Progesterone Level Early Pregnancy: A Comprehensive Guide
Progesterone is a crucial hormone during pregnancy, playing a vital role in maintaining the uterine lining and supporting the developing embryo. Understanding progesterone levels in early pregnancy can provide valuable insights into the health and progress of the pregnancy. This article delves into the significance of progesterone, its levels during early pregnancy, and the potential implications of abnormal levels.
What is Progesterone?
Progesterone is a steroid hormone primarily produced by the corpus luteum, a temporary structure that forms on the ovary after ovulation. During pregnancy, the placenta takes over progesterone production, ensuring a steady supply throughout the gestation period.
Role of Progesterone in Early Pregnancy
Progesterone’s primary function in early pregnancy is to prepare and maintain the uterine lining, known as the endometrium. It promotes the growth and development of the endometrium, creating a receptive environment for embryo implantation.
Additionally, progesterone:
- Suppresses uterine contractions, preventing premature labor
- Regulates the immune system to prevent the rejection of the embryo
- Promotes blood flow to the uterus, supporting fetal growth
- Stimulates the production of other hormones essential for pregnancy
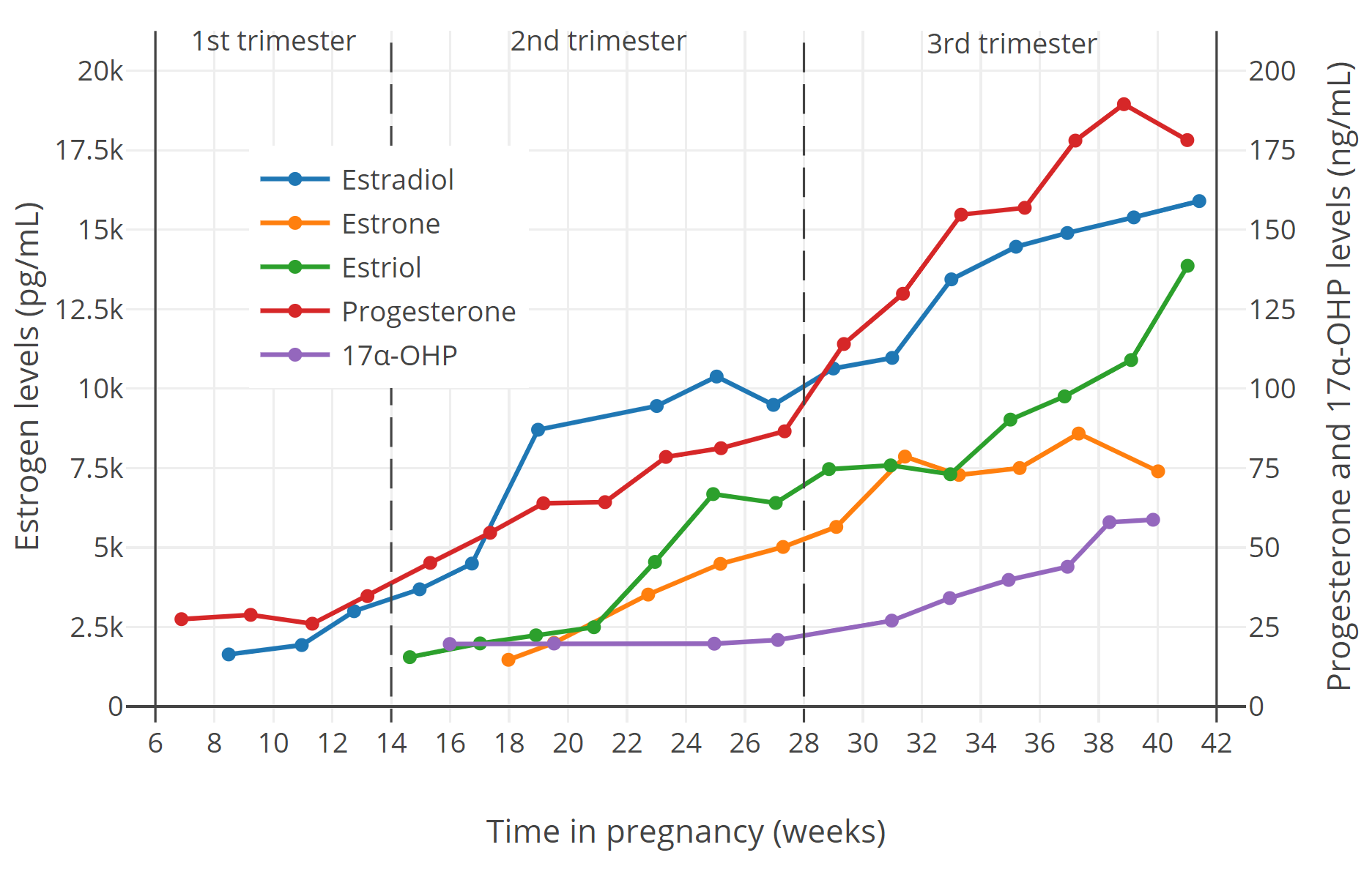
Progesterone Levels in Early Pregnancy
Progesterone levels rise significantly after ovulation and continue to increase throughout the first trimester. The following table provides approximate progesterone levels during early pregnancy:
| Gestational Age | Progesterone Level (ng/mL) |
|---|---|
| 3-4 weeks | 10-20 |
| 5-6 weeks | 20-40 |
| 7-8 weeks | 40-80 |
| 9-10 weeks | 80-120 |
| 11-12 weeks | 120-160 |
Implications of Abnormal Progesterone Levels
Abnormal progesterone levels in early pregnancy can indicate underlying health concerns.
Low Progesterone Levels:
- May impair endometrial receptivity, reducing the chances of embryo implantation
- Can lead to miscarriage or premature birth
- May be associated with luteal phase defect, a condition where the corpus luteum fails to produce adequate progesterone
High Progesterone Levels:
- Can suppress ovulation, preventing conception
- May indicate a molar pregnancy, a rare condition where abnormal placental tissue develops
- Can be associated with certain types of ovarian cysts
Testing Progesterone Levels
Progesterone levels can be measured through a blood test. Your healthcare provider may recommend testing if you have concerns about your pregnancy or have a history of progesterone-related issues.
Treatment for Abnormal Progesterone Levels
Treatment for abnormal progesterone levels depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition.
- Low Progesterone Levels: May be treated with progesterone supplements to support endometrial growth and prevent miscarriage.
- High Progesterone Levels: Treatment may involve monitoring the condition or, in some cases, surgery to remove the source of excess progesterone production.
Conclusion
Progesterone is a critical hormone that plays a pivotal role in early pregnancy. Understanding progesterone levels and their implications can provide valuable information about the health and progress of the pregnancy. If you have concerns about your progesterone levels, consult your healthcare provider for appropriate testing and guidance. By maintaining optimal progesterone levels, you can support a healthy pregnancy and increase the chances of a successful outcome.