Pregnancy and Menstruation: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
Pregnancy and menstruation are two distinct physiological processes that occur in the female reproductive system. While pregnancy involves the development of a new life within the uterus, menstruation marks the shedding of the uterine lining in the absence of pregnancy. Understanding the differences and similarities between these two processes is crucial for reproductive health and well-being.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy is the period of time from conception to birth, typically lasting around 40 weeks. It is characterized by a series of hormonal changes and physical adaptations that support the growth and development of the fetus.
Signs and Symptoms
The most common early signs of pregnancy include:
- Missed period
- Nausea and vomiting (morning sickness)
- Breast tenderness
- Fatigue
- Frequent urination
As pregnancy progresses, other symptoms may develop, such as:
- Abdominal enlargement
- Fetal movement
- Back pain
- Leg cramps
- Hemorrhoids
Hormonal Changes
Pregnancy is primarily driven by the hormones human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), estrogen, and progesterone.
- hCG: Produced by the placenta, hCG is responsible for maintaining the pregnancy by preventing the breakdown of the uterine lining.
- Estrogen: Produced by the placenta and ovaries, estrogen promotes uterine growth and prepares the breasts for lactation.
- Progesterone: Also produced by the placenta, progesterone relaxes the uterine muscles and prevents premature contractions.
Physical Adaptations
Pregnancy involves significant physical adaptations to accommodate the growing fetus. These include:
- Uterine enlargement: The uterus expands to accommodate the developing fetus, increasing in size from the size of a small fist to that of a watermelon.
- Cervical changes: The cervix softens and becomes more vascularized to prepare for childbirth.
- Pelvic floor changes: The pelvic floor muscles relax and stretch to support the weight of the uterus and fetus.
- Breast changes: The breasts enlarge and become more tender in preparation for lactation.
Menstruation
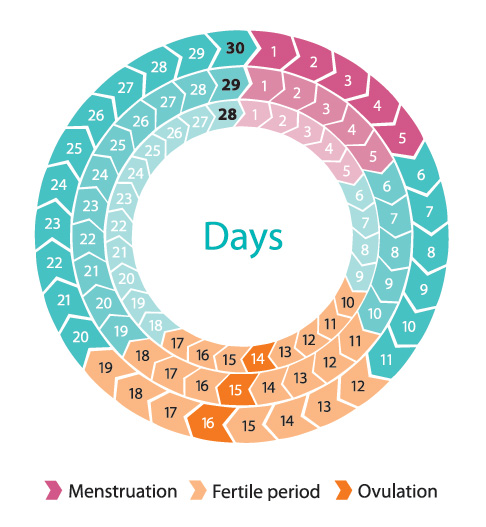
Menstruation is the process of shedding the uterine lining (endometrium) when pregnancy does not occur. It typically occurs every 28-35 days and lasts for 3-7 days.
Hormonal Regulation
Menstruation is regulated by a complex interplay of hormones, including:
- Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH): Stimulates the development of follicles in the ovaries.
- Luteinizing hormone (LH): Triggers ovulation, the release of an egg from the ovary.
- Estrogen: Produced by the developing follicle, estrogen prepares the uterine lining for implantation.
- Progesterone: Produced by the corpus luteum (the remains of the follicle after ovulation), progesterone maintains the uterine lining in preparation for pregnancy.
Phases of the Menstrual Cycle
The menstrual cycle consists of four distinct phases:
- Menstrual phase: The uterine lining is shed, resulting in menstrual bleeding.
- Follicular phase: An egg matures within a follicle in the ovary.
- Ovulatory phase: Ovulation occurs, releasing the egg from the ovary.
- Luteal phase: The corpus luteum produces progesterone, preparing the uterine lining for pregnancy. If pregnancy does not occur, the corpus luteum breaks down, leading to a decline in progesterone levels and the onset of menstruation.
Differences Between Pregnancy and Menstruation
| Feature | Pregnancy | Menstruation |
|---|---|---|
| Timing | Occurs after conception | Occurs every 28-35 days |
| Duration | Typically 40 weeks | 3-7 days |
| Hormonal changes | hCG, estrogen, progesterone | FSH, LH, estrogen, progesterone |
| Physical adaptations | Uterine enlargement, cervical changes, pelvic floor changes, breast changes | No significant physical adaptations |
| Symptoms | Missed period, nausea, breast tenderness, fatigue, frequent urination | Menstrual bleeding, cramps, mood swings, bloating |
| Purpose | Development of a new life | Shedding of the uterine lining |
Similarities Between Pregnancy and Menstruation
- Both involve hormonal changes.
- Both can cause physical symptoms, such as breast tenderness and fatigue.
- Both can be affected by factors such as stress, diet, and exercise.
Pregnancy and Menstruation After Childbirth
After childbirth, it may take several weeks or months for the menstrual cycle to return to normal. Some women may experience irregular periods or amenorrhea (absence of periods) while breastfeeding.
Conclusion
Pregnancy and menstruation are distinct physiological processes with different purposes and timelines. Understanding the differences and similarities between these two processes is essential for reproductive health and well-being. If you have any concerns about your menstrual cycle or suspect you may be pregnant, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for guidance and support.