Teen Pregnancy: A Comprehensive Overview of Statistics and Trends
Introduction
Teen pregnancy remains a significant public health concern in the United States, despite decades of efforts to reduce its prevalence. This article presents a comprehensive overview of teen pregnancy statistics, exploring the latest data on rates, trends, and disparities. By understanding the scope and nature of teen pregnancy, policymakers, healthcare providers, and community organizations can develop effective interventions and strategies to address this issue.
National Rates and Trends
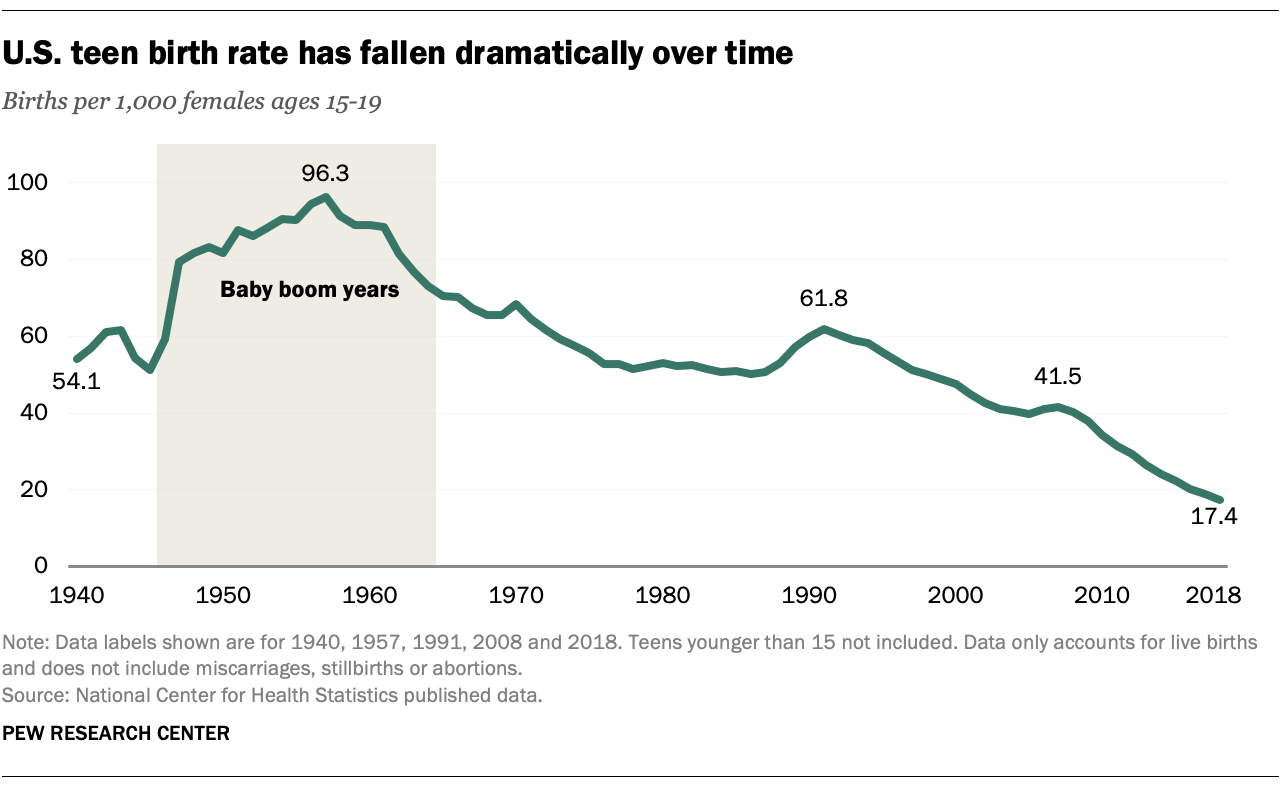
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the teen birth rate in the United States has declined significantly over the past several decades. In 1991, the teen birth rate was 61.8 per 1,000 females aged 15-19. By 2020, it had fallen to 18.4 per 1,000, representing a decline of 70%.
However, despite this overall decline, disparities in teen pregnancy rates persist across different demographic groups. Black and Hispanic teens have consistently higher teen birth rates compared to white teens. In 2020, the teen birth rate for Black teens was 26.5 per 1,000, while the rate for Hispanic teens was 20.4 per 1,000, compared to 12.9 per 1,000 for white teens.
Geographic Variations
Teen pregnancy rates also vary significantly across different geographic regions. In 2020, the highest teen birth rates were observed in the South and Midwest, with rates of 23.1 and 21.2 per 1,000, respectively. The lowest rates were found in the Northeast and West, with rates of 12.3 and 11.9 per 1,000, respectively.
Risk Factors
Numerous factors contribute to the risk of teen pregnancy, including:
- Poverty: Teens living in poverty are more likely to experience unplanned pregnancies due to limited access to healthcare, education, and other resources.
- Lack of education: Teens who drop out of school or have low educational attainment are more likely to become pregnant.
- Peer pressure: Teens who have friends or family members who are pregnant are more likely to engage in sexual activity and become pregnant themselves.
- Substance use: Teens who use alcohol or drugs are more likely to engage in risky sexual behaviors, including unprotected sex.
- Mental health issues: Teens with mental health conditions, such as depression or anxiety, are more likely to experience unplanned pregnancies.
Consequences of Teen Pregnancy
Teen pregnancy can have significant consequences for both the mother and the child. For the mother, it can lead to:
- Health risks: Teen mothers are more likely to experience premature birth, low birth weight, and other pregnancy complications.
- Educational challenges: Teen mothers are more likely to drop out of school and have lower educational attainment.
- Economic hardship: Teen mothers are more likely to live in poverty and experience unemployment.
For the child, teen pregnancy can lead to:
- Health problems: Children born to teen mothers are more likely to have low birth weight, developmental delays, and other health issues.
- Cognitive and behavioral problems: Children born to teen mothers are more likely to experience cognitive and behavioral problems, such as learning disabilities and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
- Social and emotional challenges: Children born to teen mothers are more likely to experience social and emotional challenges, such as poverty, abuse, and neglect.
Prevention Strategies
Effective teen pregnancy prevention strategies focus on addressing the underlying risk factors and providing teens with the knowledge, skills, and resources they need to make healthy choices. These strategies include:
- Comprehensive sex education: Providing teens with accurate and age-appropriate information about sexual health, contraception, and pregnancy prevention.
- Access to contraception: Ensuring that teens have access to a wide range of contraceptive methods, including condoms, birth control pills, and intrauterine devices (IUDs).
- Abstinence education: Promoting abstinence as a choice for teens who are not ready for sexual activity.
- Parent-child communication: Encouraging parents to talk to their teens about sex, relationships, and pregnancy prevention.
- Community-based programs: Providing teens with access to community-based programs that offer support, mentorship, and educational opportunities.
Conclusion
Teen pregnancy remains a significant public health concern in the United States, with persistent disparities across different demographic groups and geographic regions. Understanding the latest statistics and trends on teen pregnancy is essential for developing effective prevention strategies and reducing the number of unplanned pregnancies among teens. By addressing the underlying risk factors and providing teens with the necessary knowledge, skills, and resources, we can empower them to make healthy choices and achieve their full potential.