Teenage Pregnancy Statistics: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
Teenage pregnancy remains a significant public health concern, with far-reaching implications for both the young mothers and their children. Understanding the prevalence, trends, and contributing factors associated with teenage pregnancy is crucial for developing effective prevention and intervention strategies. This comprehensive article delves into the statistics of teenage pregnancy in the United States, examining its prevalence, disparities, and consequences.
Prevalence
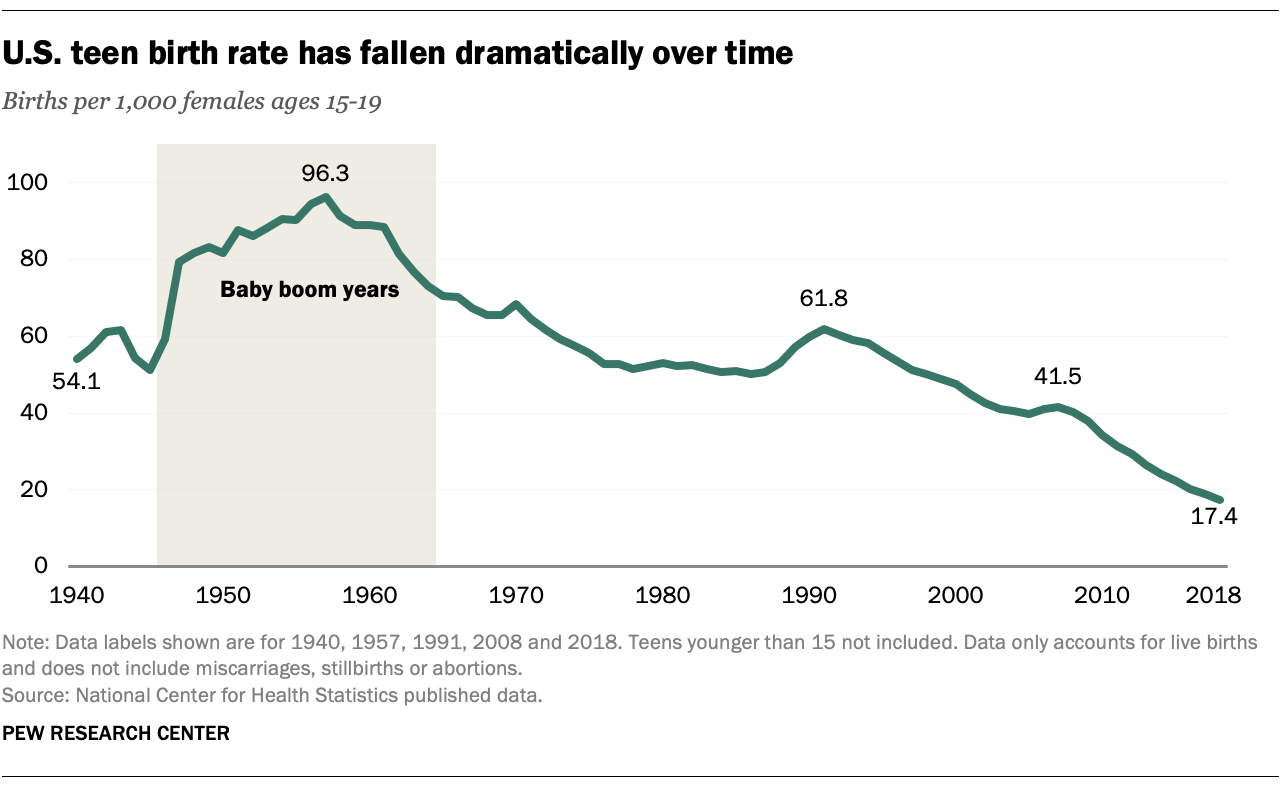
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), in 2020, the birth rate among teenagers aged 15-19 was 17.4 births per 1,000 females. This represents a decline from 27.3 births per 1,000 females in 2007, indicating a positive trend. However, the United States still has one of the highest teenage pregnancy rates among developed countries.
Disparities
Teenage pregnancy rates vary significantly across different demographic groups. In 2020, the birth rate among Hispanic teenagers was 24.4 per 1,000 females, compared to 15.3 per 1,000 females among non-Hispanic white teenagers and 26.4 per 1,000 females among non-Hispanic black teenagers. Additionally, teenagers living in poverty are more likely to experience pregnancy than those from more affluent backgrounds.
Contributing Factors
Numerous factors contribute to teenage pregnancy, including:
- Lack of access to comprehensive sex education: Many teenagers lack access to accurate and age-appropriate information about sexual health and contraception.
- Peer pressure and social norms: Teenagers may feel pressured to engage in sexual activity by their peers or by societal expectations.
- Limited access to contraception: Teenagers may face barriers to obtaining contraception, such as lack of parental consent, cost, or stigma.
- Abuse and neglect: Teenagers who experience abuse or neglect are at increased risk for pregnancy.
- Mental health issues: Teenagers with mental health issues, such as depression or anxiety, may be more likely to engage in risky sexual behaviors.
Consequences
Teenage pregnancy has significant consequences for both the young mothers and their children.
Consequences for Young Mothers
- Increased risk of health complications: Teenage mothers are more likely to experience pregnancy-related complications, such as premature birth, low birth weight, and postpartum depression.
- Lower educational attainment: Teenage mothers are less likely to complete high school and pursue higher education.
- Economic hardship: Teenage mothers are more likely to live in poverty and experience financial instability.
- Social stigma: Teenage mothers often face social stigma and judgment, which can negatively impact their mental health and well-being.
Consequences for Children
- Increased risk of health problems: Children born to teenage mothers are more likely to experience health problems, such as low birth weight, developmental delays, and chronic diseases.
- Lower educational attainment: Children born to teenage mothers are less likely to succeed in school and pursue higher education.
- Increased risk of poverty: Children born to teenage mothers are more likely to live in poverty and experience economic hardship.
Prevention and Intervention
Preventing teenage pregnancy requires a comprehensive approach that addresses the underlying factors contributing to it. Effective prevention strategies include:
- Comprehensive sex education: Providing teenagers with accurate and age-appropriate information about sexual health and contraception is essential for reducing pregnancy rates.
- Access to contraception: Ensuring that teenagers have access to a range of contraceptive methods, including condoms, birth control pills, and intrauterine devices (IUDs), is crucial.
- Parent-child communication: Open and honest communication between parents and teenagers about sexual health and relationships can help reduce pregnancy rates.
- Peer support programs: Programs that provide teenagers with peer support and mentorship can help reduce risky sexual behaviors.
- Economic support: Providing financial assistance to teenage mothers can help them stay in school and provide for their children.
Conclusion
Teenage pregnancy remains a significant public health concern, with far-reaching consequences for both the young mothers and their children. Understanding the prevalence, trends, and contributing factors associated with teenage pregnancy is crucial for developing effective prevention and intervention strategies. By addressing the underlying factors that contribute to teenage pregnancy, we can reduce its prevalence and improve the lives of young people and their families.