Ectopic Pregnancy: A Comprehensive Guide to Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Introduction
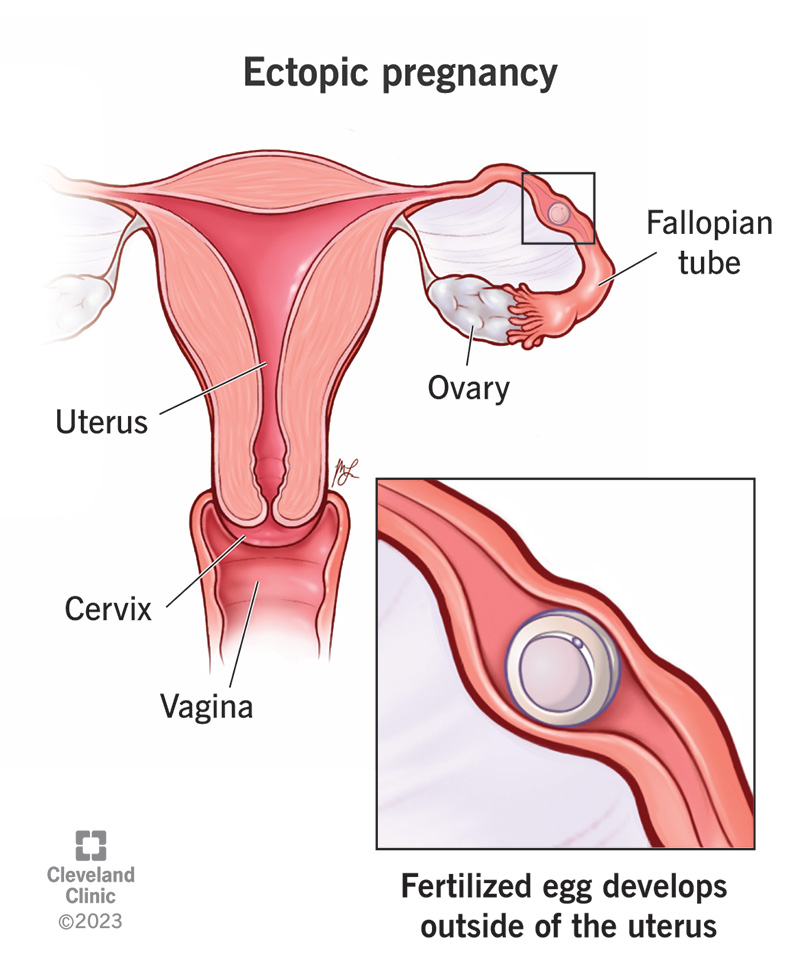
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, most commonly in the fallopian tube. This condition is potentially life-threatening and requires prompt medical attention. Understanding the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for an ectopic pregnancy is crucial for women’s health and well-being.
Symptoms
The symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy can vary depending on the location of the implantation and the stage of the pregnancy. However, some common signs and symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain: Sharp, stabbing, or cramping pain on one side of the lower abdomen is a hallmark symptom.
- Vaginal bleeding: Irregular or abnormal vaginal bleeding, which may be light or heavy, is another common sign.
- Missed period: A missed menstrual period is often an early indication of pregnancy, but it can also occur in ectopic pregnancies.
- Shoulder pain: Pain in the shoulder or neck can be a symptom of an ectopic pregnancy that has ruptured.
- Nausea and vomiting: These symptoms are common in early pregnancy, but they can also be associated with an ectopic pregnancy.
- Fatigue and weakness: Feeling excessively tired or weak can be a sign of an ectopic pregnancy.
- Pelvic pressure: A feeling of pressure or fullness in the pelvic area can be another symptom.
Risk Factors
Certain factors can increase the risk of developing an ectopic pregnancy, including:
- Previous ectopic pregnancy: Women who have had an ectopic pregnancy in the past are at a higher risk of having another one.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID): PID can damage the fallopian tubes, making it more difficult for a fertilized egg to travel to the uterus.
- Endometriosis: This condition, in which endometrial tissue grows outside the uterus, can also increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
- Tubal ligation: Women who have had their fallopian tubes tied are at a slightly increased risk of ectopic pregnancy.
- Intrauterine device (IUD): While IUDs are highly effective at preventing pregnancy, they do not completely eliminate the risk of an ectopic pregnancy.
- Smoking: Smoking can damage the fallopian tubes and increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing an ectopic pregnancy can be challenging, as the symptoms can mimic those of other conditions. Your doctor will perform a physical examination and ask about your medical history and symptoms. They may also order the following tests:
- Blood test: A blood test can measure the levels of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), a hormone produced during pregnancy. Low or rapidly rising hCG levels can indicate an ectopic pregnancy.
- Transvaginal ultrasound: This imaging test uses sound waves to create images of the uterus and fallopian tubes. It can help determine the location of the pregnancy and rule out other conditions.
Treatment
The treatment for an ectopic pregnancy depends on the location and stage of the pregnancy. The two main treatment options are:
- Medication: Methotrexate, a chemotherapy drug, can be used to stop the growth of the ectopic pregnancy and allow the body to absorb it. This treatment is only effective if the pregnancy is small and has not ruptured.
- Surgery: Laparoscopic surgery is the most common surgical treatment for an ectopic pregnancy. During this procedure, the surgeon makes small incisions in the abdomen and uses a laparoscope, a thin instrument with a camera, to remove the ectopic pregnancy.
Complications
An ectopic pregnancy can lead to serious complications, including:
- Rupture: The ectopic pregnancy can rupture, causing internal bleeding and severe pain. This is a medical emergency and requires immediate surgery.
- Infection: The ectopic pregnancy can become infected, leading to sepsis, a life-threatening condition.
- Infertility: An ectopic pregnancy can damage the fallopian tubes, making it difficult or impossible to get pregnant in the future.
Prevention
There is no surefire way to prevent an ectopic pregnancy, but there are certain steps you can take to reduce your risk:
- Get regular pelvic exams: Regular pelvic exams can help your doctor detect any abnormalities in your reproductive organs.
- Practice safe sex: Using condoms can help prevent sexually transmitted infections, which can increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
- Quit smoking: Smoking damages the fallopian tubes and increases the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
- Be aware of your risk factors: If you have any risk factors for ectopic pregnancy, such as a history of PID or endometriosis, talk to your doctor about ways to reduce your risk.
Conclusion
Ectopic pregnancy is a serious medical condition that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment. Understanding the symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options is crucial for women’s health and well-being. If you suspect you may have an ectopic pregnancy, seek medical attention immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent serious complications and improve your chances of a successful future pregnancy.