Weight Gain
Regular prenatal appointments provide an opportunity for healthcare providers to monitor weight gain and ensure it is within the recommended range. Women can also track their weight at home using a scale.
Tips for Healthy Weight Gain
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein.
- Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water.
- Exercise regularly, as recommended by your healthcare provider.
- Get enough sleep.
- Avoid smoking and alcohol.
Conclusion
Weight gain during pregnancy is a normal and necessary part of the process. Understanding the recommended weight gain guidelines and monitoring your weight regularly can help ensure optimal fetal growth and maternal well-being. By following a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and getting adequate rest, women can support their bodies and their babies throughout this transformative journey.