Progesterone Level in Early Pregnancy: A Comprehensive Guide
Progesterone is a crucial hormone that plays a pivotal role in maintaining a healthy pregnancy. Its levels fluctuate throughout the menstrual cycle, reaching their peak during the luteal phase, which is the time between ovulation and the onset of menstruation. If pregnancy occurs, progesterone levels remain elevated to support the development of the fetus and the maintenance of the pregnancy.
Role of Progesterone in Early Pregnancy
Progesterone has several essential functions in early pregnancy, including:
- Preparing the uterus for implantation: Progesterone thickens the uterine lining, making it more receptive to the implantation of the fertilized egg.
- Maintaining the uterine lining: Progesterone prevents the shedding of the uterine lining, which would otherwise occur during menstruation.
- Suppressing uterine contractions: Progesterone relaxes the uterine muscles, preventing premature contractions that could lead to miscarriage.
- Supporting placental development: Progesterone promotes the growth and development of the placenta, which is responsible for providing nutrients and oxygen to the developing fetus.
- Modulating the immune system: Progesterone helps to suppress the maternal immune response, preventing the rejection of the fetus.
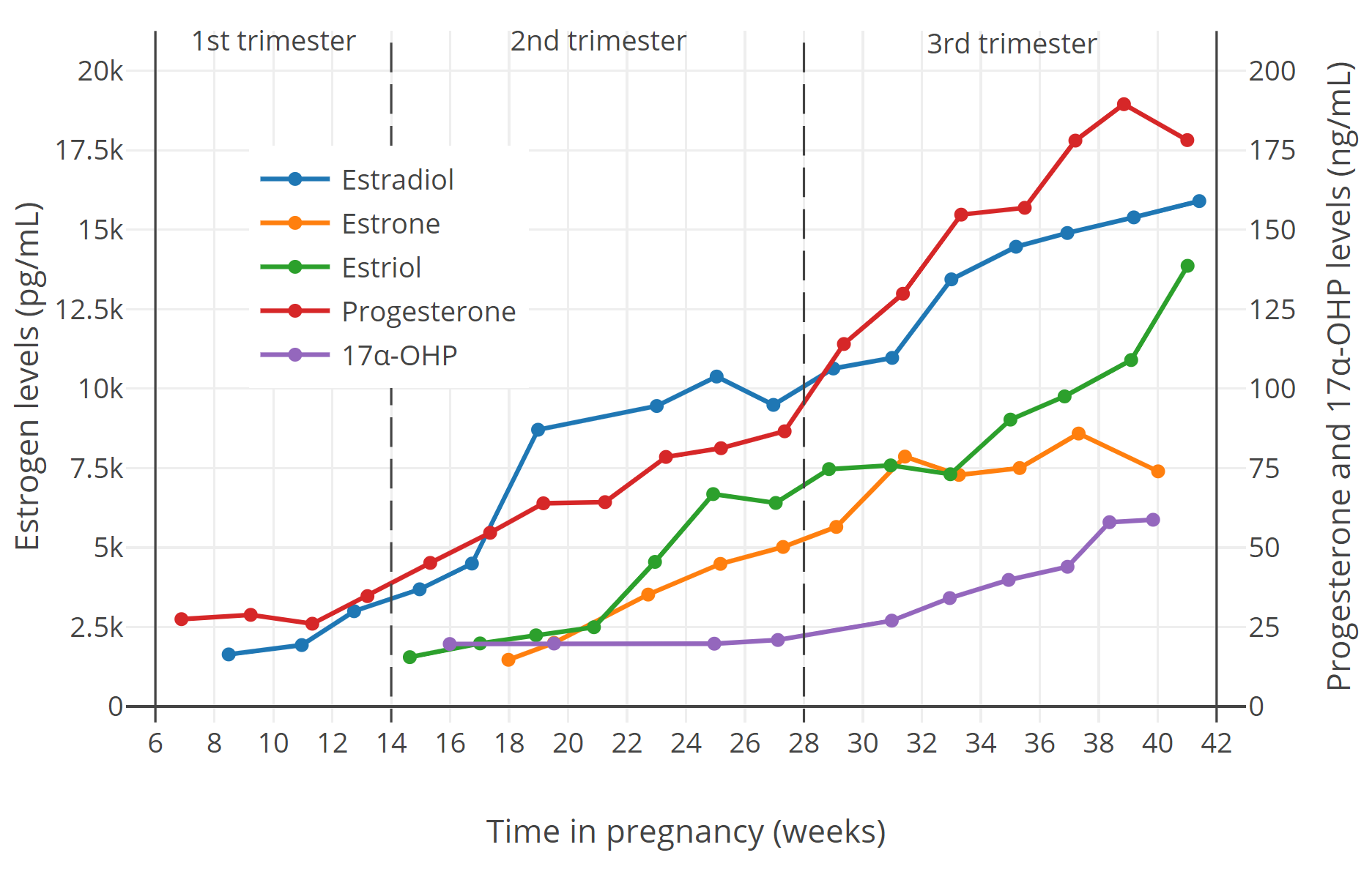
Normal Progesterone Levels in Early Pregnancy
Progesterone levels vary widely among women, but general guidelines for normal levels in early pregnancy are as follows:
- Week 4-5: 5-20 ng/mL
- Week 6-7: 10-40 ng/mL
- Week 8-10: 15-50 ng/mL
- Week 11-12: 20-80 ng/mL
It’s important to note that these are just general ranges, and individual levels may differ. Your doctor will interpret your specific progesterone levels based on your medical history and symptoms.
Low Progesterone Levels in Early Pregnancy
Low progesterone levels in early pregnancy can be a cause for concern, as they may indicate an increased risk of miscarriage. Symptoms of low progesterone may include:
- Spotting or bleeding
- Cramping
- Abdominal pain
- Back pain
- Fatigue
- Mood swings
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s crucial to contact your doctor promptly. They may recommend progesterone supplements to help support your pregnancy.
High Progesterone Levels in Early Pregnancy
High progesterone levels in early pregnancy are generally not a cause for concern. However, in some cases, they may be associated with certain conditions, such as:
- Multiple pregnancies (e.g., twins or triplets)
- Gestational trophoblastic disease (a rare condition characterized by abnormal growth of placental tissue)
- Luteal cyst (a fluid-filled cyst that forms on the ovary)
Your doctor will monitor your progesterone levels closely and investigate any underlying causes if necessary.
Testing Progesterone Levels
Progesterone levels are typically measured through a blood test. Your doctor may order a progesterone test if you have symptoms of low progesterone or if they suspect any underlying conditions. The test involves drawing a small sample of blood from a vein in your arm.
Treatment for Abnormal Progesterone Levels
Treatment for abnormal progesterone levels depends on the underlying cause. For low progesterone levels, your doctor may prescribe progesterone supplements in the form of injections, pills, or vaginal suppositories. For high progesterone levels, treatment may involve monitoring and managing any associated conditions.
Conclusion
Progesterone is a vital hormone that plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy pregnancy. Monitoring progesterone levels in early pregnancy can help identify potential problems and ensure the well-being of both the mother and the developing fetus. If you have any concerns about your progesterone levels, it’s essential to discuss them with your doctor promptly.