Diabetes and Pregnancy Complications
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels. When a woman has diabetes during pregnancy, it is known as gestational diabetes. Gestational diabetes can cause a number of complications for both the mother and the baby.
Complications for the Mother
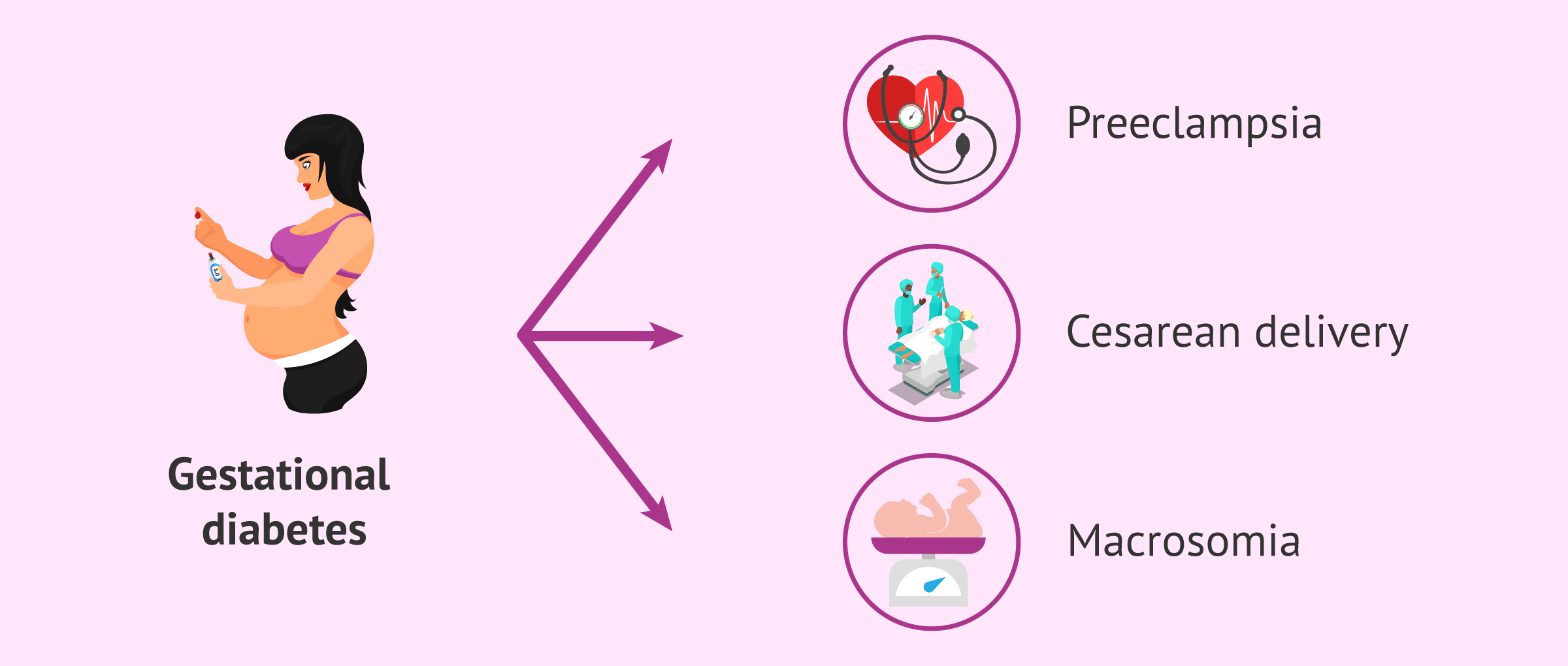
- Preeclampsia: This is a condition that can develop during pregnancy and is characterized by high blood pressure and protein in the urine. Preeclampsia can lead to serious complications, such as seizures, stroke, and kidney failure.
- Eclampsia: This is a severe form of preeclampsia that can lead to seizures and coma.
- Gestational hypertension: This is a condition that is characterized by high blood pressure during pregnancy. Gestational hypertension can increase the risk of developing preeclampsia.
- Placental abruption: This is a condition that occurs when the placenta separates from the uterus before the baby is born. Placental abruption can lead to bleeding, premature birth, and stillbirth.
- Cesarean delivery: Women with gestational diabetes are more likely to need a cesarean delivery.
Complications for the Baby
- Macrosomia: This is a condition in which the baby is born with a high birth weight. Macrosomia can increase the risk of birth injuries, such as shoulder dystocia.
- Hypoglycemia: This is a condition in which the baby’s blood sugar levels are too low. Hypoglycemia can cause seizures, coma, and death.
- Respiratory distress syndrome: This is a condition that can occur in premature babies and is characterized by difficulty breathing.
- Jaundice: This is a condition that causes the baby’s skin and eyes to turn yellow. Jaundice is caused by a buildup of bilirubin, a waste product that is produced when red blood cells are broken down.
- Stillbirth: This is the death of a baby before it is born.
Risk Factors for Gestational Diabetes
The following factors increase the risk of developing gestational diabetes:
- Obesity
- Family history of diabetes
- Age (over 35)
- Certain ethnicities (African American, Hispanic, Native American)
- Previous history of gestational diabetes
- Polycystic ovary syndrome
Diagnosis of Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is diagnosed with a glucose tolerance test. This test is usually performed between the 24th and 28th weeks of pregnancy. The test involves drinking a sugary drink and then having your blood sugar levels checked at regular intervals.
Treatment of Gestational Diabetes
The treatment for gestational diabetes involves managing blood sugar levels through diet, exercise, and medication.
- Diet: A healthy diet for women with gestational diabetes includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It is also important to limit your intake of sugary foods and drinks.
- Exercise: Exercise can help to lower blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Medication: If diet and exercise are not enough to control blood sugar levels, medication may be necessary. Insulin is the most common medication used to treat gestational diabetes.
Prevention of Gestational Diabetes
There is no sure way to prevent gestational diabetes, but there are some things you can do to reduce your risk:
- Maintain a healthy weight before pregnancy.
- Eat a healthy diet.
- Get regular exercise.
- If you have a family history of diabetes, talk to your doctor about ways to reduce your risk.
Outlook for Women with Gestational Diabetes
Most women with gestational diabetes are able to have healthy pregnancies and babies. However, it is important to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully and to manage your blood sugar levels closely.