Pregnancy Weight Gain: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
Pregnancy is a transformative journey that involves significant physiological changes, including weight gain. Understanding the recommended weight gain during pregnancy is crucial for the health and well-being of both the mother and the baby. This article provides a comprehensive guide to pregnancy weight gain, covering its importance, factors influencing it, recommended ranges, and strategies for healthy weight management.
Importance of Pregnancy Weight Gain
Adequate weight gain during pregnancy is essential for several reasons:
- Fetal Growth and Development: Weight gain provides nutrients and energy for the growing fetus, supporting its optimal growth and development.
- Maternal Health: Healthy weight gain during pregnancy reduces the risk of complications such as preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, and premature birth.
- Postpartum Recovery: Adequate weight gain during pregnancy facilitates postpartum recovery and breastfeeding.
- Long-Term Health: Maintaining a healthy weight during pregnancy can reduce the risk of obesity and chronic diseases later in life for both the mother and the child.
Factors Influencing Pregnancy Weight Gain
The amount of weight a woman gains during pregnancy varies depending on several factors, including:
- Pre-pregnancy Body Mass Index (BMI): Women with a higher pre-pregnancy BMI tend to gain less weight during pregnancy.
- Gestational Age: Weight gain typically increases gradually throughout pregnancy, with the most significant gain occurring in the third trimester.
- Multiple Gestation: Women carrying twins or multiples generally gain more weight than those carrying a single baby.
- Maternal Age: Younger women tend to gain more weight during pregnancy than older women.
- Activity Level: Physically active women may gain less weight during pregnancy than sedentary women.
- Diet: A healthy diet that meets the increased nutritional needs of pregnancy can help control weight gain.
Recommended Weight Gain Ranges
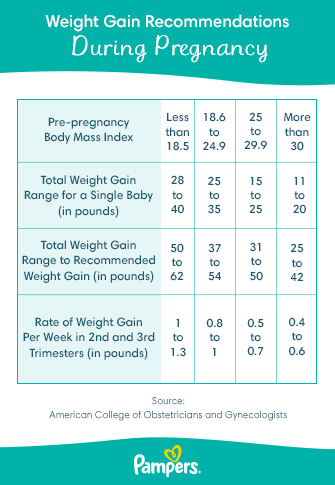
The Institute of Medicine (IOM) has established recommended weight gain ranges based on pre-pregnancy BMI:
- Underweight (BMI < 18.5): 28-40 pounds
- Normal Weight (BMI 18.5-24.9): 25-35 pounds
- Overweight (BMI 25.0-29.9): 15-25 pounds
- Obese (BMI ≥ 30.0): 11-20 pounds
Strategies for Healthy Weight Management
Managing weight gain during pregnancy requires a balanced approach that includes:
- Healthy Diet: Focus on consuming nutrient-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein. Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week, as recommended by your healthcare provider.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated.
- Prenatal Vitamins: Take prenatal vitamins to ensure adequate intake of essential nutrients.
- Monitor Weight Gain: Track your weight regularly and discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider.
- Seek Professional Guidance: Consult with a registered dietitian or other healthcare professional for personalized advice and support.
Excessive Weight Gain
Excessive weight gain during pregnancy can increase the risk of complications such as:
- Gestational Diabetes: Increased insulin resistance due to weight gain can lead to gestational diabetes.
- Preeclampsia: High blood pressure and protein in the urine associated with excessive weight gain.
- Macrosomia: Birth of a baby weighing over 4,000 grams, which can lead to delivery complications.
- Postpartum Weight Retention: Difficulty losing weight gained during pregnancy.
Insufficient Weight Gain
Insufficient weight gain during pregnancy can also be problematic, as it may affect fetal growth and development. It can also increase the risk of:
- Low Birth Weight: Babies born with a low birth weight may have health problems.
- Preterm Birth: Insufficient weight gain can contribute to preterm birth.
- Maternal Nutrient Deficiencies: Inadequate weight gain can result in nutrient deficiencies for the mother.
Conclusion
Pregnancy weight gain is an essential aspect of a healthy pregnancy. Understanding the recommended weight gain ranges and adopting healthy weight management strategies can optimize the health and well-being of both the mother and the baby. Regular monitoring, seeking professional guidance, and making lifestyle adjustments as needed are crucial for ensuring a safe and successful pregnancy journey.