DNA Testing for Pregnancy: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
Pregnancy is a life-changing event that brings immense joy and anticipation. However, it can also be a time of uncertainty and anxiety, especially for those who have experienced pregnancy loss or have concerns about their health or the health of their unborn child. DNA testing for pregnancy has emerged as a groundbreaking tool that can provide valuable information and peace of mind during this crucial period.
What is DNA Testing for Pregnancy?
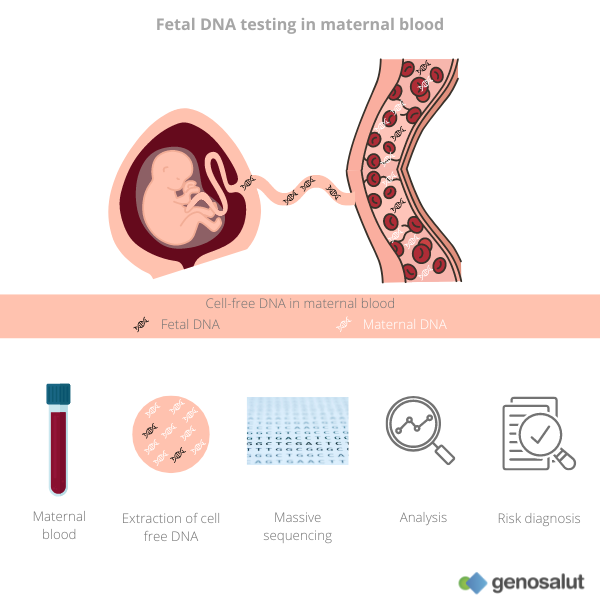
DNA testing for pregnancy is a non-invasive prenatal test that analyzes cell-free fetal DNA (cffDNA) present in the mother’s bloodstream. cffDNA is released into the maternal circulation as the placenta develops and the fetus grows. By analyzing this DNA, genetic tests can detect the presence of fetal chromosomes and identify potential genetic abnormalities.
Types of DNA Testing for Pregnancy
There are two main types of DNA testing for pregnancy:
- Non-invasive prenatal screening (NIPS): NIPS is a screening test that assesses the risk of certain genetic conditions, such as Down syndrome, Trisomy 18, and Trisomy 13. It is typically performed between 10 and 14 weeks of gestation.
- Non-invasive prenatal diagnosis (NIPD): NIPD is a diagnostic test that can confirm or rule out genetic conditions detected by NIPS. It is usually performed after 14 weeks of gestation and is more accurate than NIPS.
Benefits of DNA Testing for Pregnancy
DNA testing for pregnancy offers numerous benefits, including:
- Early detection of genetic abnormalities: NIPS and NIPD can detect genetic conditions early in pregnancy, allowing parents to make informed decisions about their healthcare and the future of their child.
- Reduced risk of miscarriage: Invasive prenatal tests, such as amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling (CVS), carry a small risk of miscarriage. DNA testing for pregnancy eliminates this risk as it does not require the insertion of needles into the uterus.
- Peace of mind: Knowing the health status of their unborn child can provide significant peace of mind for expectant parents, especially those with a history of genetic conditions or pregnancy loss.
- Personalized healthcare: DNA testing results can guide personalized healthcare decisions, such as the need for additional prenatal testing or specialized medical care.
Limitations of DNA Testing for Pregnancy
While DNA testing for pregnancy is a valuable tool, it has certain limitations:
- False positives and false negatives: NIPS is a screening test and can produce false positive or false negative results. NIPD is more accurate but can still have limitations.
- Not all conditions can be detected: DNA testing for pregnancy cannot detect all genetic conditions. It is primarily used to screen for common chromosomal abnormalities.
- Cost: DNA testing for pregnancy can be expensive, especially NIPD.
Who Should Consider DNA Testing for Pregnancy?
DNA testing for pregnancy may be recommended for individuals who:
- Have a family history of genetic conditions
- Have experienced previous pregnancy loss
- Are over 35 years of age
- Have had abnormal results on routine prenatal screening tests
How to Prepare for DNA Testing for Pregnancy
Preparing for DNA testing for pregnancy is relatively simple:
- Inform your healthcare provider: Discuss your interest in DNA testing with your healthcare provider. They can provide guidance and help you determine if it is right for you.
- Schedule an appointment: Once you have decided to proceed with DNA testing, schedule an appointment with a laboratory or healthcare facility that offers the test.
- Fasting: Some DNA tests require fasting beforehand. Follow the instructions provided by your healthcare provider.
Procedure for DNA Testing for Pregnancy
The procedure for DNA testing for pregnancy is simple and painless:
- Blood draw: A small amount of blood is drawn from your arm.
- DNA extraction: The DNA is extracted from the blood sample.
- Analysis: The extracted DNA is analyzed to detect fetal chromosomes and identify potential genetic abnormalities.
Results and Interpretation
The results of DNA testing for pregnancy are typically available within a few weeks. Your healthcare provider will interpret the results and discuss them with you.
- Negative results: If the results are negative, it means that the fetus is unlikely to have the genetic condition being tested for.
- Positive results: If the results are positive, it means that the fetus has an increased risk of having the genetic condition being tested for. Further testing may be recommended to confirm the diagnosis.
Conclusion
DNA testing for pregnancy is a valuable tool that can provide valuable information and peace of mind during pregnancy. It offers early detection of genetic abnormalities, reduces the risk of miscarriage, and allows for personalized healthcare decisions. While it has certain limitations, DNA testing for pregnancy can be a powerful resource for expectant parents seeking to ensure the health and well-being of their unborn child.