Ectopic Pregnancy: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
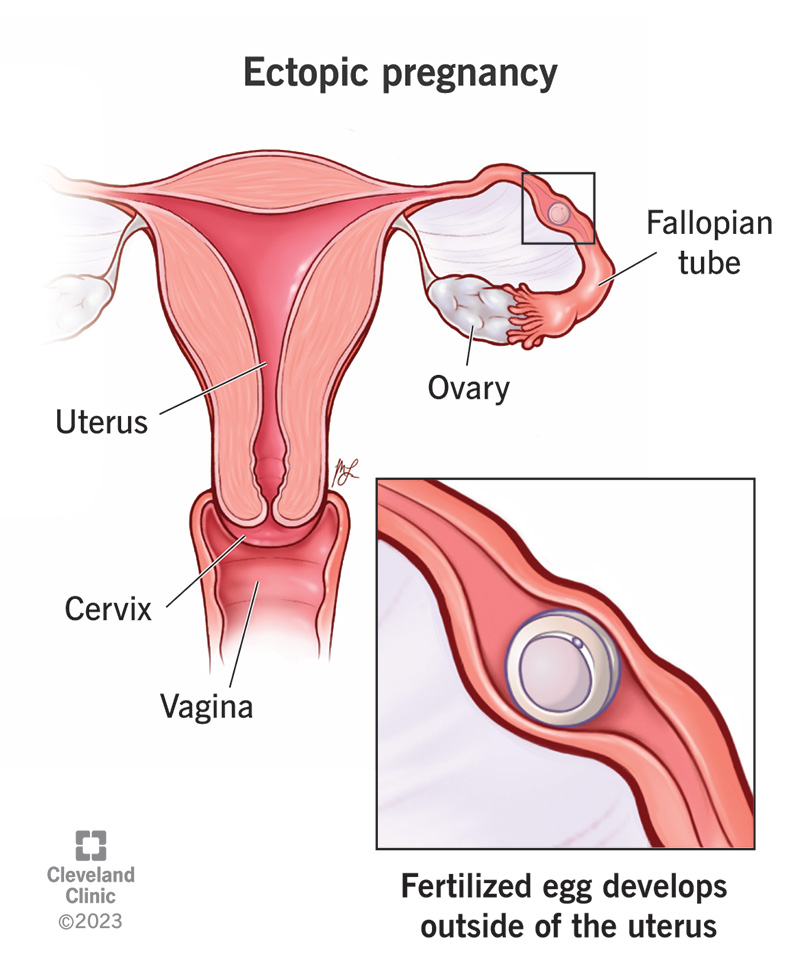
Ectopic pregnancy, a potentially life-threatening condition, occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterine cavity. This abnormal implantation can lead to serious complications, including internal bleeding, organ damage, and even death. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for ectopic pregnancy is crucial for ensuring timely and appropriate medical intervention.
Causes of Ectopic Pregnancy
The exact cause of ectopic pregnancy is often unknown, but several factors can increase the risk:
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): Inflammation of the reproductive organs, often caused by sexually transmitted infections, can damage the fallopian tubes, making them more likely to impede the passage of the fertilized egg.
- Tubal Surgery: Previous surgeries on the fallopian tubes, such as tubal ligation or sterilization, can create scarring or blockages that prevent the egg from reaching the uterus.
- Intrauterine Device (IUD): While IUDs are highly effective contraceptives, they can occasionally fail, and if pregnancy occurs, it is more likely to be ectopic.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Abnormal hormone levels can disrupt the normal functioning of the fallopian tubes, increasing the risk of ectopic implantation.
- Smoking: Smoking damages the cilia lining the fallopian tubes, impairing their ability to transport the fertilized egg.
Symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancies often present with nonspecific symptoms that can mimic other conditions, making early diagnosis challenging. Common symptoms include:
- Abdominal or pelvic pain: This pain can be sharp, stabbing, or cramping and may worsen with movement or pressure.
- Vaginal bleeding: The bleeding is typically light and irregular, but it can become heavier if the ectopic pregnancy ruptures.
- Nausea and vomiting: These symptoms are common in early pregnancy but can be more severe with an ectopic pregnancy.
- Shoulder pain: This pain is caused by internal bleeding that irritates the diaphragm.
- Weakness or dizziness: These symptoms can indicate blood loss or low blood pressure.
Diagnosis of Ectopic Pregnancy
Diagnosing an ectopic pregnancy requires a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests:
- Physical Examination: The doctor will check for tenderness or masses in the pelvic area.
- Transvaginal Ultrasound: This imaging test uses sound waves to create detailed images of the uterus and fallopian tubes, allowing the doctor to visualize the location of the pregnancy.
- Blood Tests: Measuring hormone levels, such as human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), can help determine the viability and location of the pregnancy.
Treatment Options for Ectopic Pregnancy
The primary goal of treatment for ectopic pregnancy is to remove the fertilized egg and prevent complications. The choice of treatment depends on the patient’s condition and the stage of the pregnancy:
- Medication (Methotrexate): This medication is used to terminate the pregnancy in its early stages. It is effective in about 95% of cases and is less invasive than surgery.
- Laparoscopic Surgery: This minimally invasive procedure involves making small incisions in the abdomen and using a laparoscope to visualize and remove the ectopic pregnancy.
- Salpingostomy: If the ectopic pregnancy is located in the fallopian tube, this surgical procedure can be performed to remove the pregnancy and preserve the tube.
- Salpingectomy: In severe cases, the affected fallopian tube may need to be removed to prevent further complications.
Complications of Ectopic Pregnancy
If left untreated, an ectopic pregnancy can lead to life-threatening complications:
- Tubal Rupture: The fallopian tube can rupture, causing internal bleeding and severe pain. This is a medical emergency that requires immediate surgery.
- Hemorrhage: Internal bleeding can lead to shock and organ damage.
- Infection: The ectopic pregnancy can become infected, leading to sepsis.
- Infertility: Damage to the fallopian tubes can increase the risk of future infertility.
Prognosis and Recovery
With timely diagnosis and treatment, most women recover fully from an ectopic pregnancy. However, the risk of future ectopic pregnancies is slightly increased. Women who have had an ectopic pregnancy should be closely monitored during subsequent pregnancies.
Prevention of Ectopic Pregnancy
While not all ectopic pregnancies can be prevented, certain measures can reduce the risk:
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) Prevention: Practicing safe sex and getting regular STI screenings can help prevent PID.
- Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking improves overall health and reduces the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
- Tubal Ligation: This permanent birth control method involves surgically blocking the fallopian tubes, preventing pregnancy altogether.
Conclusion
Ectopic pregnancy is a serious medical condition that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for ensuring the best possible outcome. While some ectopic pregnancies can be prevented, early detection and intervention are essential to minimize the risk of complications and preserve future fertility.