Pregnancy Complications: A Comprehensive Overview
Pregnancy is a transformative journey marked by profound physiological and emotional changes. While most pregnancies progress uneventfully, approximately 10-15% of expectant mothers encounter complications that can impact their health and the well-being of their unborn child. Understanding these complications is crucial for timely diagnosis, appropriate management, and optimal outcomes.
Types of Pregnancy Complications
Pregnancy complications encompass a wide range of conditions, each with its unique etiology, symptoms, and potential risks. Some of the most common complications include:
1. Gestational Diabetes:
Gestational diabetes is a temporary form of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It occurs when the body is unable to produce enough insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. Gestational diabetes can increase the risk of preeclampsia, macrosomia (large birth weight), and cesarean delivery.
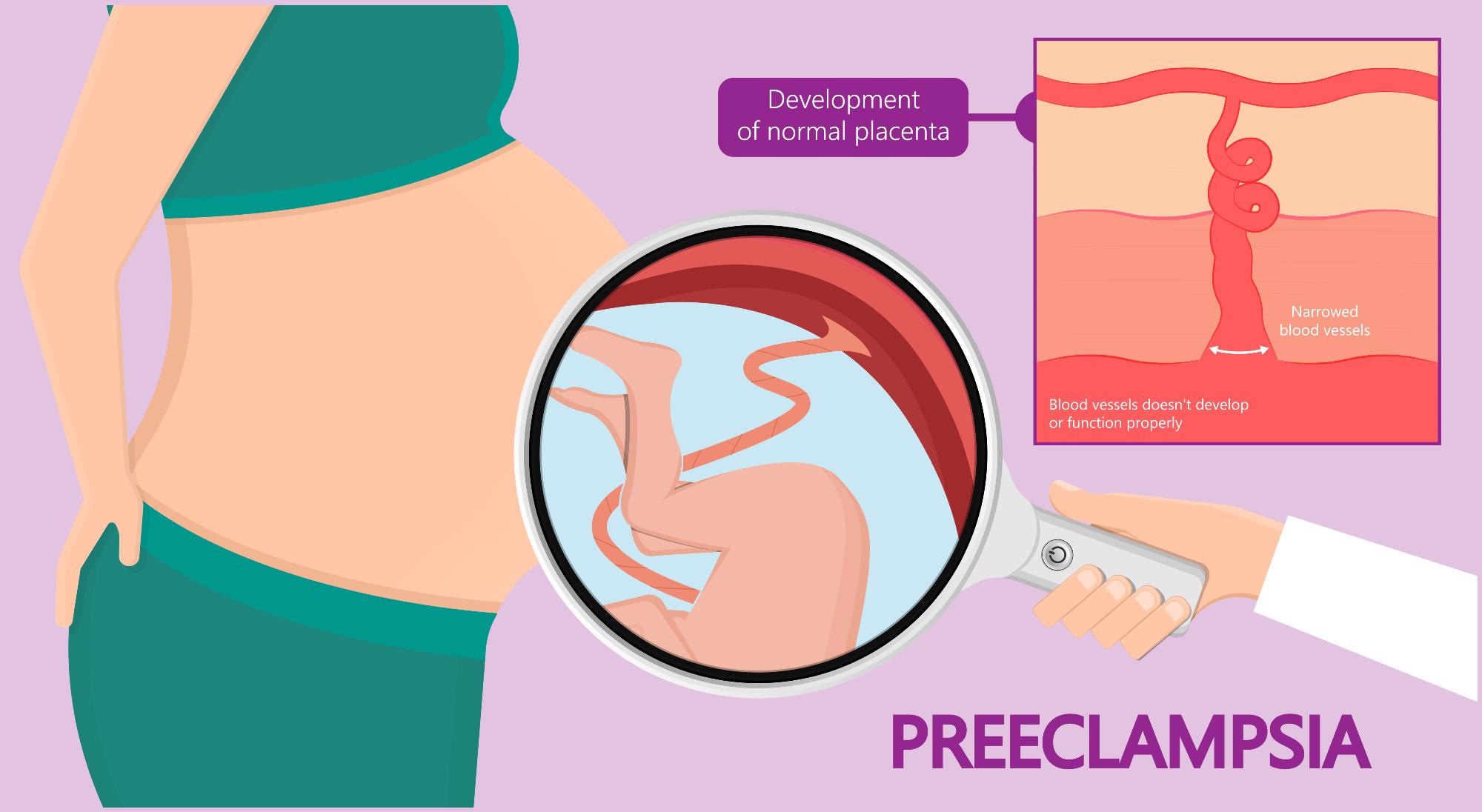
2. Preeclampsia:
Preeclampsia is a serious condition characterized by high blood pressure and protein in the urine. It typically develops after 20 weeks of gestation and can lead to severe complications for both the mother and the baby, including seizures, organ damage, and premature birth.
3. Placental Abruption:
Placental abruption occurs when the placenta separates from the uterine wall prematurely. This can cause severe bleeding, abdominal pain, and fetal distress. Placental abruption is a medical emergency that requires immediate intervention.
4. Premature Rupture of Membranes (PROM):
PROM occurs when the amniotic sac ruptures before the onset of labor. This can lead to infection, premature birth, and other complications. PROM is more common in women with multiple pregnancies or a history of uterine surgery.
5. Placenta Previa:
Placenta previa occurs when the placenta implants in the lower part of the uterus, covering the cervix. This can cause bleeding during pregnancy and labor, and may necessitate a cesarean delivery.
6. Intrauterine Growth Restriction (IUGR):
IUGR refers to a condition in which the fetus fails to grow at an appropriate rate. This can be caused by various factors, including maternal malnutrition, placental insufficiency, and genetic abnormalities. IUGR can lead to premature birth, low birth weight, and developmental delays.
7. Ectopic Pregnancy:
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when the fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, typically in the fallopian tube. This is a life-threatening condition that requires prompt medical attention.
8. Hyperemesis Gravidarum:
Hyperemesis gravidarum is a severe form of morning sickness that causes persistent nausea, vomiting, and dehydration. It can lead to electrolyte imbalances, weight loss, and hospitalization.
9. Postpartum Hemorrhage:
Postpartum hemorrhage refers to excessive bleeding after childbirth. It is a major cause of maternal mortality and can be caused by various factors, including uterine atony, retained placenta, and lacerations.
Risk Factors for Pregnancy Complications
Certain factors increase the risk of developing pregnancy complications, including:
- Advanced maternal age
- Multiple pregnancies
- History of previous pregnancy complications
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Chronic medical conditions (e.g., diabetes, hypertension)
- Family history of pregnancy complications
Diagnosis and Management of Pregnancy Complications
Early detection and appropriate management of pregnancy complications are essential for improving outcomes. Regular prenatal care and screening tests play a crucial role in identifying potential risks and implementing timely interventions.
- Gestational Diabetes: Diagnosed through glucose tolerance testing, gestational diabetes is managed with dietary modifications, exercise, and insulin therapy if necessary.
- Preeclampsia: Diagnosed based on blood pressure and urine protein levels, preeclampsia is treated with antihypertensive medications and close monitoring. In severe cases, delivery may be necessary.
- Placental Abruption: Diagnosed through ultrasound and clinical examination, placental abruption requires immediate hospitalization and blood transfusions. Delivery may be necessary to prevent further complications.
- PROM: Diagnosed through a physical exam and amniocentesis, PROM is managed with antibiotics to prevent infection and close monitoring for signs of labor.
- Placenta Previa: Diagnosed through ultrasound, placenta previa is managed with bed rest and close monitoring. A cesarean delivery is typically recommended.
- IUGR: Diagnosed through ultrasound and fetal monitoring, IUGR is managed with close monitoring, nutritional support, and potential delivery if necessary.
- Ectopic Pregnancy: Diagnosed through ultrasound and blood tests, ectopic pregnancy requires immediate surgical intervention to remove the fertilized egg.
- Hyperemesis Gravidarum: Diagnosed based on symptoms and medical history, hyperemesis gravidarum is managed with anti-nausea medications, intravenous fluids, and nutritional support.
- Postpartum Hemorrhage: Diagnosed through clinical examination and blood loss estimation, postpartum hemorrhage is managed with medications to promote uterine contractions, blood transfusions, and surgical intervention if necessary.
Prevention of Pregnancy Complications
While not all pregnancy complications can be prevented, certain measures can reduce the risk:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Quitting smoking
- Managing chronic medical conditions
- Receiving regular prenatal care
- Following a balanced diet
- Engaging in moderate exercise
Conclusion
Pregnancy complications are a significant concern for expectant mothers and healthcare providers alike. Understanding the types, risk factors, diagnosis, and management of these complications is essential for optimizing outcomes. Regular prenatal care, screening tests, and timely interventions play a crucial role in identifying and addressing potential risks, ensuring the well-being of both the mother and the unborn child.