Pregnancy Test hCG Levels: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
Pregnancy tests are an essential tool for detecting the presence of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), a hormone produced by the placenta during pregnancy. hCG levels rise rapidly in the early stages of pregnancy, making it a reliable indicator of conception. Understanding hCG levels can provide valuable information about the progression and health of a pregnancy.
What is hCG?
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a glycoprotein hormone produced by the trophoblast cells of the placenta. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the corpus luteum, which secretes progesterone to support the early stages of pregnancy. hCG also stimulates the production of estrogen and progesterone, which are essential for fetal development.
hCG Levels During Pregnancy
hCG levels rise exponentially in the early stages of pregnancy. They typically double every 48-72 hours, reaching a peak around 8-12 weeks of gestation. After this point, hCG levels gradually decline throughout the remainder of the pregnancy.
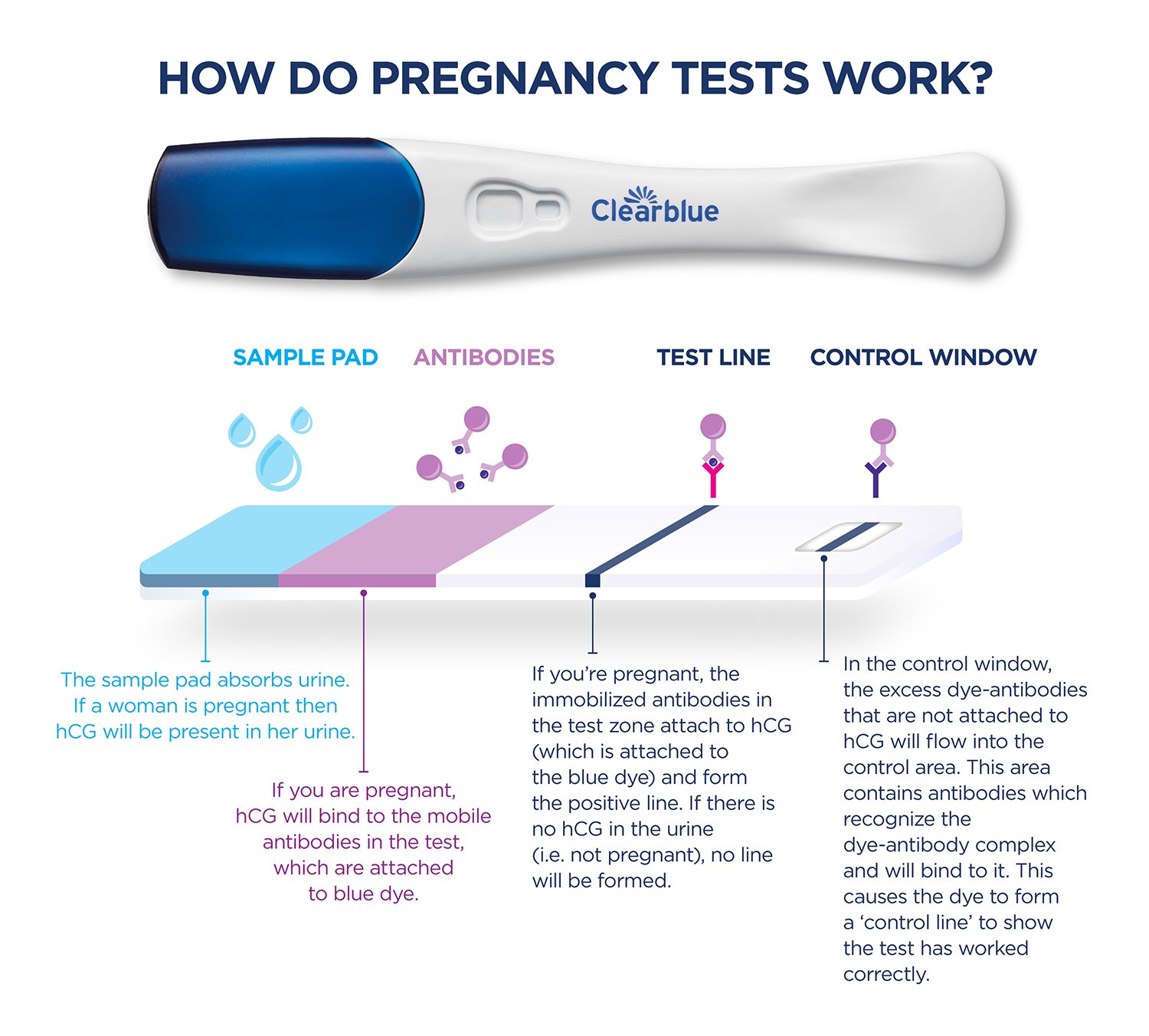
hCG Levels in Pregnancy Tests
Pregnancy tests detect hCG in urine or blood samples. Urine tests are the most common and convenient, but blood tests are more sensitive and can detect hCG earlier in pregnancy.
- Urine Tests: Most urine pregnancy tests can detect hCG levels as low as 20-25 mIU/mL. This is typically sensitive enough to detect pregnancy as early as 10-12 days after ovulation.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can detect hCG levels as low as 5-10 mIU/mL. This makes them more sensitive than urine tests and can detect pregnancy earlier, as early as 6-8 days after ovulation.
Interpreting hCG Levels
The interpretation of hCG levels depends on the stage of pregnancy and the type of test used.
- Early Pregnancy: In the early stages of pregnancy, hCG levels should double every 48-72 hours. If levels are not rising appropriately, it may indicate a potential problem, such as an ectopic pregnancy or miscarriage.
- Mid-Pregnancy: hCG levels peak around 8-12 weeks of gestation. After this point, they gradually decline throughout the remainder of the pregnancy. However, hCG levels can vary significantly between individuals, so it is important to consult with a healthcare provider to interpret the results.
- Late Pregnancy: hCG levels typically decline in the third trimester, but they may remain elevated in some cases, such as multiple pregnancies or pregnancies with certain medical conditions.
Factors Affecting hCG Levels
Several factors can affect hCG levels, including:
- Gestational Age: hCG levels rise rapidly in the early stages of pregnancy and peak around 8-12 weeks.
- Multiple Pregnancies: hCG levels are higher in multiple pregnancies, such as twins or triplets.
- Molar Pregnancy: A molar pregnancy is a rare condition in which a fertilized egg develops abnormally, resulting in high hCG levels.
- Ectopic Pregnancy: An ectopic pregnancy occurs when the fertilized egg implants outside the uterus. hCG levels may be lower than expected in this case.
- Miscarriage: hCG levels may drop or stop rising in the event of a miscarriage.
Clinical Significance of hCG Levels
hCG levels play a crucial role in the diagnosis, monitoring, and management of pregnancy.
- Diagnosis of Pregnancy: hCG levels are used to confirm pregnancy and estimate the gestational age.
- Monitoring Pregnancy: Serial hCG measurements can be used to monitor the progression and health of a pregnancy.
- Detection of Pregnancy Complications: Abnormal hCG levels may indicate potential complications, such as ectopic pregnancy, miscarriage, or molar pregnancy.
- Treatment of Pregnancy Complications: hCG levels can be used to guide treatment decisions in certain pregnancy complications, such as threatened miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy.
Conclusion
hCG levels are a valuable tool for detecting, monitoring, and managing pregnancy. Understanding the normal range of hCG levels and the factors that can affect them is essential for accurate interpretation and appropriate clinical decision-making. Regular prenatal care and consultations with a healthcare provider are crucial for ensuring the health and well-being of both the mother and the developing fetus.