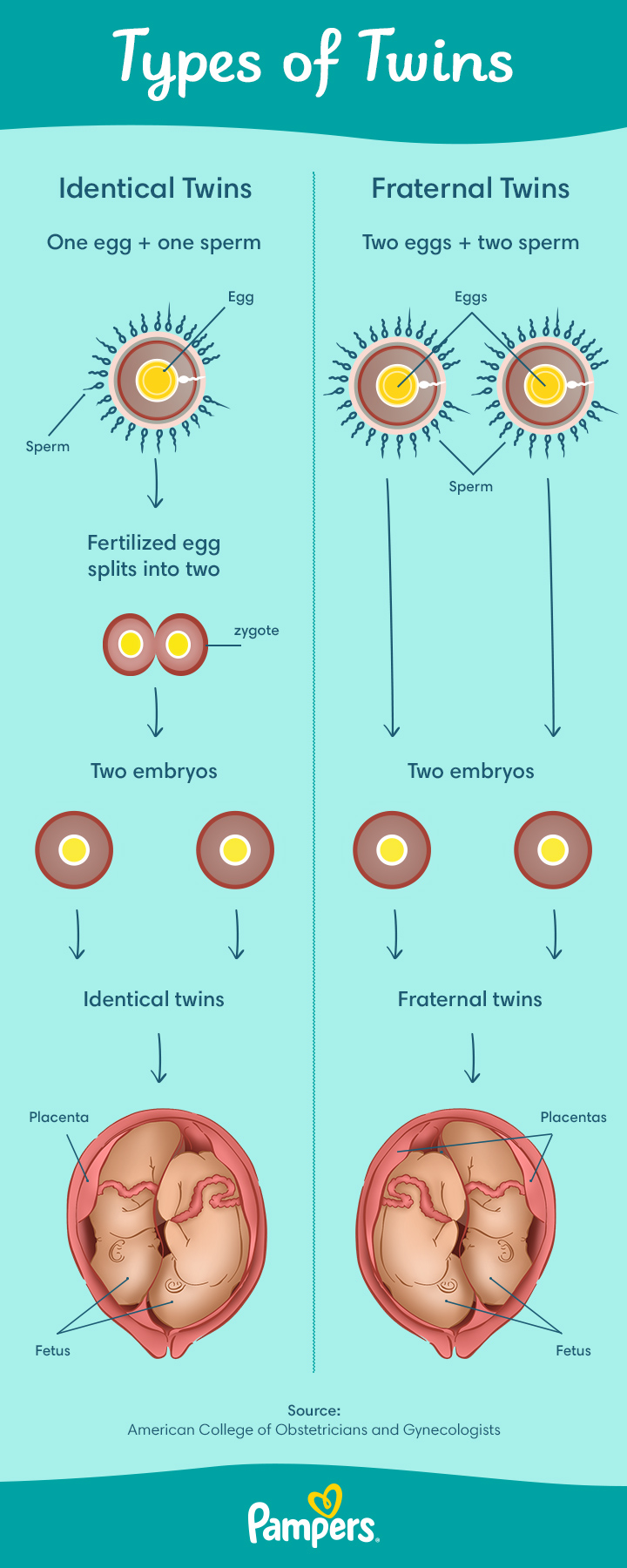
Signs and Symptoms of Twin Pregnancy
A twin pregnancy, also known as a multiple pregnancy, occurs when a woman carries two or more fetuses simultaneously. While twin pregnancies are relatively common, accounting for about 3% of all pregnancies, they can present unique challenges and require specialized care. Understanding the signs and symptoms of a twin pregnancy can help ensure early detection and appropriate management.
Early Signs
- Rapid weight gain: Due to the increased fetal mass, women carrying twins may experience more rapid weight gain than those with singleton pregnancies.
- Excessive nausea and vomiting: The hormonal changes associated with twin pregnancies can lead to more severe morning sickness.
- Early fetal movement: Some women may feel fetal movement as early as 12-14 weeks, compared to 16-20 weeks in singleton pregnancies.
- Elevated human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) levels: hCG is a hormone produced by the placenta during pregnancy. Twin pregnancies typically have higher hCG levels than singleton pregnancies.
Mid-Pregnancy Signs
- Large uterine size: The uterus expands more rapidly in twin pregnancies, leading to a larger abdominal circumference.
- Multiple fetal heartbeats: During a prenatal ultrasound, the healthcare provider may detect two or more distinct fetal heartbeats.
- Increased fetal activity: Women carrying twins often report feeling more frequent and intense fetal movements.
- Polyhydramnios: This condition refers to excessive amniotic fluid, which is more common in twin pregnancies.
Late-Pregnancy Signs
- Preterm labor: Twin pregnancies are at a higher risk of preterm labor, which occurs before 37 weeks of gestation.
- Gestational hypertension: This condition, characterized by high blood pressure during pregnancy, is more prevalent in twin pregnancies.
- Preeclampsia: A more severe form of gestational hypertension, preeclampsia involves high blood pressure and protein in the urine.
- Placental abruption: This serious condition occurs when the placenta separates from the uterine wall before delivery.
Other Symptoms
- Back pain: The increased weight and size of the uterus can put pressure on the lower back, causing discomfort.
- Frequent urination: The enlarged uterus can press on the bladder, leading to increased urinary frequency.
- Shortness of breath: The growing uterus can push against the diaphragm, making it harder to breathe.
- Leg cramps: The increased blood volume and pressure on the nerves can contribute to leg cramps.
- Varicose veins: The increased blood flow during twin pregnancies can cause varicose veins in the legs and vulva.
Diagnosis
A twin pregnancy is typically diagnosed through an ultrasound examination. During the ultrasound, the healthcare provider can visualize the number of fetuses, their position, and the presence of any abnormalities.
Management
Twin pregnancies require specialized prenatal care and monitoring to ensure the health of both the mother and the babies. Regular prenatal visits are essential to assess fetal growth, check for complications, and provide appropriate interventions.
- Prenatal vitamins: Women carrying twins may need additional prenatal vitamins, such as iron and folic acid, to support the increased nutritional demands.
- Ultrasound monitoring: More frequent ultrasounds are recommended to monitor fetal growth, check for abnormalities, and assess the position of the fetuses.
- Cervical cerclage: In some cases, a cervical cerclage may be performed to prevent preterm labor. This procedure involves placing a stitch around the cervix to keep it closed.
- Bed rest: In certain situations, such as preterm labor or other complications, the healthcare provider may recommend bed rest to reduce the risk of premature delivery.
- Delivery: Twin pregnancies typically require a cesarean section due to the increased risk of complications during vaginal delivery.
Conclusion
Understanding the signs and symptoms of a twin pregnancy is crucial for early detection and appropriate management. By being aware of these indicators, women can seek prompt medical attention and ensure the best possible outcomes for both themselves and their babies. Regular prenatal care, close monitoring, and specialized interventions are essential to navigate the unique challenges of a twin pregnancy and achieve a healthy delivery.