Low Levels of Progesterone and Early Pregnancy: A Comprehensive Overview
Progesterone, a crucial hormone during pregnancy, plays a pivotal role in maintaining a healthy uterine environment and supporting fetal development. However, low levels of progesterone in early pregnancy can raise concerns and potentially impact the viability of the pregnancy. This article delves into the significance of progesterone, explores the causes and consequences of low progesterone levels, and discusses management strategies to optimize pregnancy outcomes.
Role of Progesterone in Pregnancy
Progesterone is primarily produced by the corpus luteum, a temporary endocrine structure that forms after ovulation. Its primary functions during pregnancy include:
- Preparing the uterus for implantation: Progesterone thickens the uterine lining (endometrium), creating a receptive environment for the fertilized egg to implant.
- Maintaining uterine quiescence: Progesterone relaxes the uterine muscles, preventing premature contractions and ensuring a stable environment for fetal growth.
- Suppressing the immune system: Progesterone modulates the maternal immune response, preventing the rejection of the developing fetus.
- Promoting placental development: Progesterone supports the growth and function of the placenta, the vital organ that provides nutrients and oxygen to the fetus.
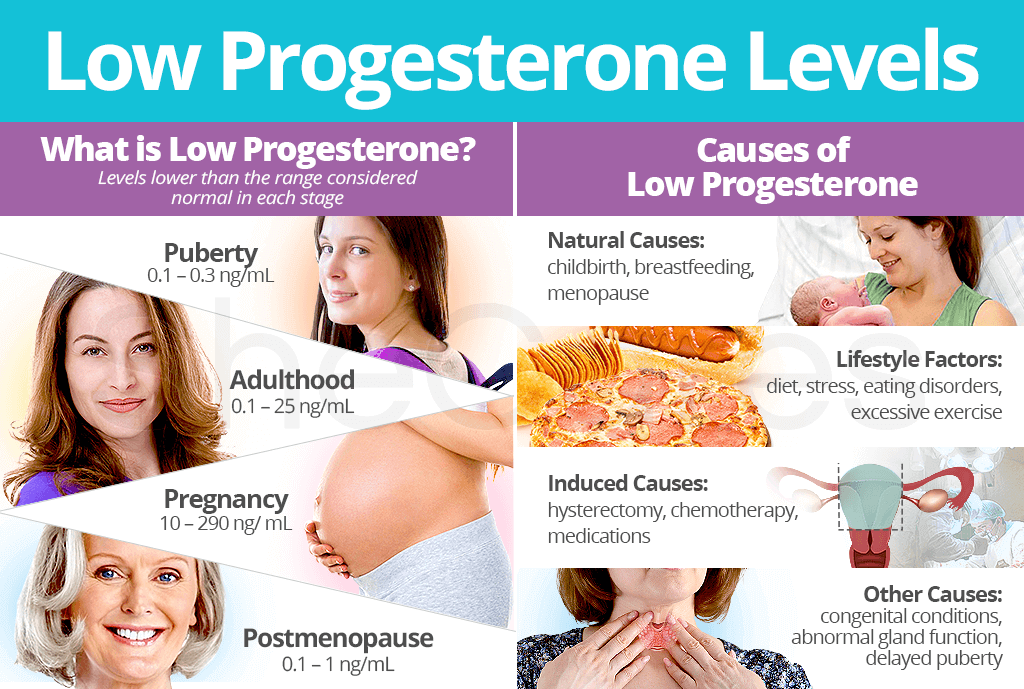
Causes of Low Progesterone Levels in Early Pregnancy
Various factors can contribute to low progesterone levels in early pregnancy, including:
- Corpus luteum insufficiency: The corpus luteum may fail to produce adequate progesterone, often due to underlying hormonal imbalances or structural abnormalities.
- Placental insufficiency: The placenta may not develop properly or function efficiently, resulting in reduced progesterone production.
- Ectopic pregnancy: A pregnancy that occurs outside the uterus, such as in the fallopian tube, may not produce sufficient progesterone.
- Threatened miscarriage: Low progesterone levels can be a sign of a threatened miscarriage, where the pregnancy is at risk of ending prematurely.
- Certain medications: Some medications, such as certain birth control pills or anti-inflammatory drugs, can interfere with progesterone production.
Consequences of Low Progesterone Levels in Early Pregnancy
Low progesterone levels in early pregnancy can have several potential consequences:
- Implantation failure: Insufficient progesterone can prevent the fertilized egg from implanting successfully in the uterus.
- Miscarriage: Low progesterone levels can weaken the uterine lining and increase the risk of miscarriage, especially in the first trimester.
- Preterm birth: Progesterone plays a crucial role in maintaining uterine quiescence. Low levels can increase the risk of premature contractions and preterm birth.
- Placental abruption: Low progesterone levels can impair placental development and increase the risk of placental abruption, a serious condition where the placenta separates from the uterus.
Management of Low Progesterone Levels in Early Pregnancy
The management of low progesterone levels in early pregnancy depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. Treatment options may include:
- Progesterone supplementation: Synthetic progesterone, in the form of injections, suppositories, or oral medications, can be administered to supplement low levels.
- Monitoring: Regular monitoring of progesterone levels and ultrasound examinations can help assess the effectiveness of treatment and track fetal development.
- Bed rest: In some cases, bed rest may be recommended to reduce uterine activity and support progesterone levels.
- Treatment of underlying causes: If an underlying condition, such as corpus luteum insufficiency or placental insufficiency, is identified, appropriate treatment will be provided to address the root cause.
Prognosis and Prevention
The prognosis for pregnancies with low progesterone levels depends on the severity of the condition and the underlying cause. With timely diagnosis and appropriate management, many pregnancies can be maintained and result in healthy outcomes.
Preventing low progesterone levels in early pregnancy is not always possible, but certain factors can increase the risk, such as:
- Age: Advanced maternal age is associated with an increased risk of corpus luteum insufficiency.
- Prior miscarriages: Women with a history of recurrent miscarriages may have underlying progesterone deficiencies.
- Certain medical conditions: Conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or thyroid disorders can affect progesterone production.
Conclusion
Low levels of progesterone in early pregnancy can have significant implications for the viability and health of the pregnancy. Understanding the causes, consequences, and management strategies is crucial for healthcare providers and patients alike. By addressing low progesterone levels promptly and effectively, the chances of a successful pregnancy and healthy fetal development can be significantly improved.