Progesterone Level and Early Pregnancy Symptoms
Progesterone is a hormone produced by the ovaries that plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy pregnancy. During the early stages of pregnancy, progesterone levels rise significantly to support the development of the fetus and prepare the body for childbirth. Understanding the role of progesterone and its impact on early pregnancy symptoms can help women navigate this important phase of their lives.
Role of Progesterone in Early Pregnancy
Progesterone has several essential functions during early pregnancy:
- Maintaining the uterine lining: Progesterone thickens and vascularizes the uterine lining, creating a supportive environment for the implantation and growth of the fertilized egg.
- Preventing uterine contractions: Progesterone relaxes the uterine muscles, reducing the risk of miscarriage and premature labor.
- Supporting fetal development: Progesterone promotes the growth and development of the fetus by regulating nutrient supply and hormone production.
- Preparing the breasts for lactation: Progesterone stimulates the development of the mammary glands, preparing them for milk production after childbirth.
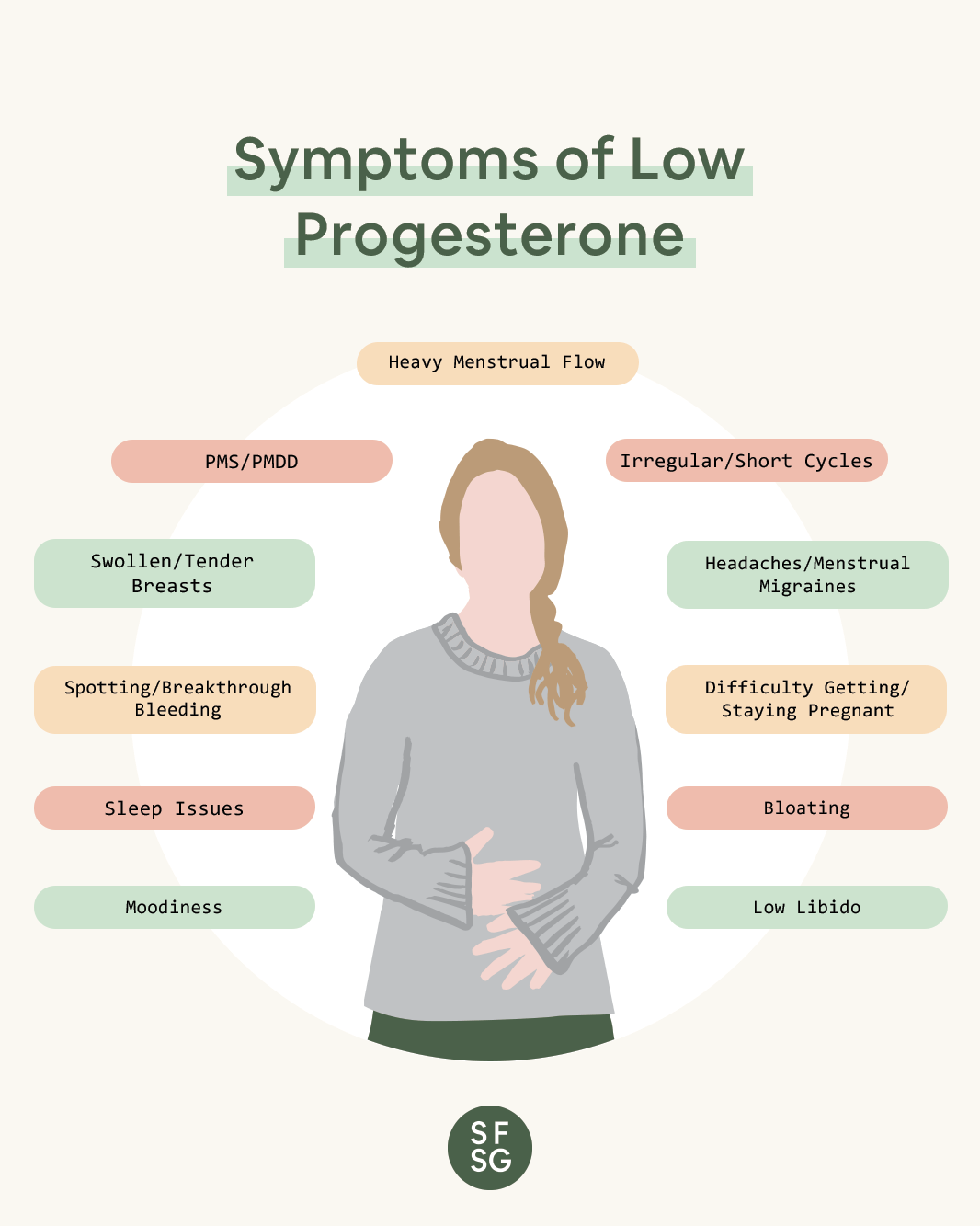
Early Pregnancy Symptoms Associated with Progesterone
As progesterone levels rise during early pregnancy, women may experience a range of symptoms:
- Breast tenderness: Progesterone can cause the breasts to become swollen, tender, and sensitive.
- Nausea and vomiting (morning sickness): Progesterone is thought to contribute to the nausea and vomiting commonly experienced in early pregnancy.
- Fatigue: Progesterone can induce feelings of tiredness and exhaustion.
- Frequent urination: Progesterone relaxes the bladder muscles, leading to increased urinary frequency.
- Mood swings: Progesterone can affect neurotransmitters in the brain, resulting in mood changes and emotional sensitivity.
- Constipation: Progesterone slows down digestion, which can cause constipation.
- Skin changes: Progesterone can increase skin pigmentation, causing darkening of the nipples and linea nigra (a dark line that runs down the abdomen).
- Increased basal body temperature: Progesterone raises the body’s temperature slightly, which can be detected through basal body temperature charting.
Monitoring Progesterone Levels
In some cases, healthcare providers may recommend monitoring progesterone levels through blood tests. This is typically done to:
- Confirm pregnancy
- Assess the risk of miscarriage
- Evaluate the effectiveness of progesterone supplements
- Rule out other underlying medical conditions
Treatment for Low Progesterone Levels
If progesterone levels are low, healthcare providers may prescribe progesterone supplements to support the pregnancy. These supplements can be administered orally, vaginally, or through injections.
Conclusion
Progesterone is a vital hormone that plays a multifaceted role in early pregnancy. Understanding the symptoms associated with progesterone levels can help women recognize and manage the challenges of this transformative period. By monitoring progesterone levels and seeking appropriate medical care when necessary, women can increase their chances of a healthy and successful pregnancy.