Teen Pregnancy Statistics: A Comparative Analysis of 2000 and 2003
Introduction
Teen pregnancy remains a significant public health concern in the United States, with far-reaching consequences for both young mothers and their children. Understanding the trends and patterns of teen pregnancy is crucial for developing effective prevention and intervention strategies. This article presents a comprehensive analysis of teen pregnancy statistics from 2000 to 2003, examining the prevalence, disparities, and potential contributing factors.
Prevalence of Teen Pregnancy
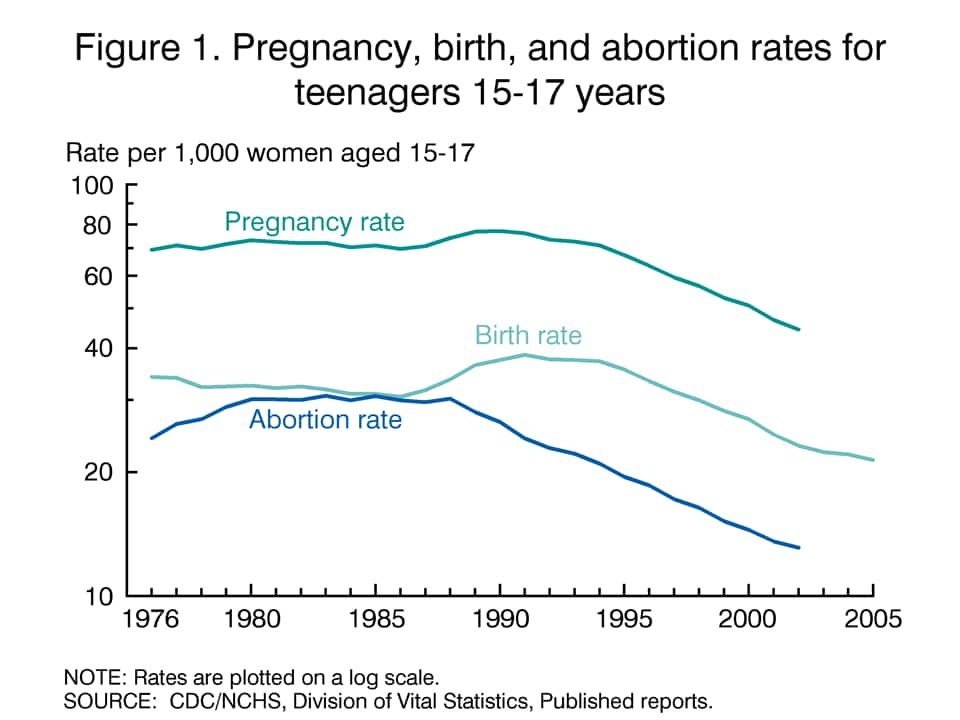
In 2000, the teen birth rate in the United States stood at 51.1 births per 1,000 females aged 15-19. By 2003, this rate had declined slightly to 47.9 births per 1,000 females. While this decrease is encouraging, the United States still has one of the highest teen birth rates among developed countries.
Disparities in Teen Pregnancy
Teen pregnancy rates vary significantly across demographic groups. In 2003, the teen birth rate for Hispanic females was 86.2 births per 1,000 females, compared to 42.7 births per 1,000 females for non-Hispanic white females and 127.3 births per 1,000 females for non-Hispanic black females. These disparities highlight the need for targeted interventions to address the unique challenges faced by minority youth.
Contributing Factors to Teen Pregnancy
Numerous factors contribute to teen pregnancy, including:
- Socioeconomic status: Poverty, lack of education, and limited access to healthcare are all associated with higher teen pregnancy rates.
- Peer influence: Teens who have friends who are pregnant or have children are more likely to become pregnant themselves.
- Family environment: Unstable family structures, lack of parental support, and exposure to violence can increase the risk of teen pregnancy.
- Media influences: Media portrayals of teen pregnancy and sexuality can influence young people’s attitudes and behaviors.
- Lack of access to contraception: Limited access to affordable and effective contraception is a major barrier to preventing teen pregnancy.
Consequences of Teen Pregnancy
Teen pregnancy has serious consequences for both young mothers and their children. Young mothers are more likely to drop out of school, have lower incomes, and experience health problems. Their children are more likely to be born prematurely, have low birth weight, and experience developmental delays.
Prevention and Intervention Strategies
Preventing teen pregnancy requires a comprehensive approach that addresses the underlying factors that contribute to it. Effective strategies include:
- Comprehensive sex education: Providing teens with accurate and age-appropriate information about sexual health and reproduction.
- Access to contraception: Ensuring that teens have access to affordable and effective contraception.
- Parent-child communication: Encouraging open and honest communication between parents and teens about sexual health.
- Community-based programs: Providing teens with access to support services, such as mentoring, counseling, and job training.
Conclusion
Teen pregnancy remains a significant public health challenge in the United States. While there has been a slight decline in teen birth rates in recent years, disparities persist across demographic groups. Addressing the underlying factors that contribute to teen pregnancy, such as poverty, lack of education, and limited access to contraception, is essential for reducing rates and improving the health and well-being of young people and their children.