Pregnancy Rate: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
Pregnancy rate, a crucial indicator of reproductive health, is the number of pregnancies that occur within a specific population over a defined period. It plays a significant role in understanding fertility patterns, population dynamics, and healthcare planning. This article delves into the intricacies of pregnancy rate, exploring its determinants, implications, and strategies for monitoring and management.
Determinants of Pregnancy Rate
Numerous factors influence pregnancy rate, including:
- Age: Fertility peaks during the reproductive years, typically between 20 and 35. After 35, fertility gradually declines.
- Reproductive Health: Underlying medical conditions, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or endometriosis, can impact fertility.
- Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and obesity can lower pregnancy rates.
- Contraception Use: The use of effective contraception methods, such as condoms or birth control pills, reduces pregnancy rates.
- Socioeconomic Status: Education, income, and access to healthcare can influence pregnancy rates.
Implications of Pregnancy Rate
Pregnancy rate has far-reaching implications for individuals, families, and society as a whole:
- Individual Health: Unplanned pregnancies can lead to health risks for both the mother and the child.
- Family Planning: Understanding pregnancy rates is essential for individuals and couples to make informed decisions about family planning.
- Population Growth: High pregnancy rates can contribute to population growth, while low pregnancy rates can lead to population decline.
- Healthcare Planning: Healthcare systems need to anticipate and prepare for the number of pregnancies that will occur in a given population.
Monitoring and Management of Pregnancy Rate
Monitoring and managing pregnancy rate is crucial for public health and family planning efforts. Several strategies are employed:
- Data Collection: Collecting accurate data on pregnancies is essential for understanding trends and patterns.
- Surveillance Systems: Establishing surveillance systems allows for ongoing monitoring of pregnancy rates and identification of areas of concern.
- Family Planning Programs: Access to family planning services, including contraception and counseling, can help reduce unintended pregnancies.
- Health Education: Raising awareness about reproductive health and family planning can empower individuals to make informed choices.
- Prenatal Care: Providing prenatal care to pregnant women ensures the health of both the mother and the child.
Pregnancy Rate in the United States
In the United States, the pregnancy rate has been declining since the 1990s. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the pregnancy rate among women aged 15-44 was 55.7 per 1,000 women in 2019. This decline is attributed to factors such as increased contraceptive use and delayed childbearing.
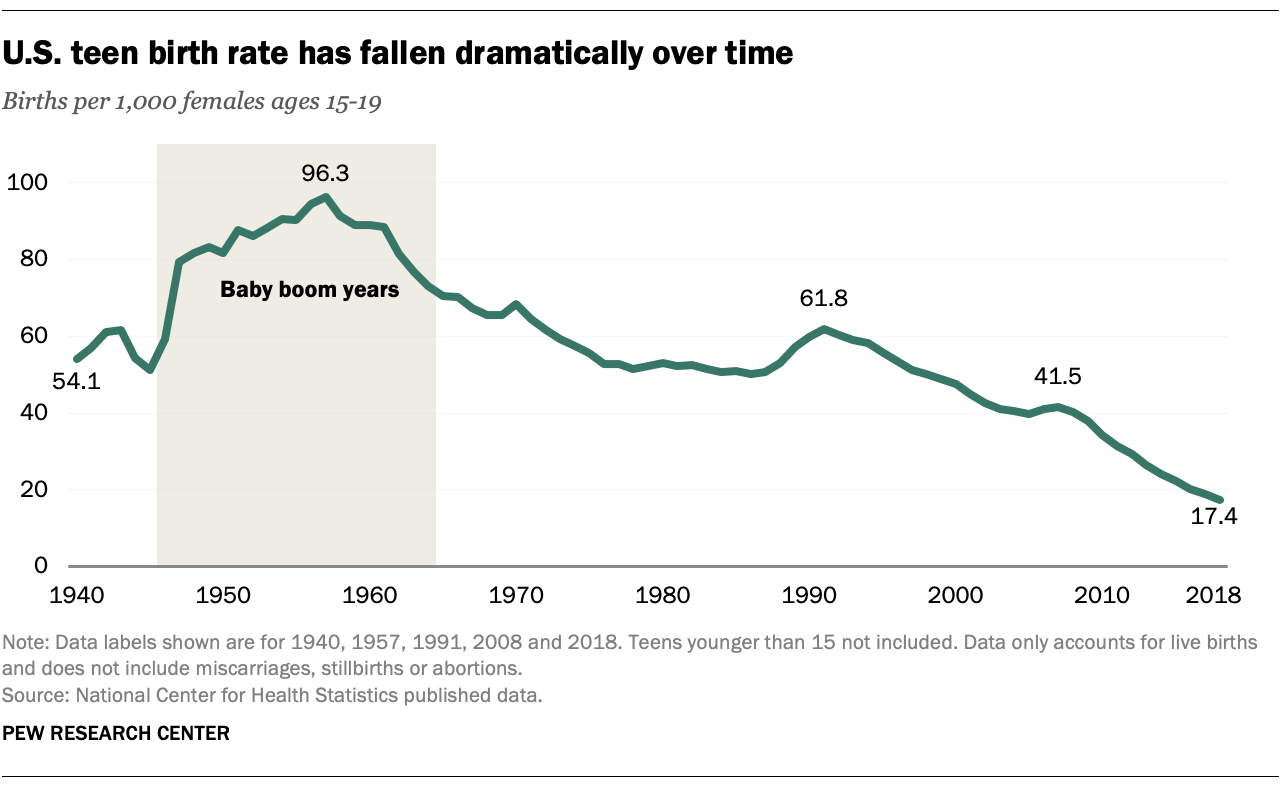
Teenage Pregnancy
Teenage pregnancy remains a significant concern in the United States. In 2019, the pregnancy rate among girls aged 15-19 was 18.8 per 1,000 girls. Teenage pregnancy is associated with higher risks for both the mother and the child, including premature birth, low birth weight, and educational challenges.
Racial and Ethnic Disparities
Pregnancy rates vary significantly across racial and ethnic groups in the United States. In 2019, the pregnancy rate among Hispanic women was 82.9 per 1,000 women, compared to 52.3 per 1,000 women among white women and 67.4 per 1,000 women among black women. These disparities are influenced by socioeconomic factors, access to healthcare, and cultural norms.
Conclusion
Pregnancy rate is a complex and multifaceted indicator of reproductive health. Understanding its determinants, implications, and strategies for monitoring and management is essential for improving reproductive outcomes, reducing unintended pregnancies, and promoting population health. By addressing the factors that influence pregnancy rate and implementing effective interventions, we can create a society where every pregnancy is planned and every child is born into a healthy and supportive environment.