Teen Pregnancy: A Comprehensive Statistical Overview
Introduction
Teen pregnancy remains a prevalent issue with far-reaching consequences for individuals, families, and society as a whole. This comprehensive statistical overview aims to shed light on the magnitude, trends, and disparities associated with teen pregnancy in the United States. By examining data from reputable sources, we can gain a deeper understanding of this complex issue and inform evidence-based interventions.
Prevalence and Trends
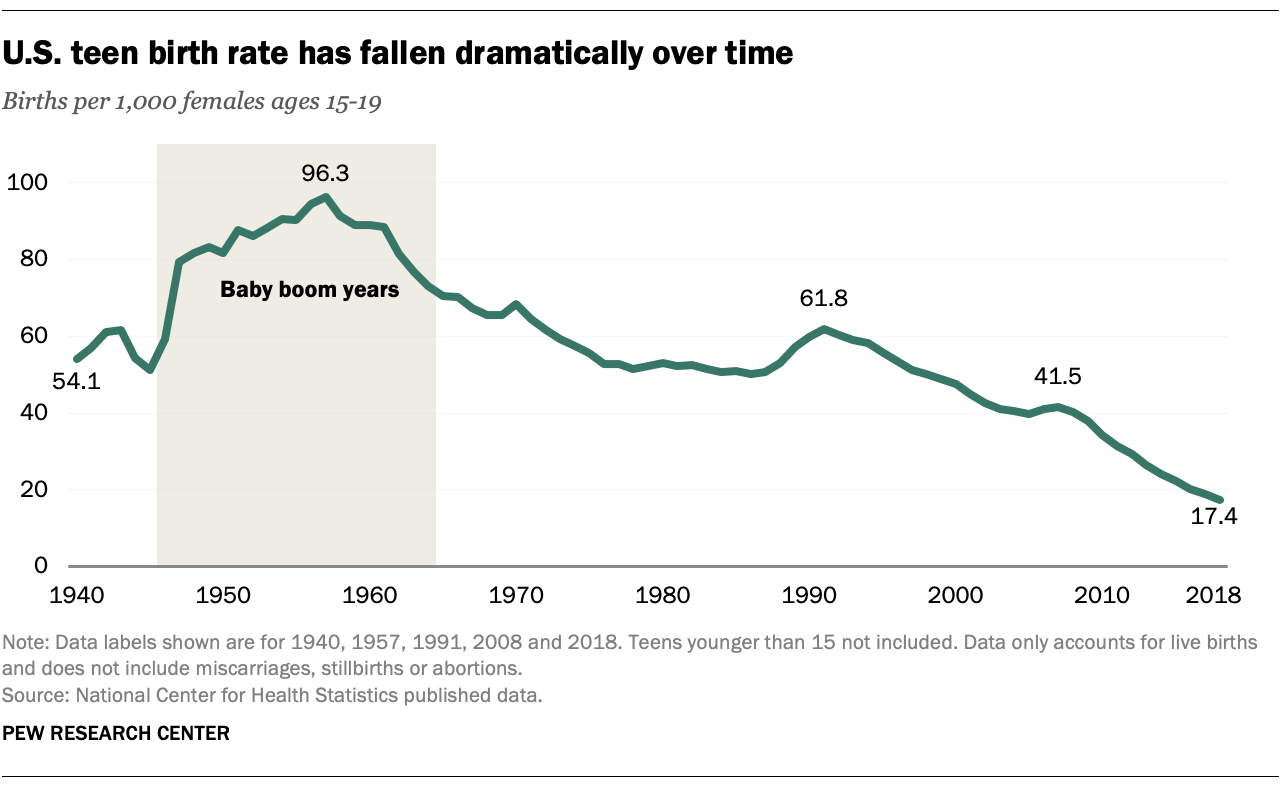
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), in 2020, the birth rate among females aged 15-19 was 18.4 per 1,000. This represents a significant decline from the peak of 61.8 per 1,000 in 1991. However, teen pregnancy rates remain higher in the United States compared to other developed countries.
Racial and Ethnic Disparities
Teen pregnancy rates vary significantly across racial and ethnic groups. In 2020, the birth rate among Black teenagers was 33.2 per 1,000, more than double the rate among White teenagers (14.4 per 1,000). Hispanic teenagers had a birth rate of 20.4 per 1,000, while Asian teenagers had the lowest rate at 5.8 per 1,000.
Socioeconomic Factors
Teen pregnancy is closely linked to socioeconomic factors. Adolescents living in poverty, with low educational attainment, and in unstable family environments are at increased risk of becoming pregnant. Research has shown that teens from low-income households are more likely to have a child before the age of 20 compared to those from high-income households.
Consequences for Teen Mothers
Teen pregnancy can have significant consequences for young mothers. They are more likely to drop out of school, experience economic hardship, and face health problems. Teen mothers are also at increased risk of postpartum depression and low birth weight infants.
Consequences for Children of Teen Mothers
Children born to teen mothers face a range of challenges. They are more likely to be born prematurely, have low birth weight, and experience developmental delays. They are also more likely to live in poverty and face educational and behavioral problems.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing teen pregnancy requires a comprehensive approach that addresses the underlying social, economic, and health factors that contribute to the issue. Effective prevention strategies include:
- Comprehensive sex education: Providing accurate and age-appropriate information about sexual health and contraception.
- Access to affordable contraception: Ensuring that teens have access to a range of contraceptive methods, including long-acting reversible contraceptives (LARCs).
- Youth development programs: Supporting teens with mentorship, skill-building, and opportunities for positive youth development.
- Parent-child communication: Encouraging open and honest communication between parents and teens about sexual health and relationships.
Conclusion
Teen pregnancy remains a complex and multifaceted issue with significant consequences for individuals, families, and society. While progress has been made in reducing teen pregnancy rates, disparities persist across racial, ethnic, and socioeconomic lines. Addressing the underlying factors that contribute to teen pregnancy, implementing evidence-based prevention strategies, and providing support to teen mothers and their children are essential for creating a future where all young people have the opportunity to reach their full potential.