Signs of Tubal Pregnancy: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
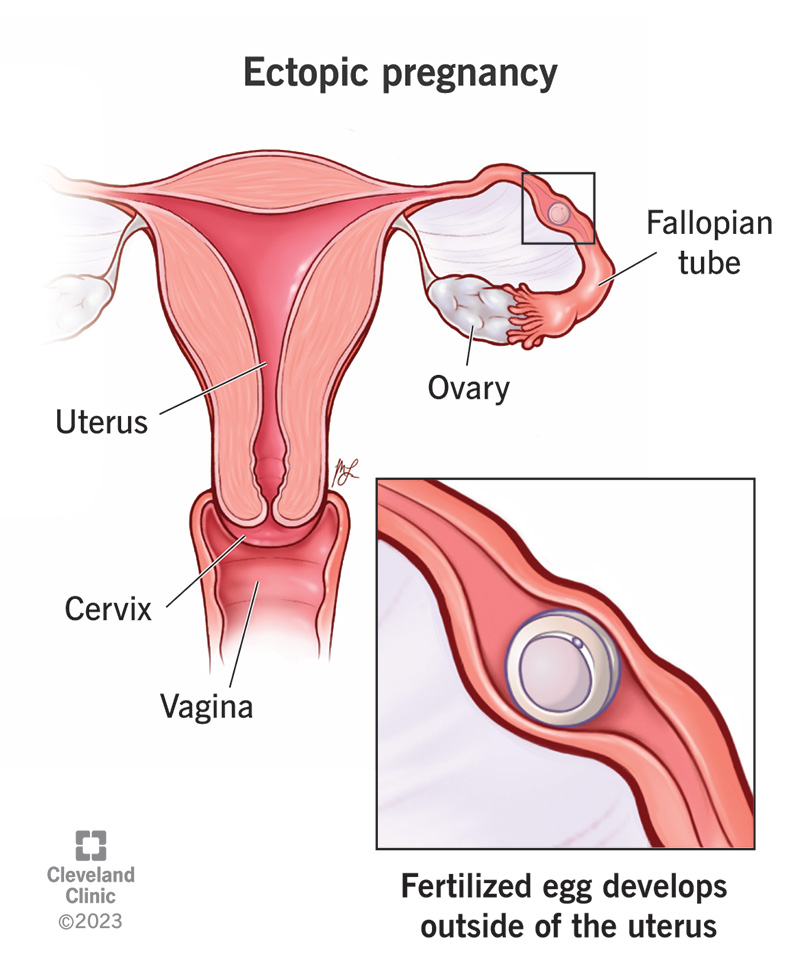
A tubal pregnancy, also known as an ectopic pregnancy, occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, most commonly in the fallopian tube. This condition is a medical emergency and requires prompt treatment to prevent life-threatening complications. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of a tubal pregnancy is crucial for early diagnosis and timely intervention.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of tubal pregnancies is unknown, but certain factors increase the risk of developing this condition:
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID): Infection of the reproductive organs can damage the fallopian tubes, making them more likely to trap a fertilized egg.
- Previous tubal surgery: Procedures such as tubal ligation or sterilization can alter the structure of the fallopian tubes, increasing the risk of ectopic implantation.
- Assisted reproductive technologies (ART): In vitro fertilization (IVF) and other fertility treatments can increase the risk of tubal pregnancy by altering the normal transport of the fertilized egg.
- Smoking: Nicotine can damage the fallopian tubes, making them more susceptible to ectopic implantation.
- Intrauterine device (IUD): While IUDs are highly effective in preventing pregnancy, they do not completely eliminate the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
Signs and Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of a tubal pregnancy can vary depending on the stage of the pregnancy and the location of the implantation. However, some common symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain: Pain in the lower abdomen or pelvis, which may be sharp, stabbing, or cramping.
- Vaginal bleeding: Irregular or abnormal vaginal bleeding, which may be light or heavy.
- Missed period: A missed menstrual period is a common early sign of pregnancy, including ectopic pregnancy.
- Nausea and vomiting: These symptoms are common in early pregnancy, but can also occur with a tubal pregnancy.
- Shoulder pain: Pain in the shoulder or neck may occur due to irritation of the diaphragm by bleeding from the ectopic pregnancy.
- Fainting or dizziness: These symptoms can occur due to blood loss from a ruptured tubal pregnancy.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing a tubal pregnancy requires a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests:
- Medical history: Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, menstrual history, and any risk factors for ectopic pregnancy.
- Physical examination: Your doctor will perform a pelvic exam to check for tenderness or masses in the fallopian tubes.
- Transvaginal ultrasound: This imaging test uses sound waves to create images of the uterus and fallopian tubes, which can help identify an ectopic pregnancy.
- Blood tests: Blood tests can measure levels of the pregnancy hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), which can help confirm pregnancy and assess its location.
Treatment
The treatment for a tubal pregnancy depends on the stage of the pregnancy and the patient’s condition:
- Medical management: In some cases, a tubal pregnancy can be treated with medication called methotrexate, which stops the growth of the fertilized egg.
- Surgical management: In most cases, surgical intervention is necessary to remove the ectopic pregnancy. This can be done through laparoscopy, a minimally invasive procedure, or laparotomy, an open surgical procedure.
Complications
If a tubal pregnancy is not treated promptly, it can lead to serious complications:
- Tubal rupture: The fallopian tube can rupture due to the growing ectopic pregnancy, causing internal bleeding and life-threatening complications.
- Hemorrhagic shock: Severe blood loss from a ruptured tubal pregnancy can lead to hemorrhagic shock, which can be fatal.
- Infection: An ectopic pregnancy can become infected, leading to pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) and other complications.
- Infertility: A tubal pregnancy can damage the fallopian tube, increasing the risk of future infertility.
Prevention
There is no surefire way to prevent tubal pregnancy, but reducing risk factors can help:
- Avoid pelvic inflammatory disease (PID): Practice safe sex, use condoms, and get regular pelvic exams to detect and treat infections early.
- Quit smoking: Smoking damages the fallopian tubes, increasing the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
- Consider ART carefully: Discuss the risks and benefits of assisted reproductive technologies with your doctor before undergoing treatment.
- Be aware of the signs and symptoms: If you experience any symptoms of a tubal pregnancy, seek medical attention immediately.
Conclusion
Tubal pregnancy is a serious medical condition that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of this condition is crucial for early intervention and prevention of life-threatening complications. If you suspect you may have a tubal pregnancy, seek medical attention immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve the chances of a successful outcome and reduce the risk of future complications.