The Second Trimester of Pregnancy: A Comprehensive Guide
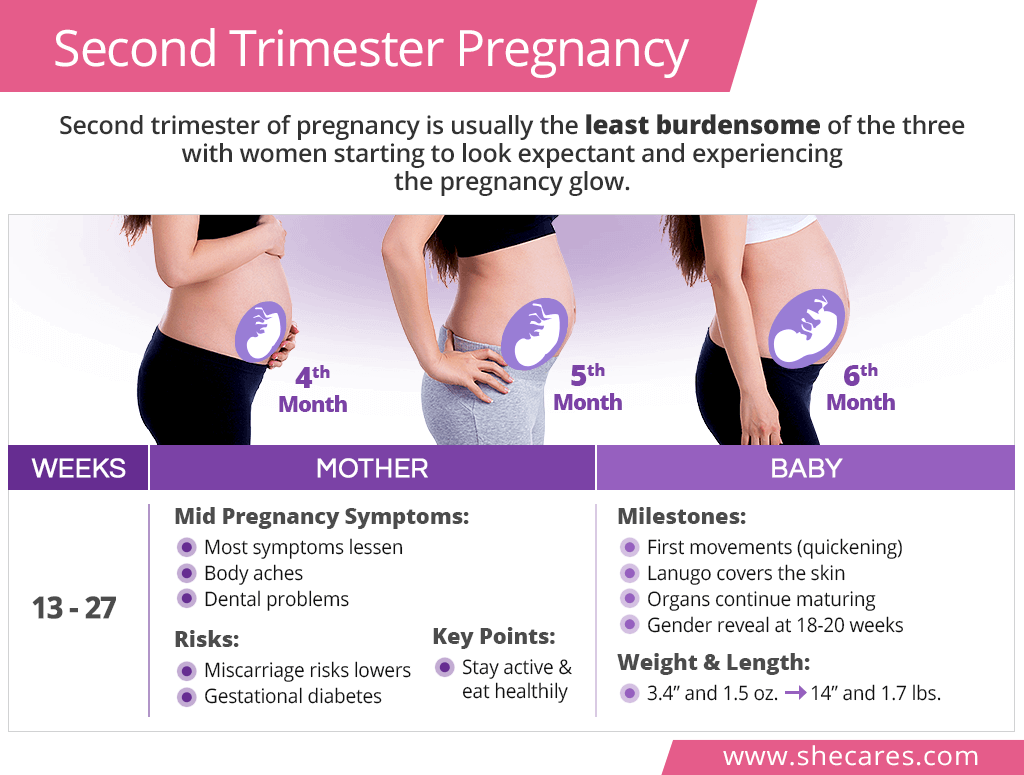
The second trimester of pregnancy is a time of significant growth and development for both the mother and the baby. This period, which spans from weeks 13 to 27, is often characterized by increased energy levels, a growing baby bump, and a variety of physical and emotional changes.
Physical Changes
- Enlarged uterus: The uterus continues to expand rapidly during the second trimester, accommodating the growing fetus. This can lead to an increase in abdominal size and pressure on the bladder, resulting in frequent urination.
- Breast growth: The breasts begin to prepare for breastfeeding, becoming larger and more tender. The nipples may also darken and become more prominent.
- Skin changes: The skin may become darker, especially around the nipples, areolas, and midline of the abdomen (linea nigra). Stretch marks may also appear on the abdomen, thighs, and breasts.
- Hair growth: Some women experience increased hair growth on the face, arms, and legs.
- Varicose veins: The increased blood volume during pregnancy can lead to the development of varicose veins, which are swollen, twisted veins that can appear on the legs and feet.
- Hemorrhoids: Hemorrhoids, which are swollen veins in the rectum, can also develop during the second trimester due to increased pressure on the pelvic area.
Emotional Changes
- Mood swings: Hormonal fluctuations can lead to mood swings, including feelings of happiness, sadness, irritability, and anxiety.
- Increased energy: Many women experience a surge in energy levels during the second trimester, known as the "pregnancy glow."
- Improved sleep: As the uterus moves out of the pelvis, pressure on the bladder decreases, leading to improved sleep quality.
- Increased appetite: The baby’s growth and development require additional nutrients, resulting in an increased appetite.
- Nesting instinct: Some women experience a strong urge to prepare for the baby’s arrival, known as the nesting instinct. This may involve cleaning, organizing, and decorating the home.
Fetal Development
- Week 13: The fetus is about the size of a peach and weighs approximately 1 ounce. The facial features begin to develop, and the eyelids fuse shut.
- Week 16: The fetus is about the size of an avocado and weighs approximately 4 ounces. The arms and legs become more defined, and the fetus begins to move around more actively.
- Week 20: The fetus is about the size of a banana and weighs approximately 12 ounces. The eyes open, and the fetus can respond to light and sound.
- Week 24: The fetus is about the size of a cantaloupe and weighs approximately 1 pound. The lungs begin to develop, and the fetus can make breathing movements.
- Week 28: The fetus is about the size of a pineapple and weighs approximately 2 pounds. The skin becomes thicker, and the fetus begins to store fat.
Prenatal Care
Regular prenatal care is essential during the second trimester to monitor the health of both the mother and the baby. Prenatal appointments typically include:
- Physical exam: The doctor will check the mother’s weight, blood pressure, and overall health.
- Fetal heartbeat monitoring: The doctor will use a Doppler to listen to the baby’s heartbeat.
- Ultrasound: An ultrasound may be performed to assess the baby’s growth and development.
- Blood tests: Blood tests may be ordered to check for anemia, gestational diabetes, and other potential complications.
- Urine tests: Urine tests may be performed to check for infections and other health concerns.
Lifestyle Considerations
- Diet: A healthy diet is important for both the mother and the baby. Focus on consuming nutrient-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein.
- Exercise: Regular exercise is safe and beneficial during pregnancy. Choose low-impact activities that do not put excessive strain on the body, such as walking, swimming, or prenatal yoga.
- Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep each night. Use pillows to support your body and elevate your legs to reduce swelling.
- Stress management: Stress can have negative effects on both the mother and the baby. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercise, meditation, or spending time in nature.
- Smoking and alcohol: Smoking and alcohol consumption are strictly prohibited during pregnancy. These substances can harm the baby’s development and increase the risk of complications.
Common Concerns
- Morning sickness: While morning sickness typically subsides by the end of the first trimester, some women may continue to experience it into the second trimester.
- Constipation: Increased levels of progesterone can slow down digestion, leading to constipation.
- Heartburn: The growing uterus can put pressure on the stomach, causing heartburn.
- Leg cramps: Leg cramps are common during pregnancy due to increased blood volume and pressure on the nerves.
- Round ligament pain: The round ligaments, which support the uterus, can stretch and cause pain in the lower abdomen or groin.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It is important to contact your healthcare provider immediately if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- Severe abdominal pain
- Vaginal bleeding
- Fever
- Chills
- Headache that does not go away
- Blurred vision
- Swelling in the hands, feet, or face
- Difficulty breathing
Conclusion
The second trimester of pregnancy is a time of significant physical, emotional, and fetal development. By following a healthy lifestyle, attending regular prenatal appointments, and addressing any concerns promptly, you can help ensure a healthy pregnancy and a safe and healthy delivery.