Drug Use During Pregnancy: A Comprehensive Overview
Drug use during pregnancy is a serious public health concern with far-reaching consequences for both the mother and the developing fetus. Understanding the risks associated with substance use during this critical period is essential for healthcare providers, policymakers, and expectant mothers alike. This comprehensive overview will delve into the prevalence, types, and effects of drug use during pregnancy, as well as strategies for prevention and intervention.
Prevalence and Types of Drug Use
Drug use during pregnancy is a global problem, affecting an estimated 10-15% of pregnant women worldwide. The most commonly used substances include:
- Alcohol: Alcohol is the most widely used drug during pregnancy, with approximately 50% of pregnant women reporting alcohol consumption.
- Tobacco: Smoking during pregnancy is prevalent in 10-20% of women.
- Marijuana: Marijuana use during pregnancy has increased significantly in recent years, with up to 15% of pregnant women reporting use.
- Opioids: Opioid use during pregnancy, including prescription pain relievers and illicit drugs like heroin, has become a major public health crisis.
- Cocaine: Cocaine use during pregnancy is associated with significant health risks for both the mother and the fetus.
- Methamphetamine: Methamphetamine use during pregnancy can lead to premature birth, low birth weight, and developmental problems.
Effects on Maternal and Fetal Health
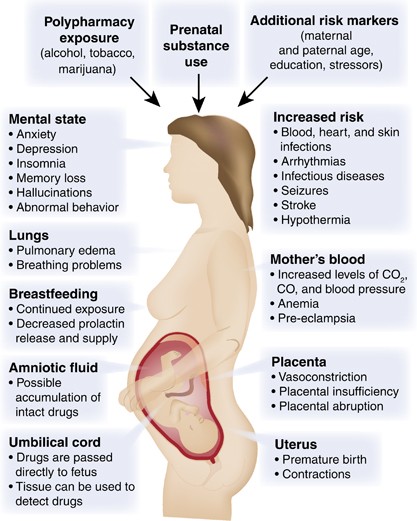
Drug use during pregnancy can have a wide range of adverse effects on both the mother and the developing fetus. These effects vary depending on the type of drug used, the amount and frequency of use, and the stage of pregnancy.
Maternal Effects:
- Increased risk of miscarriage, premature birth, and low birth weight
- Placental abruption, a condition where the placenta separates from the uterus
- Gestational diabetes and preeclampsia
- Postpartum depression and anxiety
Fetal Effects:
- Fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS), a cluster of birth defects caused by alcohol exposure
- Preterm birth and low birth weight
- Developmental delays and cognitive impairment
- Increased risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS)
Prevention and Intervention
Preventing drug use during pregnancy is a multi-faceted challenge that requires a collaborative effort from healthcare providers, policymakers, and communities. Key strategies include:
- Education and Awareness: Providing expectant mothers with accurate information about the risks of drug use during pregnancy is crucial.
- Screening and Early Intervention: Screening for drug use during prenatal care allows healthcare providers to identify and intervene early, reducing the potential for harm.
- Treatment and Support: Women who are struggling with substance use disorders during pregnancy need access to comprehensive treatment and support services, including medication-assisted treatment (MAT) for opioid use disorder.
- Social and Economic Support: Addressing the underlying social and economic factors that contribute to drug use during pregnancy, such as poverty, lack of education, and trauma, is essential for long-term prevention.
Conclusion
Drug use during pregnancy is a complex and multifaceted issue with significant consequences for both the mother and the developing fetus. Understanding the prevalence, types, and effects of drug use is crucial for developing effective prevention and intervention strategies. By working together, healthcare providers, policymakers, and communities can reduce the incidence of drug use during pregnancy and improve the health outcomes of both mothers and their children.