Pregnancy Test While Implantation Bleeding: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
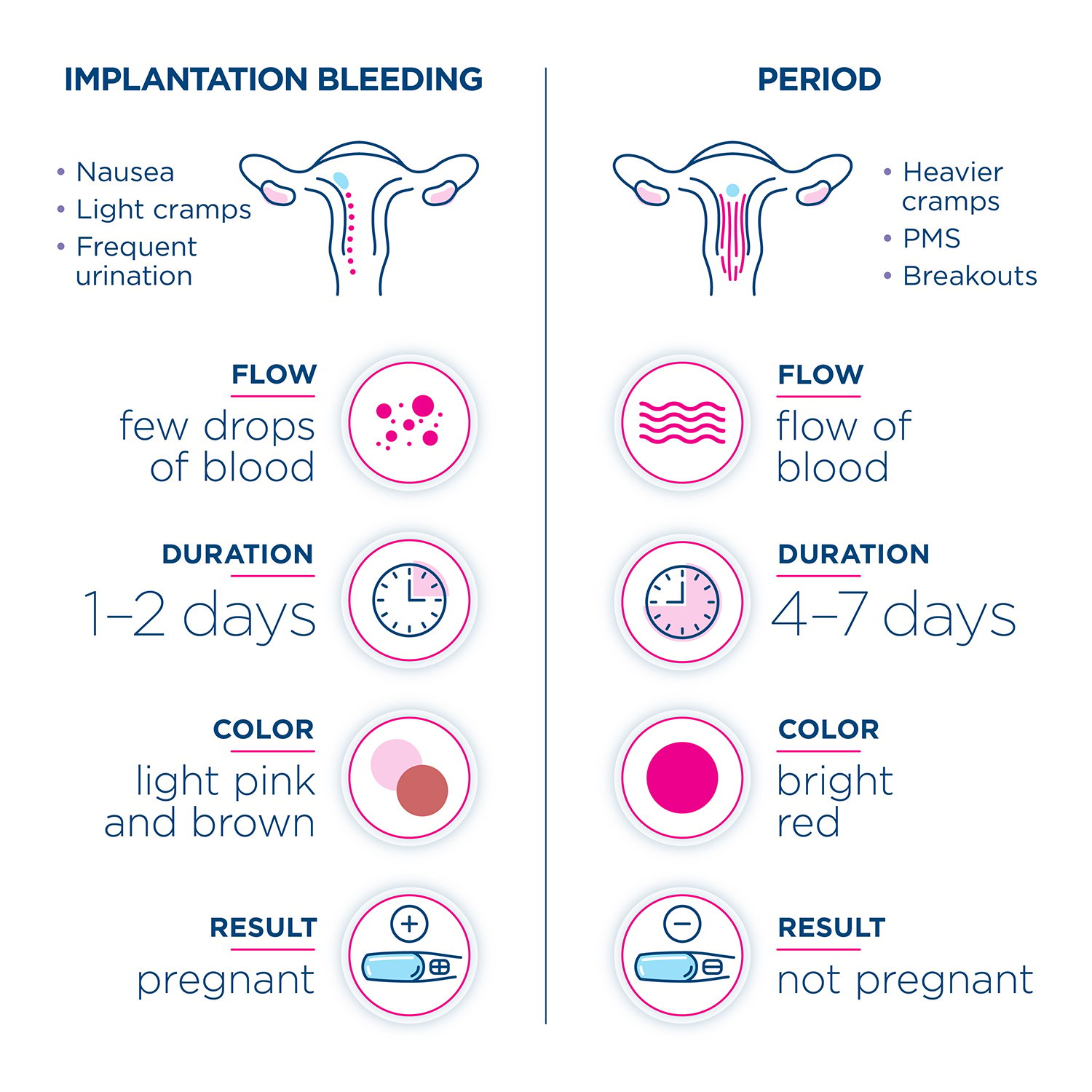
Implantation bleeding is a common occurrence during early pregnancy, affecting approximately 25% of women. It occurs when the fertilized egg implants into the lining of the uterus, causing light bleeding or spotting. This bleeding can often be mistaken for a menstrual period, making it challenging to determine if you are pregnant. Pregnancy tests can provide valuable information during this time, but understanding their accuracy and limitations is crucial.
What is Implantation Bleeding?
Implantation bleeding occurs when the fertilized egg attaches to the uterine lining. This process can cause the release of small blood vessels, resulting in light bleeding or spotting. Implantation bleeding typically occurs 10-14 days after ovulation and lasts for a few hours to a few days. It is usually lighter in color than menstrual bleeding and may be accompanied by mild cramping.
Pregnancy Tests During Implantation Bleeding
Pregnancy tests detect the presence of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), a hormone produced by the developing placenta. hCG levels rise rapidly during early pregnancy, doubling every 2-3 days. However, hCG levels may not be high enough to be detected by a pregnancy test during implantation bleeding.
Accuracy of Pregnancy Tests
The accuracy of pregnancy tests depends on several factors, including the sensitivity of the test, the timing of the test, and the individual’s hCG levels.
- Sensitivity: Pregnancy tests have different sensitivities, which indicate the lowest level of hCG they can detect. Tests with higher sensitivity can detect pregnancy earlier.
- Timing: Pregnancy tests should be taken after the expected period of implantation bleeding. Taking a test too early may result in a false negative.
- hCG Levels: Individual hCG levels vary, and some women may have lower levels during implantation bleeding, making it more difficult to detect pregnancy.
Types of Pregnancy Tests
There are two main types of pregnancy tests:
- Urine Tests: These tests are the most common and are available over-the-counter. They detect hCG in urine samples.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests measure hCG levels in the blood and are more sensitive than urine tests. They can detect pregnancy earlier and are often used to confirm a positive urine test.
Interpreting Results
Pregnancy test results are typically either positive or negative.
- Positive Result: A positive result indicates the presence of hCG and suggests that you are pregnant.
- Negative Result: A negative result does not necessarily mean you are not pregnant. It may indicate that hCG levels are not yet high enough to be detected or that the test was taken too early.
False Positives and False Negatives
Pregnancy tests can occasionally produce false positives or false negatives.
- False Positives: A false positive occurs when the test indicates pregnancy, but you are not actually pregnant. This can be caused by certain medications, medical conditions, or chemical pregnancies.
- False Negatives: A false negative occurs when the test indicates you are not pregnant, but you are actually pregnant. This can be caused by taking the test too early, low hCG levels, or a faulty test.
Recommendations
If you experience implantation bleeding and are unsure if you are pregnant, consider the following recommendations:
- Wait: If possible, wait a few days after implantation bleeding before taking a pregnancy test. This will allow hCG levels to rise and increase the likelihood of an accurate result.
- Use a Sensitive Test: Choose a pregnancy test with a high sensitivity, which can detect lower levels of hCG.
- Take Multiple Tests: If you get a negative result but still suspect you may be pregnant, take another test a few days later.
- Consider a Blood Test: If you have persistent doubts or a negative urine test despite symptoms, consider a blood test for confirmation.
Conclusion
Implantation bleeding can make it challenging to determine pregnancy status. Pregnancy tests can provide valuable information, but understanding their accuracy and limitations is crucial. By following the recommendations outlined above, you can increase the likelihood of obtaining an accurate result and make informed decisions regarding your health and pregnancy. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional if you have any concerns or questions.