Pregnancy Progesterone Levels: A Comprehensive Guide
Progesterone, a hormone produced by the corpus luteum during the menstrual cycle, plays a crucial role in maintaining pregnancy. Its levels fluctuate throughout the menstrual cycle, reaching their peak during the luteal phase. If pregnancy occurs, progesterone levels remain elevated to support the developing fetus.
Progesterone’s Role in Pregnancy
Progesterone has several essential functions during pregnancy:
- Maintaining the Uterine Lining: Progesterone prepares the uterine lining (endometrium) for implantation by thickening and vascularizing it.
- Preventing Uterine Contractions: Progesterone relaxes the uterine muscles, preventing premature contractions that could lead to miscarriage.
- Supporting Placental Development: Progesterone promotes the growth and development of the placenta, which is responsible for nutrient and oxygen exchange between the mother and fetus.
- Suppressing the Immune System: Progesterone suppresses the maternal immune system to prevent rejection of the fetus, which is recognized as foreign tissue.
- Promoting Breast Development: Progesterone prepares the breasts for lactation by stimulating the growth of milk-producing glands.
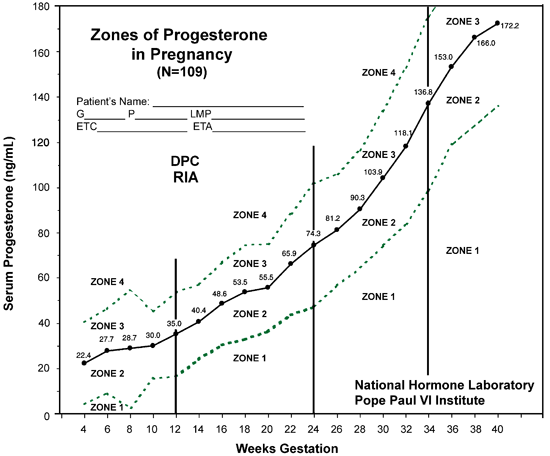
Progesterone Levels During Pregnancy
Progesterone levels rise rapidly after ovulation and reach their peak in the mid-luteal phase. If pregnancy occurs, the corpus luteum continues to produce progesterone until the placenta takes over this function at around 10-12 weeks of gestation.
The normal range of progesterone levels during pregnancy varies depending on the trimester:
- First Trimester: 10-90 ng/mL
- Second Trimester: 20-150 ng/mL
- Third Trimester: 50-300 ng/mL
Low Progesterone Levels During Pregnancy
Low progesterone levels during pregnancy can be a sign of an underlying medical condition or pregnancy complication. Common causes include:
- Corpus Luteum Deficiency: Failure of the corpus luteum to produce sufficient progesterone.
- Placental Abnormalities: Placental insufficiency or detachment can lead to decreased progesterone production.
- Ectopic Pregnancy: A pregnancy that occurs outside the uterus, where the corpus luteum cannot support progesterone production.
- Miscarriage: Low progesterone levels can be a symptom of an impending miscarriage.
Symptoms of Low Progesterone Levels
Low progesterone levels during pregnancy can cause a range of symptoms, including:
- Vaginal bleeding or spotting
- Pelvic pain or cramping
- Breast tenderness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fatigue
- Mood swings
Treatment for Low Progesterone Levels
Treatment for low progesterone levels during pregnancy typically involves progesterone supplementation. This can be administered through vaginal suppositories, injections, or oral medications. The type and dosage of progesterone will depend on the underlying cause and the severity of the progesterone deficiency.
High Progesterone Levels During Pregnancy
High progesterone levels during pregnancy are less common than low levels. They can be caused by:
- Molar Pregnancy: A rare type of pregnancy in which a fertilized egg develops into a mass of cysts instead of a fetus.
- Multiple Gestations: Carrying twins or more can lead to higher progesterone levels.
- Gestational Trophoblastic Disease: A group of rare conditions that involve abnormal growth of placental tissue.
Symptoms of High Progesterone Levels
High progesterone levels during pregnancy can cause symptoms such as:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fatigue
- Breast tenderness
- Mood swings
- Fluid retention
- Constipation
Treatment for High Progesterone Levels
Treatment for high progesterone levels during pregnancy may involve monitoring the condition and addressing any underlying medical issues. In some cases, medications may be used to lower progesterone levels.
Monitoring Progesterone Levels
Progesterone levels are typically monitored during pregnancy through blood tests. Your doctor may recommend regular blood tests to assess progesterone levels and ensure they are within the normal range.
Conclusion
Progesterone is a crucial hormone that plays a vital role in maintaining pregnancy. Understanding progesterone levels and their significance can help ensure a healthy pregnancy and early detection of any potential complications. If you experience any symptoms of low or high progesterone levels, it is important to consult your doctor promptly for evaluation and appropriate treatment.