Ovulation and Pregnancy Calendar: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
Understanding ovulation and the menstrual cycle is crucial for women who are trying to conceive or avoid pregnancy. An ovulation and pregnancy calendar can be a valuable tool in this regard, providing a visual representation of the fertile and infertile periods throughout the month. This article will delve into the intricacies of ovulation and pregnancy calendars, explaining how they work, how to use them effectively, and their limitations.
What is Ovulation?
Ovulation is the process by which a mature egg is released from one of the ovaries. It typically occurs 14 days before the start of the next menstrual period, assuming a regular 28-day cycle. During ovulation, the egg travels through the fallopian tube, where it can be fertilized by sperm. If fertilization occurs, the fertilized egg implants in the lining of the uterus, leading to pregnancy.
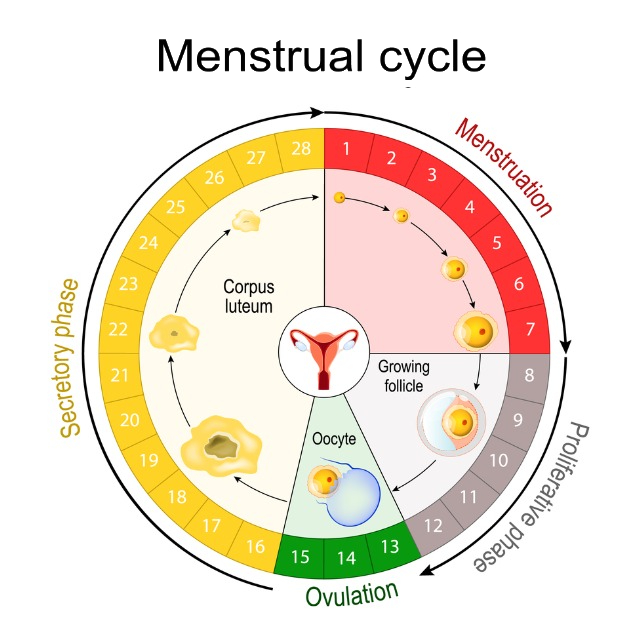
The Menstrual Cycle
The menstrual cycle is a monthly process that involves the release of an egg from the ovary and the preparation of the uterus for pregnancy. It consists of four main phases:
- Menstrual phase: The shedding of the uterine lining, resulting in menstrual bleeding.
- Follicular phase: The development of a follicle (a sac containing an egg) in the ovary.
- Ovulatory phase: The release of the egg from the ovary (ovulation).
- Luteal phase: The preparation of the uterine lining for implantation of a fertilized egg.
Ovulation and Pregnancy Calendars
Ovulation and pregnancy calendars are tools that help women track their menstrual cycles and predict their fertile and infertile periods. They can be used to:
- Identify the most likely time of ovulation
- Plan for pregnancy or avoid it
- Monitor cycle regularity
- Detect potential fertility issues
How Ovulation and Pregnancy Calendars Work
Ovulation and pregnancy calendars typically use one or more of the following methods to predict ovulation:
- Calendar method: Based on the average length of the menstrual cycle, this method estimates the day of ovulation as 14 days before the start of the next period.
- Cervical mucus method: This method involves observing the changes in cervical mucus throughout the cycle. Fertile mucus is clear, stretchy, and slippery, indicating the approach of ovulation.
- Basal body temperature (BBT) method: This method involves taking daily temperature readings. A slight rise in temperature after ovulation indicates the luteal phase.
- Ovulation predictor kits (OPKs): These kits detect the surge in luteinizing hormone (LH) that occurs before ovulation.
Using an Ovulation and Pregnancy Calendar
To use an ovulation and pregnancy calendar effectively, follow these steps:
- Track your menstrual cycle: Note the start and end dates of each period.
- Determine the length of your cycle: Calculate the number of days between the start of one period and the start of the next.
- Estimate the day of ovulation: Use the calendar method or another method to predict the day of ovulation.
- Mark fertile and infertile periods: The fertile period typically extends from 5 days before ovulation to the day of ovulation. The infertile period includes the remaining days of the cycle.
Limitations of Ovulation and Pregnancy Calendars
While ovulation and pregnancy calendars can be helpful tools, they have certain limitations:
- Accuracy: The accuracy of these calendars depends on the regularity of the menstrual cycle. Irregular cycles can make it difficult to predict ovulation accurately.
- Individual variability: Ovulation can vary from woman to woman and even from cycle to cycle within the same woman.
- External factors: Stress, illness, and certain medications can affect ovulation and disrupt the menstrual cycle.
Conclusion
Ovulation and pregnancy calendars can be valuable aids in understanding the menstrual cycle and predicting fertile and infertile periods. However, it is important to use them in conjunction with other methods, such as cervical mucus observation or BBT charting, to improve accuracy. Additionally, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional if you have concerns about your fertility or menstrual cycle.