Progesterone Level and Pregnancy: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
Progesterone, a hormone produced by the ovaries, plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy pregnancy. Its levels fluctuate throughout the menstrual cycle, with a significant increase during pregnancy. Understanding progesterone levels and their impact on pregnancy is essential for both expectant mothers and healthcare providers.
Progesterone Levels During the Menstrual Cycle
During the menstrual cycle, progesterone levels are typically low in the follicular phase, which occurs before ovulation. After ovulation, progesterone levels rise sharply as the corpus luteum (a structure that forms on the ovary after ovulation) produces progesterone. This rise in progesterone helps to prepare the uterus for implantation of a fertilized egg.
If fertilization does not occur, the corpus luteum breaks down, leading to a drop in progesterone levels. This drop triggers the onset of menstruation.
Progesterone Levels During Pregnancy
If fertilization occurs, the corpus luteum continues to produce progesterone, which is essential for maintaining the pregnancy. Progesterone levels rise steadily throughout the first trimester, reaching their peak in the second trimester. This high level of progesterone helps to:
- Maintain the uterine lining (endometrium)
- Prevent uterine contractions
- Suppress ovulation
- Promote the growth and development of the fetus
Progesterone Levels and Pregnancy Complications
Abnormal progesterone levels can be associated with pregnancy complications, including:
- Miscarriage: Low progesterone levels can lead to miscarriage, especially in the early stages of pregnancy.
- Preterm birth: Premature babies are often born to mothers with low progesterone levels.
- Placental abruption: This condition occurs when the placenta separates from the uterine wall, which can be caused by low progesterone levels.
- Preeclampsia: A pregnancy-related condition characterized by high blood pressure and protein in the urine, is associated with low progesterone levels.
Measuring Progesterone Levels
Progesterone levels are typically measured through a blood test. The test can be done at any time during the menstrual cycle or pregnancy.
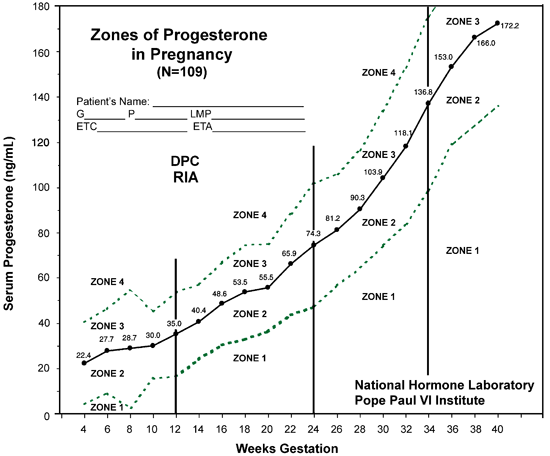
Normal Progesterone Levels
Normal progesterone levels vary depending on the stage of the menstrual cycle or pregnancy. Here are some general guidelines:
- Follicular phase: 0.5-2 ng/mL
- Ovulation: 5-20 ng/mL
- Luteal phase: 10-25 ng/mL
- Early pregnancy: 10-40 ng/mL
- Second trimester: 20-80 ng/mL
- Third trimester: 100-200 ng/mL
Treatment for Abnormal Progesterone Levels
If progesterone levels are abnormally low, treatment may be necessary to support the pregnancy. This may involve:
- Progesterone supplements: Synthetic progesterone can be administered orally or vaginally to increase progesterone levels.
- Corpus luteum rescue: A procedure where the corpus luteum is stimulated to produce more progesterone.
- In vitro fertilization (IVF): IVF involves fertilizing eggs in the laboratory and transferring them to the uterus. Progesterone supplements may be used to support the pregnancy after IVF.
Conclusion
Progesterone is a vital hormone for maintaining a healthy pregnancy. Understanding progesterone levels and their impact on pregnancy is crucial for ensuring the well-being of both the mother and the developing fetus. Abnormal progesterone levels can be associated with pregnancy complications, but treatment options are available to support the pregnancy and improve outcomes. Regular monitoring of progesterone levels during pregnancy is recommended to ensure optimal levels for a successful pregnancy.