Urine Pregnancy Test Accuracy: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
Urine pregnancy tests are widely used to detect the presence of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), a hormone produced during pregnancy, in a woman’s urine. These tests are readily available over-the-counter and provide a convenient and affordable way to determine if a woman is pregnant. However, it is important to understand the accuracy of urine pregnancy tests and the factors that can affect their reliability.
How Urine Pregnancy Tests Work
Urine pregnancy tests detect the presence of hCG, which is produced by the placenta after implantation of a fertilized egg. hCG levels rise rapidly in the early stages of pregnancy, reaching their peak around the eighth week. Urine pregnancy tests use antibodies that bind specifically to hCG, producing a visible result if the hormone is present.
Types of Urine Pregnancy Tests
There are two main types of urine pregnancy tests:
- Qualitative tests: These tests simply indicate whether hCG is present or not, without providing a specific measurement of the hormone level.
- Quantitative tests: These tests measure the amount of hCG in the urine, providing a more precise indication of the stage of pregnancy.
Accuracy of Urine Pregnancy Tests
Urine pregnancy tests are generally considered to be highly accurate. However, their accuracy can vary depending on several factors:
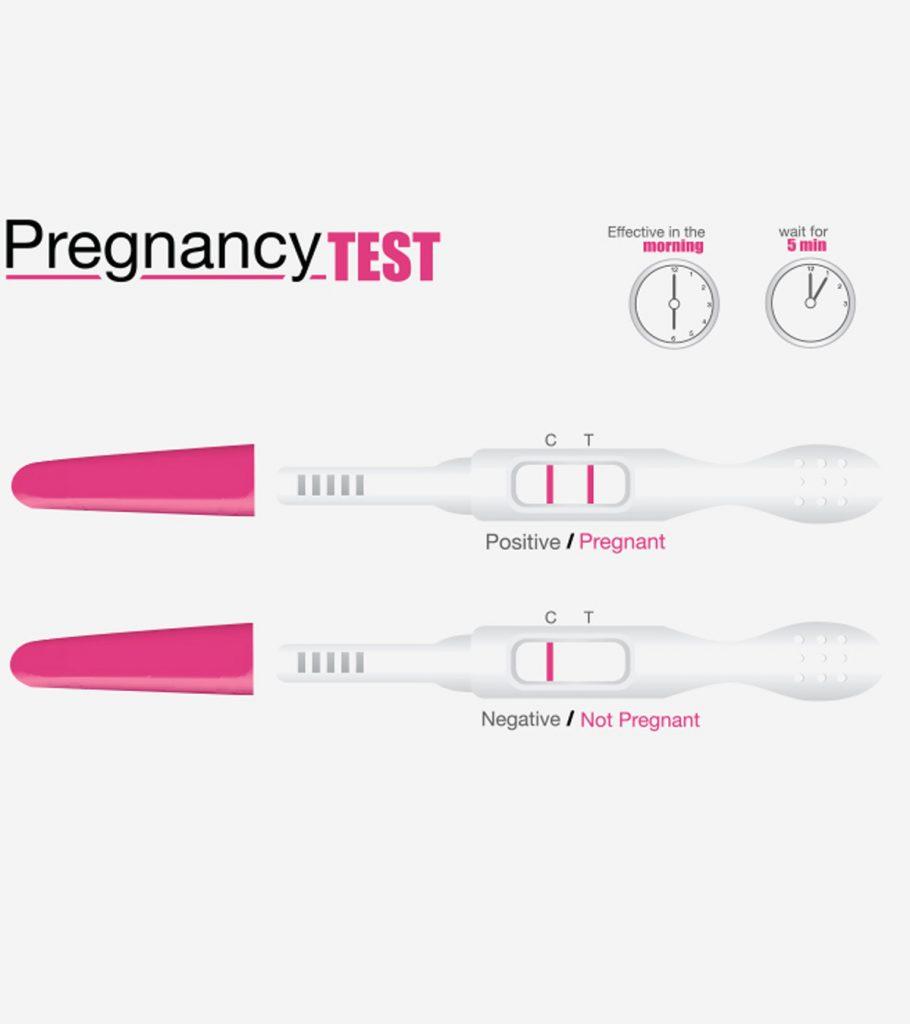
- Time of testing: hCG levels are highest in the morning, so testing first thing in the morning is recommended for optimal accuracy.
- Sensitivity: Different tests have different sensitivities, meaning they can detect varying levels of hCG. More sensitive tests are able to detect pregnancy earlier.
- User error: Following the test instructions carefully is essential to ensure accurate results.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as thyroid disorders or recent pregnancy loss, can affect hCG levels and potentially interfere with test accuracy.
False Positives and False Negatives
- False positives: A false positive result occurs when the test indicates pregnancy when the woman is not actually pregnant. This can be caused by factors such as certain medications, hormonal imbalances, or a chemical pregnancy (a fertilized egg that does not implant).
- False negatives: A false negative result occurs when the test indicates no pregnancy when the woman is actually pregnant. This can be caused by testing too early, using a less sensitive test, or having low hCG levels due to certain medical conditions.
Interpreting Results
- Positive result: If the test line is as dark or darker than the control line, the result is considered positive and indicates pregnancy.
- Negative result: If the test line is lighter than the control line or not visible, the result is considered negative and indicates no pregnancy.
- Invalid result: If the control line is not visible, the test is invalid and should be repeated.
Factors Affecting Accuracy
- Early pregnancy: Urine pregnancy tests are less accurate in the early stages of pregnancy when hCG levels are still low.
- Ectopic pregnancy: An ectopic pregnancy occurs when the fertilized egg implants outside the uterus. Urine pregnancy tests may be less accurate in detecting ectopic pregnancies.
- Recent miscarriage: hCG levels can remain elevated for several weeks after a miscarriage, potentially leading to a false positive result.
- Certain medications: Some medications, such as fertility drugs or birth control pills, can interfere with urine pregnancy test accuracy.
Limitations
Urine pregnancy tests have certain limitations:
- They cannot determine the age of the pregnancy or the viability of the pregnancy.
- They cannot detect all pregnancies, especially in the early stages.
- They cannot rule out an ectopic pregnancy.
When to Seek Medical Advice
If you receive a positive pregnancy test result, it is important to seek medical advice to confirm the pregnancy and discuss prenatal care. If you receive a negative result but suspect you may be pregnant, you should also seek medical advice for further evaluation.
Conclusion
Urine pregnancy tests are a convenient and affordable way to determine if a woman is pregnant. However, it is important to understand the accuracy of these tests and the factors that can affect their reliability. By following the test instructions carefully and being aware of the potential limitations, women can use urine pregnancy tests effectively to detect pregnancy and make informed decisions about their reproductive health.