Symptoms of Rupture with Ectopic Pregnancy
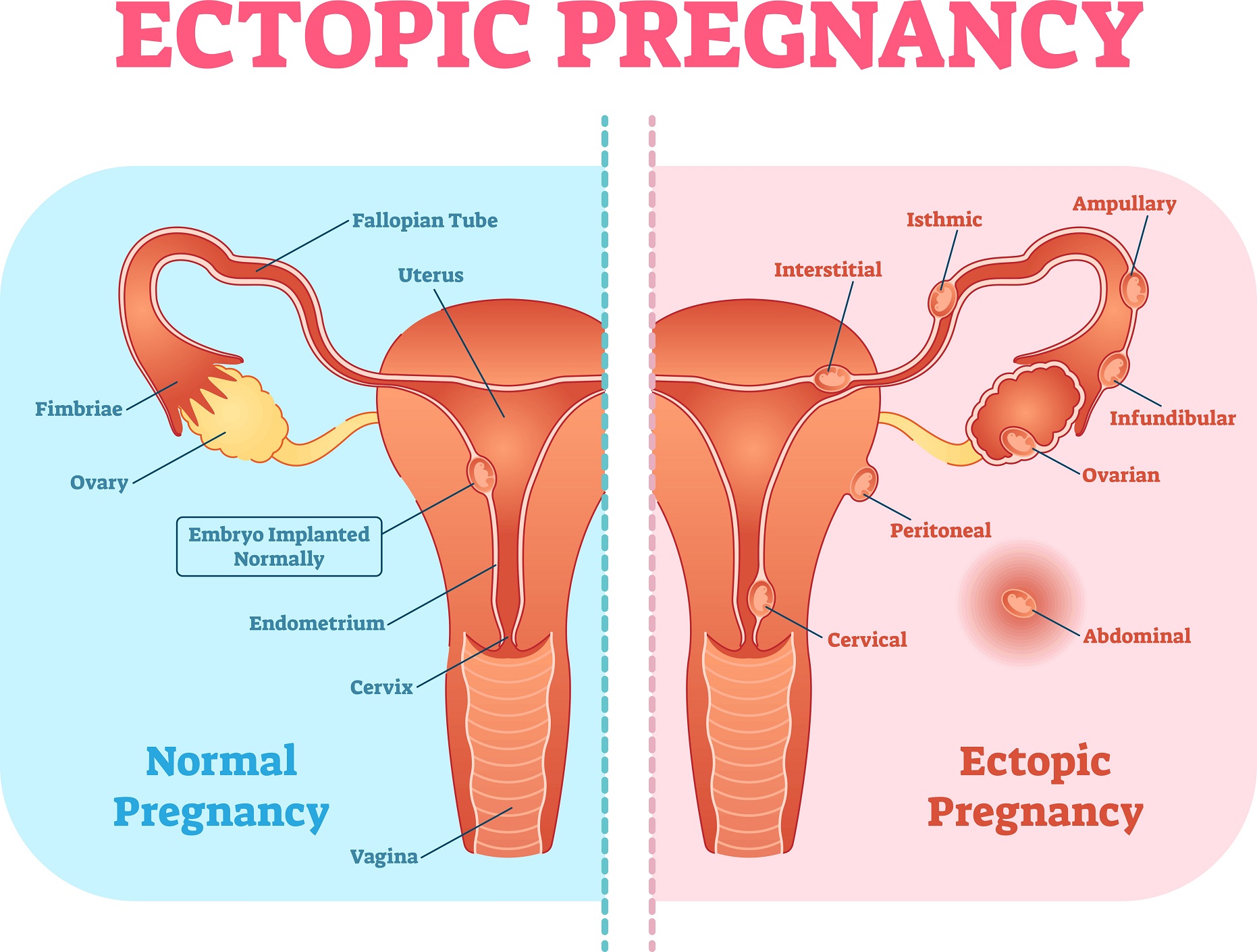
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, typically in the fallopian tube. This condition can be life-threatening if the fallopian tube ruptures, causing internal bleeding. Recognizing the symptoms of a ruptured ectopic pregnancy is crucial for prompt medical attention and timely intervention.
What is a Ruptured Ectopic Pregnancy?
A ruptured ectopic pregnancy occurs when the fallopian tube, where the fertilized egg has implanted, bursts open. This can happen as the embryo grows and expands, putting pressure on the fallopian tube. The rupture causes internal bleeding and can lead to severe complications.
Symptoms of a Ruptured Ectopic Pregnancy
The symptoms of a ruptured ectopic pregnancy can vary depending on the severity of the rupture and the individual’s pain tolerance. However, common signs and symptoms include:
- Sudden and severe abdominal pain: This pain is typically sharp and one-sided, located in the lower abdomen or pelvis.
- Vaginal bleeding: The bleeding may be light or heavy, and it may be accompanied by clots.
- Shoulder pain: This pain is caused by blood irritating the nerves in the diaphragm.
- Nausea and vomiting: These symptoms are common during pregnancy but can be more severe with an ectopic pregnancy.
- Lightheadedness or dizziness: These symptoms indicate low blood pressure due to internal bleeding.
- Weakness or fainting: These symptoms are also associated with low blood pressure.
Risk Factors for a Ruptured Ectopic Pregnancy
Certain factors increase the risk of developing a ruptured ectopic pregnancy, including:
- History of ectopic pregnancy: Women who have had an ectopic pregnancy in the past are at a higher risk of having another one.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID): This infection can damage the fallopian tubes, making them more susceptible to ectopic pregnancy.
- Endometriosis: This condition involves the growth of uterine tissue outside the uterus, which can block or narrow the fallopian tubes.
- Tubal ligation: This surgical procedure to prevent pregnancy can increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy if the fallopian tubes are not completely blocked.
- Use of an intrauterine device (IUD): IUDs can slightly increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
- Smoking: Smoking can damage the fallopian tubes and increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
Diagnosis of a Ruptured Ectopic Pregnancy
Diagnosing a ruptured ectopic pregnancy requires a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests.
- Medical history: The doctor will ask about the patient’s symptoms, menstrual history, and any risk factors for ectopic pregnancy.
- Physical examination: The doctor will perform a pelvic exam to check for tenderness or a mass in the fallopian tube.
- Transvaginal ultrasound: This imaging test uses sound waves to create images of the uterus and fallopian tubes, allowing the doctor to visualize the location of the pregnancy.
- Blood tests: Blood tests can measure hormone levels and detect anemia, which can indicate internal bleeding.
Treatment for a Ruptured Ectopic Pregnancy
Treatment for a ruptured ectopic pregnancy typically involves emergency surgery to remove the damaged fallopian tube and stop the bleeding. The type of surgery performed depends on the severity of the rupture and the patient’s overall health.
- Laparoscopy: This minimally invasive surgery involves making small incisions in the abdomen and inserting a laparoscope, a thin tube with a camera, to visualize the fallopian tubes and perform the necessary repairs.
- Laparotomy: This open surgery involves making a larger incision in the abdomen to access the fallopian tubes and perform the necessary repairs.
Complications of a Ruptured Ectopic Pregnancy
A ruptured ectopic pregnancy can lead to several complications, including:
- Hemorrhagic shock: This life-threatening condition occurs when the body loses a large amount of blood, causing a drop in blood pressure and organ failure.
- Infection: The rupture of the fallopian tube can introduce bacteria into the abdomen, leading to infection.
- Infertility: A ruptured ectopic pregnancy can damage the fallopian tube, making it difficult or impossible to conceive in the future.
Prevention of a Ruptured Ectopic Pregnancy
Preventing a ruptured ectopic pregnancy is not always possible, but certain measures can reduce the risk:
- Avoid risk factors: Women with risk factors for ectopic pregnancy, such as a history of PID or endometriosis, should be aware of the increased risk and seek medical attention promptly if they experience any symptoms.
- Use contraception: Using effective contraception can prevent unwanted pregnancies, reducing the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
- Quit smoking: Smoking damages the fallopian tubes and increases the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
- Seek medical attention promptly: If you experience any symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy, seek medical attention immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent a rupture and its associated complications.
Conclusion
A ruptured ectopic pregnancy is a serious medical emergency that requires prompt medical attention. Recognizing the symptoms and seeking medical help immediately can help prevent life-threatening complications and improve the chances of a successful recovery. By understanding the risk factors, symptoms, and treatment options, women can be empowered to protect their health and well-being.