Pregnancy Test hCG Levels: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
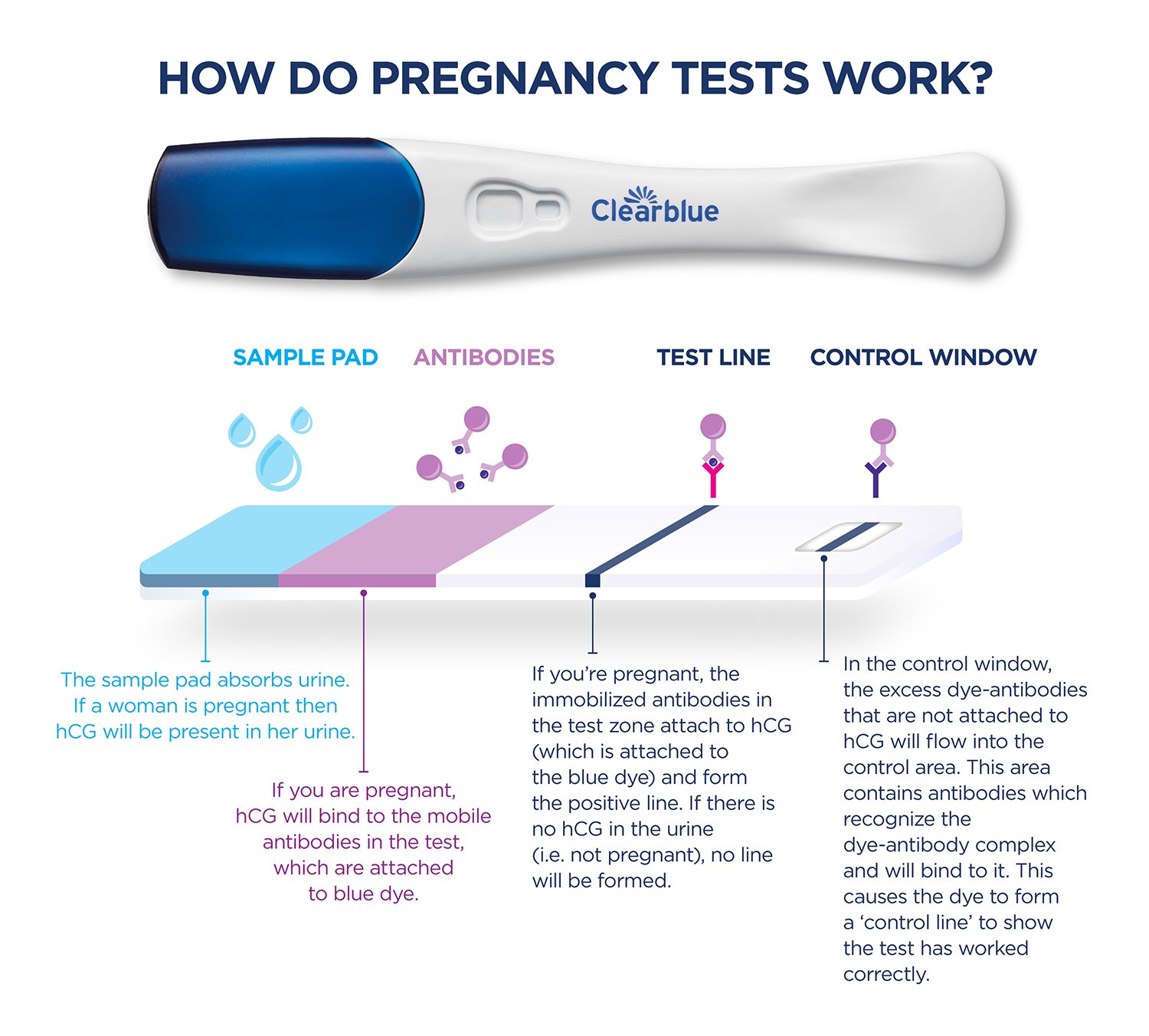
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a hormone produced by the placenta during pregnancy. Pregnancy tests detect hCG levels in urine or blood to determine if a woman is pregnant. Understanding hCG levels can provide valuable information about the progression of a pregnancy and potential complications.
hCG Production and Function
hCG production begins shortly after implantation of the fertilized egg in the uterine lining. Its primary function is to maintain the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone and estrogen. These hormones support the growth and development of the uterine lining and prevent menstruation.
hCG Levels During Pregnancy
hCG levels rise rapidly in early pregnancy, doubling every 2-3 days. They typically peak between 8-12 weeks of gestation and then gradually decline throughout the remainder of the pregnancy.
Normal hCG Levels
The following table provides an approximate range of normal hCG levels at different stages of pregnancy:
| Gestational Age | hCG Level (mIU/mL) |
|---|---|
| 3-4 weeks | 5-50 |
| 4-5 weeks | 10-426 |
| 5-6 weeks | 18-7,340 |
| 6-7 weeks | 1,080-56,500 |
| 7-8 weeks | 7,650-229,000 |
| 8-12 weeks | 25,700-288,000 |
| 12-16 weeks | 13,300-254,000 |
| 16-20 weeks | 4,060-165,400 |
| 20-24 weeks | 3,640-117,000 |
| 24-28 weeks | 2,530-90,200 |
| 28-32 weeks | 1,930-63,700 |
| 32-36 weeks | 1,230-47,300 |
| 36-40 weeks | 670-22,900 |
Factors Affecting hCG Levels
Several factors can affect hCG levels, including:
- Multiple pregnancies: hCG levels are typically higher in women carrying multiples.
- Gestational age: hCG levels increase with gestational age, peaking between 8-12 weeks.
- Ectopic pregnancy: hCG levels may be lower or rise more slowly in ectopic pregnancies.
- Miscarriage: hCG levels may decline or stop rising in cases of miscarriage.
- Certain medical conditions: Some medical conditions, such as thyroid disorders or pituitary tumors, can affect hCG production.
Interpretation of hCG Levels
- Positive pregnancy test: A positive pregnancy test indicates the presence of hCG in urine or blood.
- Negative pregnancy test: A negative pregnancy test may indicate that the woman is not pregnant or that hCG levels are too low to be detected.
- Low hCG levels: Low hCG levels may be associated with ectopic pregnancy, miscarriage, or an inaccurate gestational age estimate.
- High hCG levels: High hCG levels may be associated with multiple pregnancies, molar pregnancies, or certain medical conditions.
hCG Doubling Time
In early pregnancy, hCG levels should double every 2-3 days. A slower doubling time may be a sign of a potential problem, such as an ectopic pregnancy or miscarriage.
hCG Decline
After peaking between 8-12 weeks of gestation, hCG levels gradually decline throughout the remainder of the pregnancy. A sudden or significant decline in hCG levels may indicate a problem, such as a miscarriage or fetal distress.
Blood vs. Urine hCG Tests
Both blood and urine hCG tests can be used to detect pregnancy. Blood tests are more sensitive and can detect hCG earlier than urine tests. However, urine tests are more convenient and less invasive.
Conclusion
hCG levels are a valuable tool for diagnosing pregnancy and monitoring its progression. Understanding normal hCG levels and factors that can affect them can help women and healthcare providers make informed decisions about their pregnancy care. If you have any concerns about your hCG levels, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider.