Progesterone in Pregnancy: A Comprehensive Guide
Progesterone is a hormone that plays a crucial role in maintaining pregnancy. It is produced by the corpus luteum, a temporary structure that forms on the ovary after ovulation. Progesterone levels rise during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle and remain elevated if pregnancy occurs.
Role of Progesterone in Pregnancy
Progesterone has several important functions during pregnancy, including:
- Preparing the uterus for implantation: Progesterone thickens the uterine lining (endometrium) and makes it more receptive to implantation of the fertilized egg.
- Maintaining the uterine lining: Progesterone prevents the shedding of the uterine lining, which would otherwise occur during menstruation.
- Suppressing uterine contractions: Progesterone relaxes the uterine muscles, preventing premature contractions that could lead to miscarriage.
- Promoting placental development: Progesterone stimulates the growth and development of the placenta, which is responsible for nutrient and oxygen exchange between the mother and fetus.
- Regulating immune function: Progesterone modulates the immune system to prevent the mother’s body from rejecting the fetus.
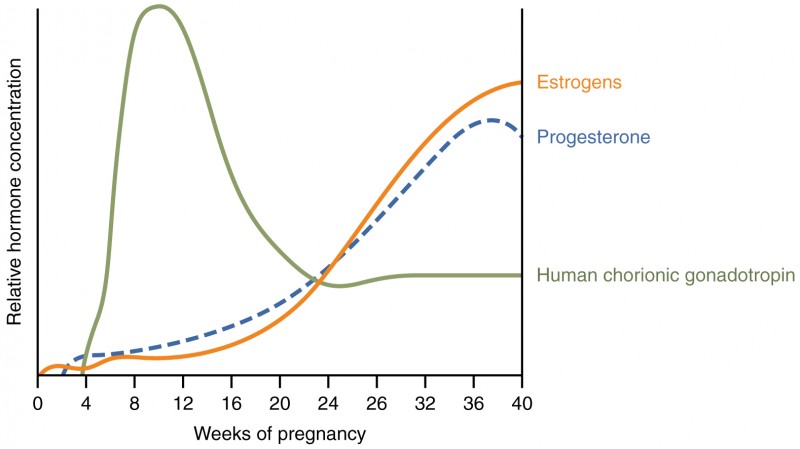
Progesterone Levels During Pregnancy
Progesterone levels rise steadily during the first trimester of pregnancy, reaching a peak in the second trimester. They then decline slightly in the third trimester but remain elevated until delivery.
Low Progesterone Levels in Pregnancy
Low progesterone levels during pregnancy can lead to several complications, including:
- Miscarriage: Progesterone deficiency can cause the uterine lining to thin and become less receptive to implantation, increasing the risk of miscarriage.
- Preterm birth: Low progesterone levels can weaken the uterine muscles and increase the risk of premature contractions.
- Placental abruption: Progesterone deficiency can impair placental development and increase the risk of placental abruption, a condition in which the placenta separates from the uterine wall.
Causes of Low Progesterone Levels in Pregnancy
Several factors can contribute to low progesterone levels in pregnancy, including:
- Corpus luteum insufficiency: The corpus luteum may not produce enough progesterone, which can occur due to factors such as luteal phase defect or ovarian dysfunction.
- Placental insufficiency: The placenta may not produce enough progesterone, which can occur in conditions such as placental abruption or placenta previa.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as birth control pills and anti-progestins, can interfere with progesterone production.
- Underlying medical conditions: Conditions such as thyroid disease, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders can affect progesterone levels.
Treatment for Low Progesterone Levels in Pregnancy
Treatment for low progesterone levels in pregnancy typically involves progesterone supplementation. Progesterone can be administered through injections, vaginal suppositories, or oral capsules. The dosage and duration of treatment will vary depending on the individual patient and the underlying cause of the progesterone deficiency.
Monitoring Progesterone Levels in Pregnancy
Progesterone levels are typically monitored during pregnancy to ensure they are within the normal range. This is done through blood tests or saliva tests. Regular monitoring is especially important for women who have a history of progesterone deficiency or who are at risk for pregnancy complications.
Conclusion
Progesterone is an essential hormone for maintaining a healthy pregnancy. Low progesterone levels can lead to serious complications, but they can be effectively treated with progesterone supplementation. Regular monitoring of progesterone levels during pregnancy is important to ensure optimal fetal development and maternal well-being.