Effects of Smoking on Pregnancy: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
Smoking during pregnancy is a major public health concern, as it poses significant risks to both the mother and the developing fetus. The harmful effects of smoking on pregnancy are well-documented and extend beyond the immediate consequences to encompass long-term health implications for both the mother and child. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the effects of smoking on pregnancy, highlighting the risks and potential complications associated with this harmful habit.
Effects on the Mother
-
Increased risk of pregnancy complications: Smoking during pregnancy increases the risk of various pregnancy complications, including premature birth, placental abruption, and preeclampsia. Premature birth, which occurs before 37 weeks of gestation, is associated with increased risks of respiratory distress syndrome, cerebral palsy, and other developmental problems. Placental abruption is a condition in which the placenta separates from the uterine wall before delivery, leading to bleeding and potential fetal distress. Preeclampsia is a pregnancy-induced hypertensive disorder that can cause serious health problems for both the mother and the baby.
-
Reduced fertility: Smoking has been linked to reduced fertility in both men and women. In women, smoking can damage the eggs and ovaries, making it more difficult to conceive. In men, smoking can reduce sperm count and motility, impairing fertility.
-
Increased risk of miscarriage: Smoking during pregnancy increases the risk of miscarriage, which is the loss of a pregnancy before 20 weeks of gestation. The chemicals in cigarettes can damage the developing embryo and increase the likelihood of miscarriage.
-
Other health risks: Smoking during pregnancy can also increase the mother’s risk of developing other health problems, such as respiratory infections, gum disease, and cervical cancer.
Effects on the Fetus
-
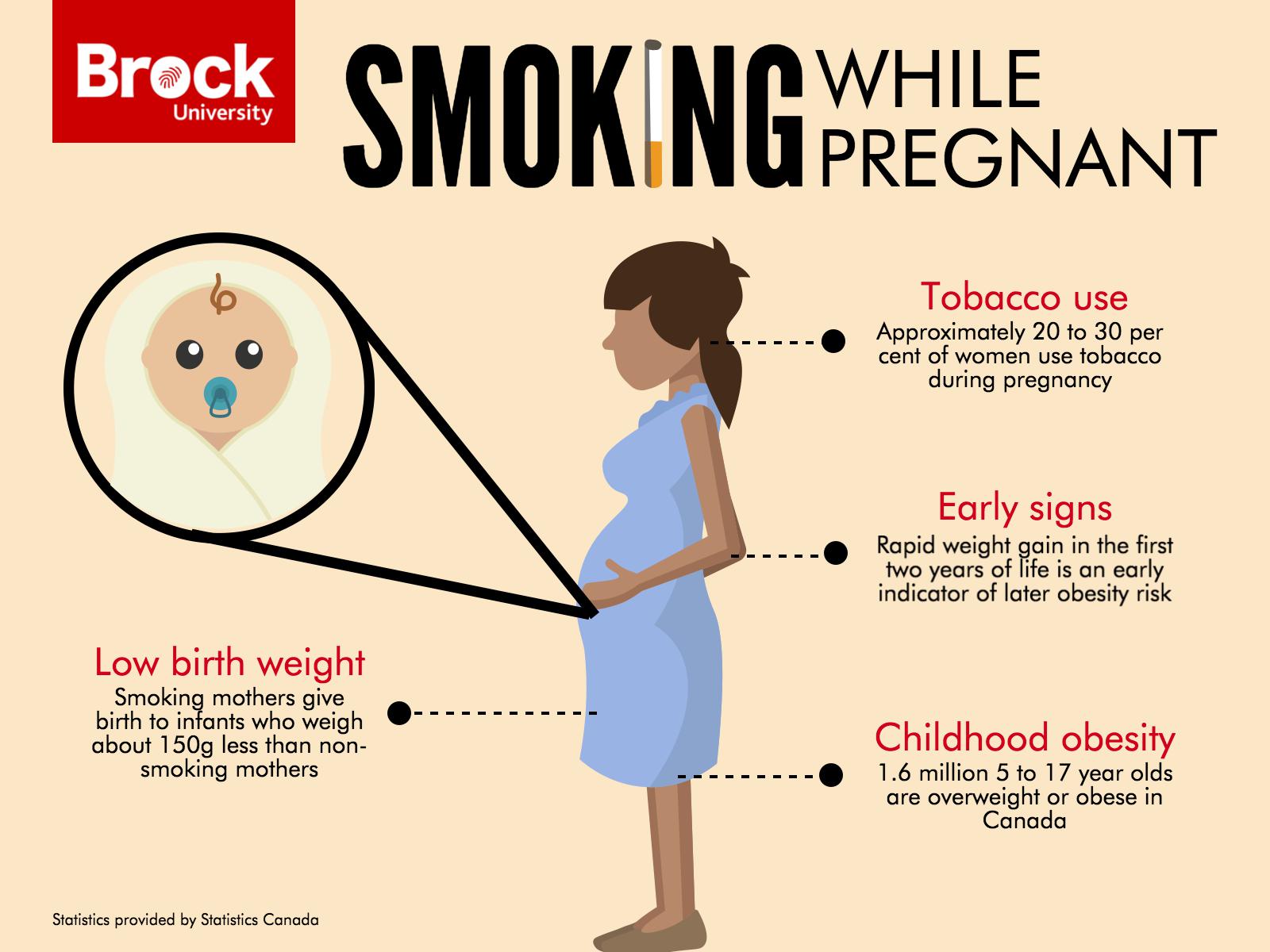
Low birth weight: Smoking during pregnancy is a major cause of low birth weight, which is defined as a birth weight below 2,500 grams (5 pounds, 8 ounces). Low birth weight infants are at increased risk of health problems, including respiratory distress syndrome, cerebral palsy, and developmental delays.
-
Preterm birth: As mentioned earlier, smoking during pregnancy increases the risk of preterm birth, which is associated with a range of health problems for the baby.
-
Congenital anomalies: Smoking during pregnancy has been linked to an increased risk of certain congenital anomalies, such as cleft lip and palate, heart defects, and neural tube defects.
-
Sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS): Smoking during pregnancy has been identified as a risk factor for SIDS, which is the sudden and unexplained death of an infant under one year of age.
-
Long-term health effects: Children exposed to tobacco smoke in utero may have an increased risk of developing respiratory problems, such as asthma and bronchitis, as well as cardiovascular disease and certain types of cancer later in life.
Mechanism of Action
The harmful effects of smoking on pregnancy are primarily attributed to the toxic chemicals present in cigarette smoke. These chemicals, which include nicotine, carbon monoxide, and tar, cross the placenta and reach the developing fetus.
-
Nicotine: Nicotine is a highly addictive substance that constricts blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the placenta and the fetus. This can lead to oxygen deprivation and impaired fetal growth.
-
Carbon monoxide: Carbon monoxide binds to hemoglobin in the blood, reducing the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood. This can also lead to oxygen deprivation and impaired fetal growth.
-
Tar: Tar is a sticky substance that contains numerous carcinogens and other harmful chemicals. Tar can damage the placenta and increase the risk of placental abruption.
Prevention and Cessation
Preventing smoking during pregnancy is crucial for protecting the health of both the mother and the baby. Healthcare providers should routinely screen pregnant women for tobacco use and provide counseling and support to help them quit. Effective cessation interventions include behavioral therapy, nicotine replacement therapy, and medications.
Quitting smoking at any point during pregnancy is beneficial, as it reduces the risks associated with smoking and improves the health outcomes for both the mother and the child.
Conclusion
Smoking during pregnancy is a serious public health issue that poses significant risks to both the mother and the developing fetus. The harmful effects of smoking on pregnancy extend beyond the immediate consequences to encompass long-term health implications for both the mother and child. Preventing smoking during pregnancy is essential for protecting the health of future generations. Healthcare providers, public health organizations, and society as a whole have a vital role to play in promoting smoking cessation and supporting pregnant women in their efforts to quit.