Pregnancy Weight Gain: A Comprehensive Guide
Pregnancy is a transformative journey that brings about numerous physical and physiological changes in a woman’s body. One of the most noticeable changes is weight gain, which is essential for the growth and development of the baby. However, understanding the recommended guidelines, potential risks, and strategies for healthy weight gain during pregnancy is crucial.
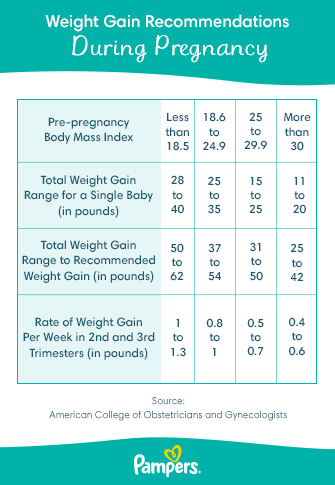
Recommended Weight Gain Guidelines
The amount of weight a woman should gain during pregnancy varies depending on her pre-pregnancy body mass index (BMI). The Institute of Medicine (IOM) has established the following guidelines:
- Underweight (BMI < 18.5): 28-40 pounds
- Normal weight (BMI 18.5-24.9): 25-35 pounds
- Overweight (BMI 25-29.9): 15-25 pounds
- Obese (BMI ≥ 30): 11-20 pounds
Potential Risks of Excessive Weight Gain
While weight gain is necessary during pregnancy, excessive weight gain can pose risks to both the mother and the baby.
-
Maternal Risks:
- Gestational diabetes
- Preeclampsia
- Cesarean delivery
- Postpartum weight retention
-
Fetal Risks:
- Macrosomia (large birth weight)
- Birth defects
- Stillbirth
Strategies for Healthy Weight Gain
To ensure healthy weight gain during pregnancy, it is essential to follow a balanced diet and engage in regular physical activity.
Diet:
- Consume nutrient-rich foods: Focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein.
- Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats: These foods provide empty calories and contribute to weight gain.
- Hydrate adequately: Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Consider prenatal vitamins: They provide essential nutrients that may not be obtained from diet alone.
Physical Activity:
- Aim for 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week: This can include brisk walking, swimming, or cycling.
- Choose activities that are safe for pregnancy: Avoid contact sports or activities that involve jumping or lying on your back.
- Listen to your body: Rest when you need to and avoid overexertion.
Monitoring Weight Gain
Regular prenatal appointments are crucial for monitoring weight gain and ensuring it aligns with the recommended guidelines. Your healthcare provider will:
- Measure your weight and BMI at each visit.
- Track your weight gain progress over time.
- Provide guidance and support if necessary.
Managing Weight Gain
If you are gaining weight too quickly or too slowly, your healthcare provider may recommend adjustments to your diet or exercise plan.
- For excessive weight gain: Reduce calorie intake, increase physical activity, and consult with a registered dietitian.
- For insufficient weight gain: Increase calorie intake, focus on nutrient-dense foods, and consider dietary supplements if needed.
Postpartum Weight Loss
After delivery, it is important to lose the weight gained during pregnancy gradually and healthily.
- Breastfeed if possible: Breastfeeding can help burn calories and promote weight loss.
- Follow a balanced diet: Continue to eat nutrient-rich foods and limit processed foods.
- Engage in regular physical activity: Gradually increase your activity level as you recover from childbirth.
- Be patient: Losing weight after pregnancy takes time and effort. Avoid crash diets or extreme measures.
Conclusion
Pregnancy weight gain is an essential aspect of a healthy pregnancy. By following the recommended guidelines, adopting healthy dietary and exercise habits, and monitoring weight gain regularly, women can ensure optimal outcomes for both themselves and their babies. Remember to consult with your healthcare provider for personalized guidance and support throughout your pregnancy journey.