2003 Teen Pregnancy Rate in the United States: A Comprehensive Analysis
Introduction
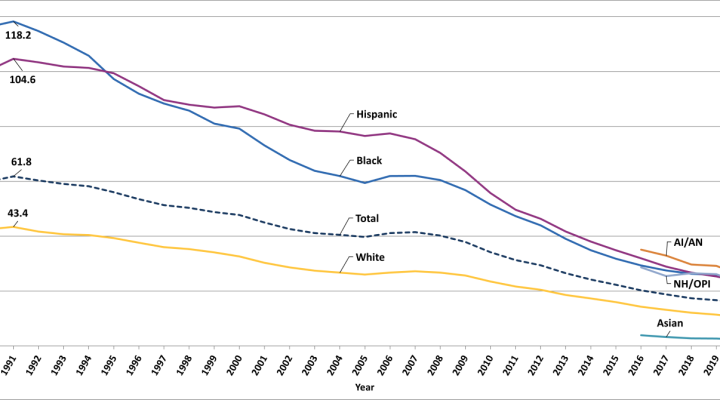
Teen pregnancy remains a significant public health concern in the United States, with far-reaching implications for both the young mothers and their children. In 2003, the teen pregnancy rate in the US stood at 71.5 pregnancies per 1,000 females aged 15-19, a rate that has remained relatively stable over the past decade. This article aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of the 2003 teen pregnancy rate in the US, examining its causes, consequences, and potential solutions.
Causes of Teen Pregnancy
The causes of teen pregnancy are multifaceted and complex, involving a combination of individual, social, and economic factors.
-
Individual Factors:
- Early sexual initiation
- Lack of knowledge about contraception
- Substance use
- Mental health issues
- History of abuse
-
Social Factors:
- Peer pressure
- Media influences
- Lack of parental support
- Poverty
- Educational disparities
-
Economic Factors:
- Limited access to healthcare
- Lack of job opportunities
- Housing instability
Consequences of Teen Pregnancy
Teen pregnancy has significant consequences for both the young mothers and their children.
-
Maternal Health Risks:
- Preeclampsia
- Anemia
- Preterm birth
- Low birth weight infants
-
Educational and Economic Challenges:
- Increased likelihood of dropping out of school
- Lower earning potential
- Limited job opportunities
-
Child Health Risks:
- Prematurity
- Low birth weight
- Developmental delays
- Increased risk of chronic diseases
-
Social and Emotional Challenges:
- Stigma and discrimination
- Relationship difficulties
- Mental health issues
Solutions to Teen Pregnancy
Addressing teen pregnancy requires a comprehensive approach that involves multiple stakeholders, including parents, educators, healthcare providers, and policymakers.
-
Education and Prevention:
- Comprehensive sex education programs
- Access to contraception
- Parent-child communication
-
Economic Support:
- Job training and placement programs
- Affordable housing
- Healthcare coverage
-
Social Support:
- Mentoring programs
- Peer support groups
- Community outreach
-
Policy Changes:
- Raising the minimum age for marriage
- Restricting access to alcohol and tobacco
- Providing paid parental leave
Conclusion
The 2003 teen pregnancy rate in the US highlights the ongoing challenges faced by young people in preventing unplanned pregnancies. While the rate has remained relatively stable over the past decade, it remains significantly higher than in other developed countries. Addressing teen pregnancy requires a multifaceted approach that addresses the underlying causes, provides support to young mothers and their children, and promotes healthy decision-making among adolescents. By investing in comprehensive prevention and support programs, we can create a society where all young people have the opportunity to reach their full potential.
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2004). Teen Pregnancy in the United States: 2003. Atlanta, GA: Author.
- Guttmacher Institute. (2006). Teen Pregnancy and Childbearing in the United States: 2003. New York, NY: Author.
- National Campaign to Prevent Teen and Unplanned Pregnancy. (2005). The State of Teen Pregnancy in the United States. Washington, DC: Author.