Pregnancy Tests: Understanding hCG Levels
Introduction
Pregnancy tests are a crucial tool for women seeking to confirm or rule out pregnancy. These tests detect the presence of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), a hormone produced by the placenta during pregnancy. Understanding hCG levels and their interpretation in pregnancy tests is essential for accurate results and informed decision-making.
What is hCG?
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a glycoprotein hormone produced by the trophoblast cells of the developing placenta. Its primary function is to maintain the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone, a hormone necessary for maintaining the uterine lining and supporting early pregnancy.
hCG Levels in Pregnancy
hCG levels rise rapidly during the first trimester of pregnancy, reaching their peak around the 8th to 10th week. After this, they gradually decline throughout the remainder of the pregnancy. The following table provides an overview of typical hCG levels at different stages of pregnancy:
| Gestational Age | hCG Level (mIU/mL) |
|---|---|
| 3-4 weeks | 5-50 |
| 4-5 weeks | 10-426 |
| 5-6 weeks | 18-7,340 |
| 6-7 weeks | 1,080-56,500 |
| 7-8 weeks | 7,650-229,000 |
| 8-10 weeks | 25,700-288,000 |
| 10-12 weeks | 13,300-254,000 |
| 12-16 weeks | 4,060-165,400 |
| 16-20 weeks | 3,640-117,000 |
| 20-24 weeks | 2,290-78,500 |
| 24-28 weeks | 1,230-58,000 |
| 28-32 weeks | 930-55,000 |
| 32-36 weeks | 660-42,200 |
| 36-40 weeks | 470-33,200 |
Pregnancy Tests and hCG Levels
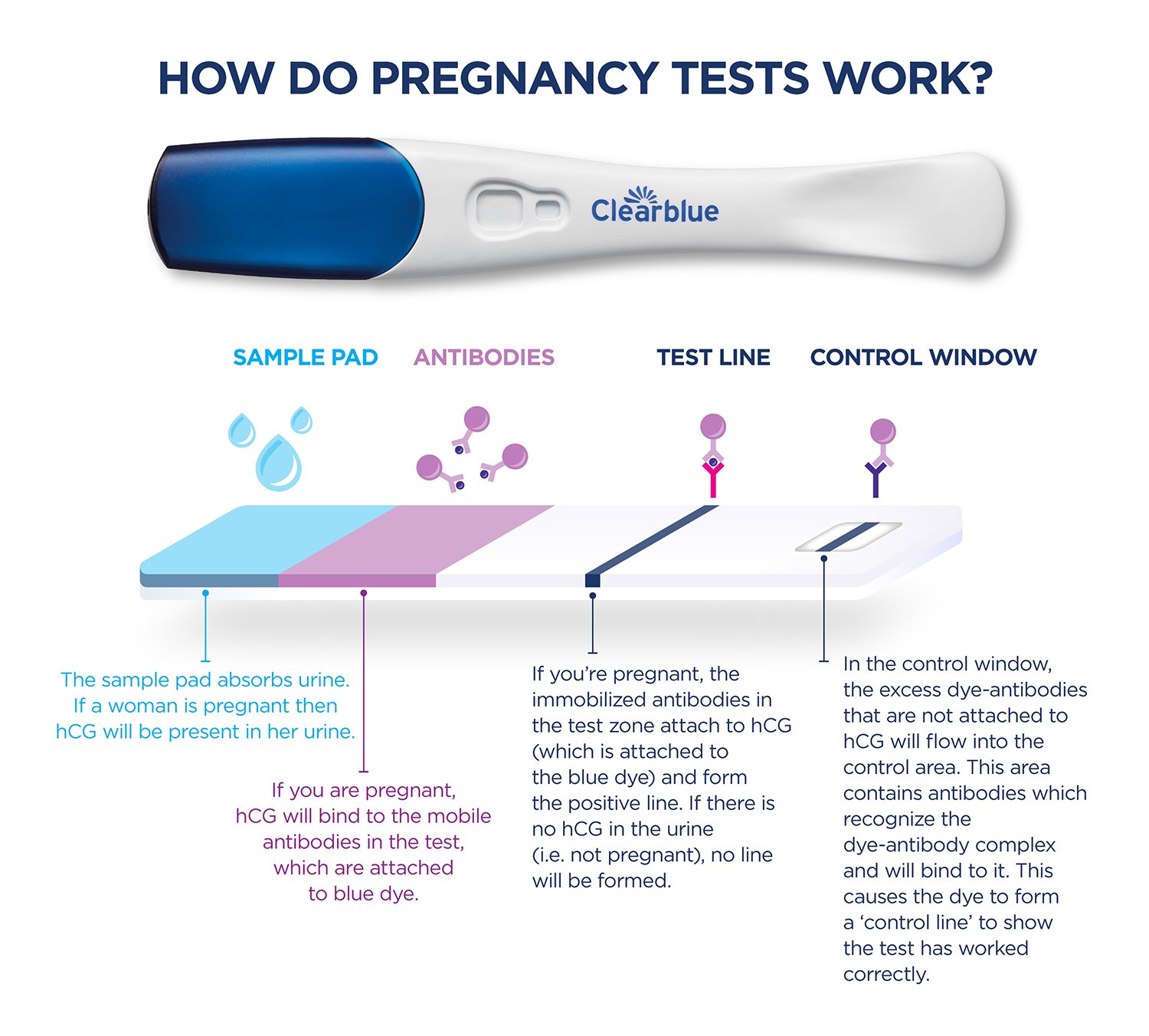
Pregnancy tests work by detecting hCG in urine or blood. Most home pregnancy tests are urine-based and measure hCG levels as low as 20-25 mIU/mL. This sensitivity allows for early detection of pregnancy, typically around 10-14 days after ovulation.
Blood tests, known as quantitative hCG tests, are more sensitive and can detect hCG levels as low as 5 mIU/mL. These tests are often used to confirm pregnancy, monitor hCG levels during early pregnancy, or diagnose ectopic pregnancies.
Interpreting hCG Test Results
Positive Result: A positive pregnancy test indicates the presence of hCG in the urine or blood, suggesting pregnancy. However, it is important to note that false positives can occur due to factors such as recent miscarriage, certain medications, or medical conditions.
Negative Result: A negative pregnancy test indicates that hCG levels are below the detectable threshold, suggesting the absence of pregnancy. However, it is possible to obtain false negatives if the test is taken too early or if hCG levels are low.
Quantitative hCG Test Results: Quantitative hCG test results provide a numerical value that represents the hCG level in the blood. These results can be used to:
- Confirm pregnancy
- Monitor hCG levels during early pregnancy
- Diagnose ectopic pregnancies
- Assess fetal well-being
Factors Affecting hCG Levels
Several factors can affect hCG levels during pregnancy, including:
- Gestational age: hCG levels rise rapidly during the first trimester and gradually decline thereafter.
- Multiple pregnancies: hCG levels are typically higher in multiple pregnancies, such as twins or triplets.
- Molar pregnancy: hCG levels are abnormally high in molar pregnancies, a rare condition characterized by abnormal placental growth.
- Ectopic pregnancy: hCG levels may be lower or rise more slowly in ectopic pregnancies, where the fertilized egg implants outside the uterus.
- Miscarriage: hCG levels may decline or plateau in cases of miscarriage.
Limitations of Pregnancy Tests
While pregnancy tests are generally reliable, they have certain limitations:
- False Positives: False positives can occur due to factors such as recent miscarriage, certain medications, or medical conditions.
- False Negatives: False negatives can occur if the test is taken too early or if hCG levels are low.
- Timing: Pregnancy tests should be taken after a missed period for optimal accuracy.
- Confirmation: A positive pregnancy test should be confirmed with a blood test or a visit to a healthcare provider.
Conclusion
Understanding hCG levels and their interpretation in pregnancy tests is crucial for accurate results and informed decision-making. By considering the timing of the test, potential factors affecting hCG levels, and the limitations of pregnancy tests, individuals can confidently use these tools to confirm or rule out pregnancy and seek appropriate medical care as needed.