Teen Pregnancy: A Comprehensive Statistical Overview
Introduction
Teen pregnancy remains a significant public health concern, with far-reaching implications for both the young mothers and their children. This article presents a comprehensive statistical overview of teen pregnancy in the United States, examining its prevalence, risk factors, and consequences. By understanding these statistics, policymakers, healthcare providers, and educators can develop effective strategies to address this complex issue.
Prevalence of Teen Pregnancy
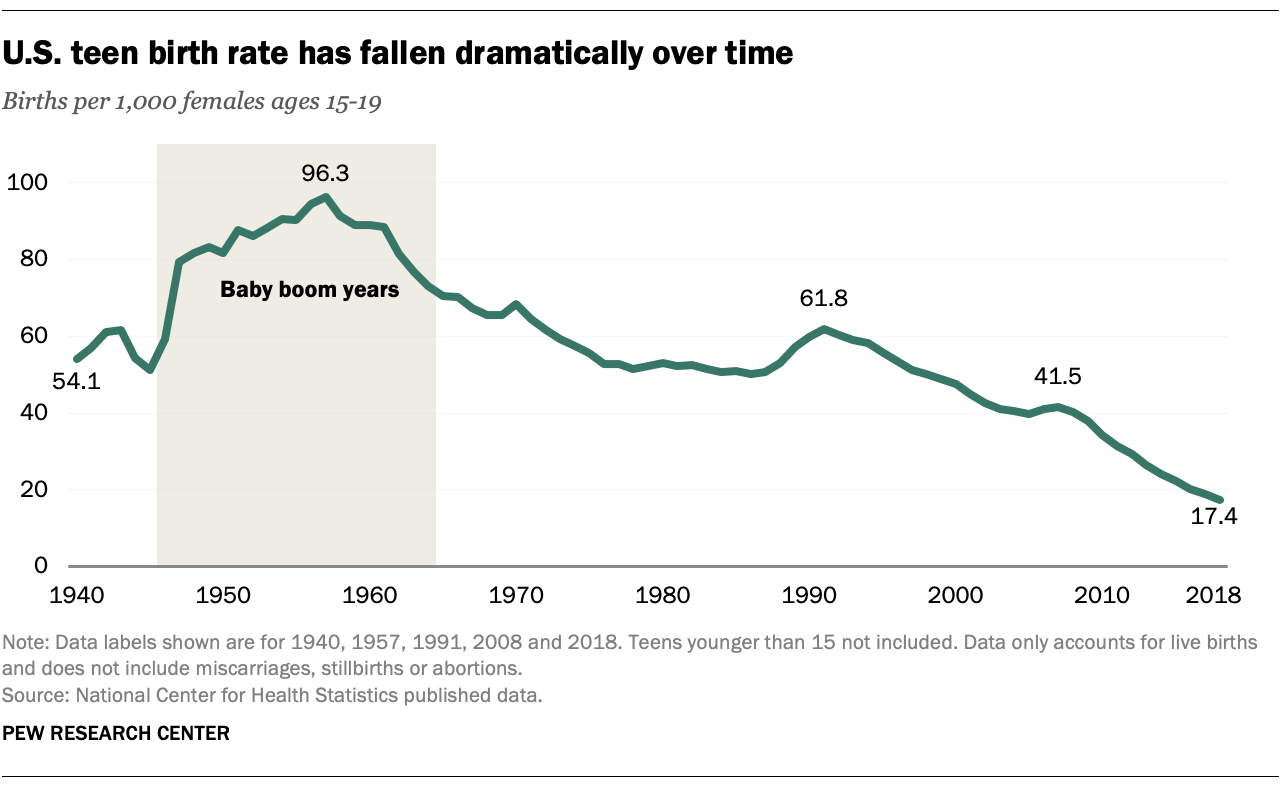
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the teen birth rate in the United States has declined significantly in recent decades. In 1991, the teen birth rate was 61.8 births per 1,000 females aged 15-19. By 2020, this rate had fallen to 18.4 births per 1,000 females in the same age group.
However, despite this decline, the United States still has one of the highest teen birth rates among developed countries. In 2019, the United States ranked 34th out of 38 developed countries in terms of teen birth rates.
Risk Factors for Teen Pregnancy
Numerous factors can increase a teenager’s risk of becoming pregnant, including:
- Socioeconomic factors: Teenagers living in poverty or from disadvantaged backgrounds are more likely to become pregnant.
- Educational attainment: Teenagers who drop out of school or have low educational aspirations are at higher risk.
- Family environment: Teenagers who come from unstable or unsupportive family environments are more likely to engage in risky sexual behavior.
- Peer pressure: Teenagers who have friends who are sexually active or pregnant are more likely to become pregnant themselves.
- Lack of access to contraception: Teenagers who do not have access to affordable and reliable contraception are more likely to become pregnant.
Consequences of Teen Pregnancy
Teen pregnancy can have significant consequences for both the young mothers and their children.
Consequences for Young Mothers:
- Increased risk of health problems: Teen mothers are more likely to experience pregnancy complications, such as premature birth and low birth weight. They are also more likely to develop chronic health conditions, such as hypertension and diabetes.
- Lower educational attainment: Teen mothers are more likely to drop out of school or have lower educational aspirations. This can limit their future employment opportunities and earning potential.
- Increased risk of poverty: Teen mothers are more likely to live in poverty and rely on public assistance.
- Mental health problems: Teen mothers are more likely to experience depression, anxiety, and other mental health problems.
Consequences for Children of Teen Mothers:
- Increased risk of health problems: Children of teen mothers are more likely to be born prematurely, have low birth weight, and experience developmental delays. They are also more likely to develop chronic health conditions, such as asthma and obesity.
- Lower educational attainment: Children of teen mothers are more likely to have lower educational aspirations and achievement.
- Increased risk of poverty: Children of teen mothers are more likely to live in poverty and rely on public assistance.
- Increased risk of involvement in the criminal justice system: Children of teen mothers are more likely to be arrested and incarcerated.
Prevention Strategies
Addressing teen pregnancy requires a comprehensive approach that includes:
- Improving access to contraception: Providing teenagers with affordable and reliable contraception is essential for preventing unplanned pregnancies.
- Comprehensive sex education: Teenagers need access to accurate and age-appropriate information about sex, contraception, and pregnancy.
- Family support programs: Supporting families in providing a stable and supportive environment for teenagers can help reduce their risk of engaging in risky sexual behavior.
- Community outreach programs: Community outreach programs can provide teenagers with access to resources and support, such as mentoring, after-school programs, and job training.
- Policy changes: Policy changes, such as raising the minimum age for marriage and providing paid family leave, can help reduce the risk of teen pregnancy.
Conclusion
Teen pregnancy remains a significant public health concern in the United States. While the teen birth rate has declined in recent decades, the United States still has one of the highest rates among developed countries. Understanding the statistics of teen pregnancy, including its prevalence, risk factors, and consequences, is essential for developing effective prevention strategies. By addressing the underlying causes of teen pregnancy and providing support to young mothers and their children, we can help improve the health and well-being of future generations.