Pregnancy Weight Gain Week by Week
Pregnancy is a transformative journey that brings about numerous physical changes, including weight gain. Understanding the recommended weight gain during pregnancy is crucial for both the mother’s health and the baby’s well-being. This article provides a comprehensive guide to pregnancy weight gain week by week, outlining the expected weight gain ranges and factors that influence weight gain.
Recommended Weight Gain Ranges
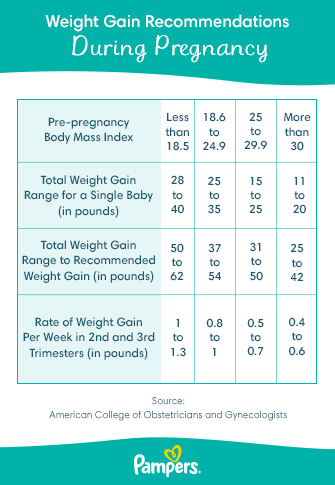
The Institute of Medicine (IOM) has established guidelines for recommended weight gain during pregnancy based on the mother’s pre-pregnancy body mass index (BMI). These guidelines are as follows:
- Underweight (BMI < 18.5): 28-40 pounds
- Normal weight (BMI 18.5-24.9): 25-35 pounds
- Overweight (BMI 25-29.9): 15-25 pounds
- Obese (BMI ≥ 30): 11-20 pounds
Week-by-Week Weight Gain
First Trimester (Weeks 1-12)
- Weeks 1-8: Minimal weight gain, typically less than 5 pounds
- Weeks 9-12: Gradual weight gain, averaging 1-2 pounds per week
Second Trimester (Weeks 13-28)
- Weeks 13-16: Steady weight gain, averaging 1-2.5 pounds per week
- Weeks 17-20: Accelerated weight gain, averaging 2-3 pounds per week
- Weeks 21-24: Continued rapid weight gain, averaging 2.5-3.5 pounds per week
- Weeks 25-28: Gradual decrease in weight gain, averaging 1.5-2.5 pounds per week
Third Trimester (Weeks 29-40)
- Weeks 29-32: Steady weight gain, averaging 1-2 pounds per week
- Weeks 33-36: Gradual increase in weight gain, averaging 1.5-2.5 pounds per week
- Weeks 37-40: Slowing of weight gain, averaging 0.5-1 pound per week
Factors Influencing Weight Gain
Several factors can influence weight gain during pregnancy, including:
- Pre-pregnancy BMI: Women with a higher pre-pregnancy BMI tend to gain less weight during pregnancy.
- Multiple pregnancy: Carrying twins or more can lead to increased weight gain.
- Gestational age: Weight gain typically accelerates in the second trimester and slows down in the third trimester.
- Activity level: Exercise can help regulate weight gain during pregnancy.
- Diet: A healthy diet that meets nutritional needs can support appropriate weight gain.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as gestational diabetes, can affect weight gain.
Consequences of Excessive or Insufficient Weight Gain
Excessive or insufficient weight gain during pregnancy can have implications for both the mother and the baby.
Excessive Weight Gain
- Increased risk of gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, and cesarean delivery
- Higher birth weight, which can lead to complications during labor and delivery
- Postpartum weight retention
Insufficient Weight Gain
- Low birth weight, which can increase the risk of health problems for the baby
- Preterm birth
- Intrauterine growth restriction
Monitoring Weight Gain
Regular prenatal checkups are essential for monitoring weight gain during pregnancy. Your healthcare provider will measure your weight and assess your overall health to ensure that you are gaining weight within the recommended range.
Tips for Healthy Weight Gain
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats
- Engage in regular physical activity, as recommended by your healthcare provider
- Get adequate sleep and manage stress
- Follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for weight gain
Conclusion
Understanding pregnancy weight gain week by week is crucial for maintaining a healthy pregnancy. By following the recommended weight gain ranges and considering the factors that influence weight gain, you can support both your own well-being and the health of your baby. Regular prenatal checkups and a healthy lifestyle are essential for ensuring optimal weight gain throughout your pregnancy journey.