Pregnancy Testing, Birth Control, and Family Planning: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
Family planning is a crucial aspect of reproductive health that empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their reproductive lives. It encompasses a range of practices, including pregnancy testing, birth control, and family planning methods, which enable individuals to plan and achieve their desired family size and spacing. This article provides a comprehensive overview of pregnancy testing, birth control, and family planning, empowering individuals with the knowledge and resources necessary to make informed choices.
Pregnancy Testing
Pregnancy testing is a vital tool for detecting the presence of pregnancy early on. There are two main types of pregnancy tests:
- Home pregnancy tests: These over-the-counter tests can be performed in the privacy of one’s home and provide results within minutes. They detect the presence of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), a hormone produced by the placenta during pregnancy.
- Blood pregnancy tests: These tests are performed in a laboratory and measure the levels of hCG in the blood. They are more sensitive than home pregnancy tests and can detect pregnancy earlier, typically within 10-14 days of conception.
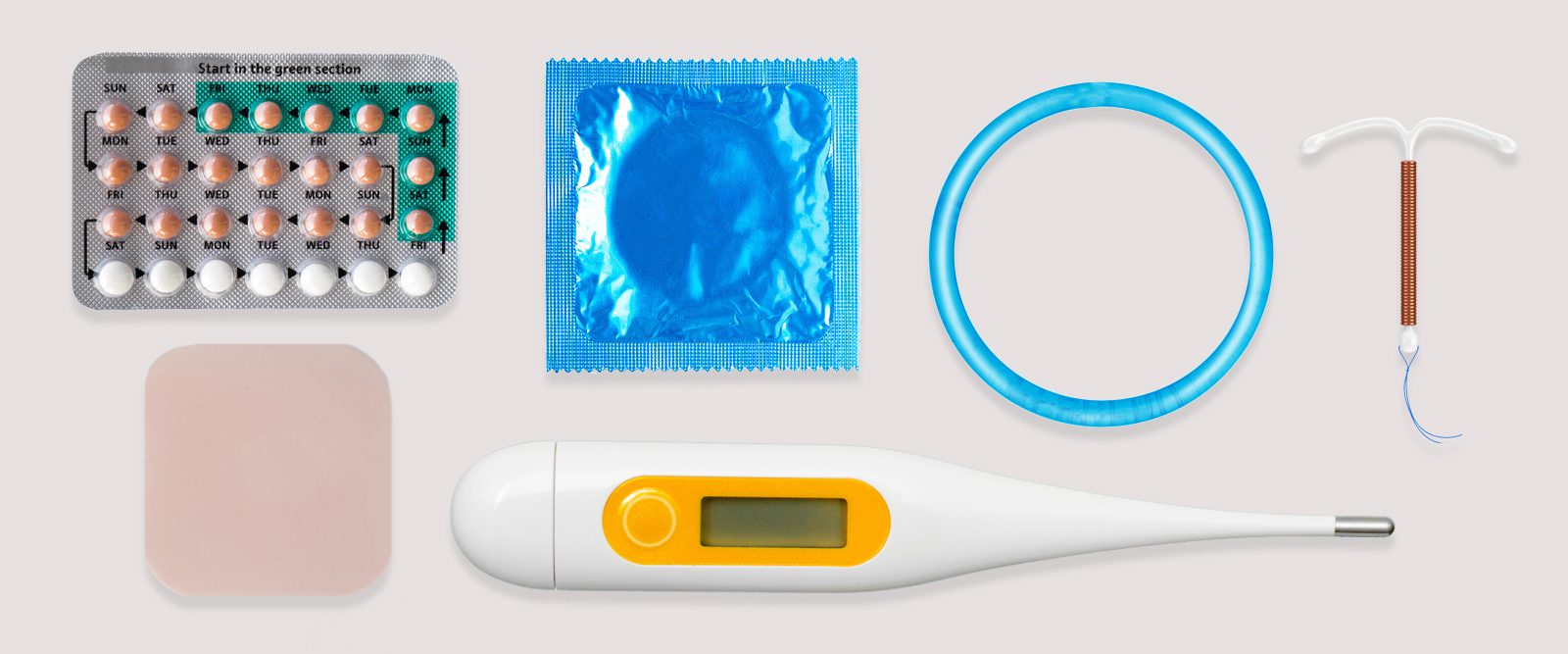
Birth Control
Birth control, also known as contraception, is a method or device used to prevent pregnancy. There are various types of birth control available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
- Barrier methods: These methods physically block sperm from reaching the egg. Examples include condoms, diaphragms, and cervical caps.
- Hormonal methods: These methods use hormones to prevent ovulation, thicken cervical mucus, or alter the uterine lining to prevent implantation. Examples include birth control pills, patches, rings, and injections.
- Intrauterine devices (IUDs): These small, T-shaped devices are inserted into the uterus by a healthcare provider and release hormones or copper to prevent pregnancy.
- Implants: These small, rod-shaped devices are inserted under the skin of the upper arm and release hormones to prevent pregnancy.
- Sterilization: This is a permanent method of birth control that involves surgically blocking the fallopian tubes in women or the vas deferens in men.
Family Planning
Family planning involves making informed decisions about the timing and spacing of pregnancies. It includes:
- Natural family planning: This method relies on tracking a woman’s menstrual cycle to identify fertile and infertile periods.
- Counseling: Family planning counselors provide information and guidance on birth control options, pregnancy testing, and other reproductive health topics.
- Access to healthcare: Affordable and accessible healthcare services are essential for effective family planning.
Benefits of Family Planning
Family planning offers numerous benefits for individuals, families, and communities:
- Improved maternal and child health: Planned pregnancies allow women to receive adequate prenatal care, reducing the risk of complications during pregnancy and childbirth. It also ensures that children are born into stable and supportive environments.
- Economic empowerment: Family planning enables women to pursue education, careers, and other opportunities, contributing to their economic independence and the well-being of their families.
- Reduced population growth: Family planning helps control population growth, ensuring that resources are available to meet the needs of present and future generations.
- Improved quality of life: Family planning allows individuals to have the number of children they desire and space them according to their circumstances, enhancing their overall quality of life.
Challenges to Family Planning
Despite its benefits, family planning faces several challenges:
- Access to information and services: In some regions, access to accurate information about family planning and reproductive health services is limited.
- Cultural and religious beliefs: Cultural and religious beliefs can influence attitudes towards family planning and birth control.
- Lack of education: Lack of education about reproductive health can lead to unintended pregnancies and poor reproductive outcomes.
- Gender inequality: Gender inequality can limit women’s access to family planning services and decision-making power over their reproductive lives.
Conclusion
Pregnancy testing, birth control, and family planning are essential components of reproductive health that empower individuals to make informed decisions about their reproductive lives. By understanding the available options and addressing the challenges, we can promote access to comprehensive family planning services and improve the health and well-being of individuals, families, and communities worldwide.