Teenage Pregnancy: A Comprehensive Statistical Analysis
Introduction
Teenage pregnancy remains a significant public health concern, with far-reaching consequences for both the young mothers and their children. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of the latest statistics on teen pregnancy in the United States, examining trends, risk factors, and the impact on society.
Prevalence and Trends
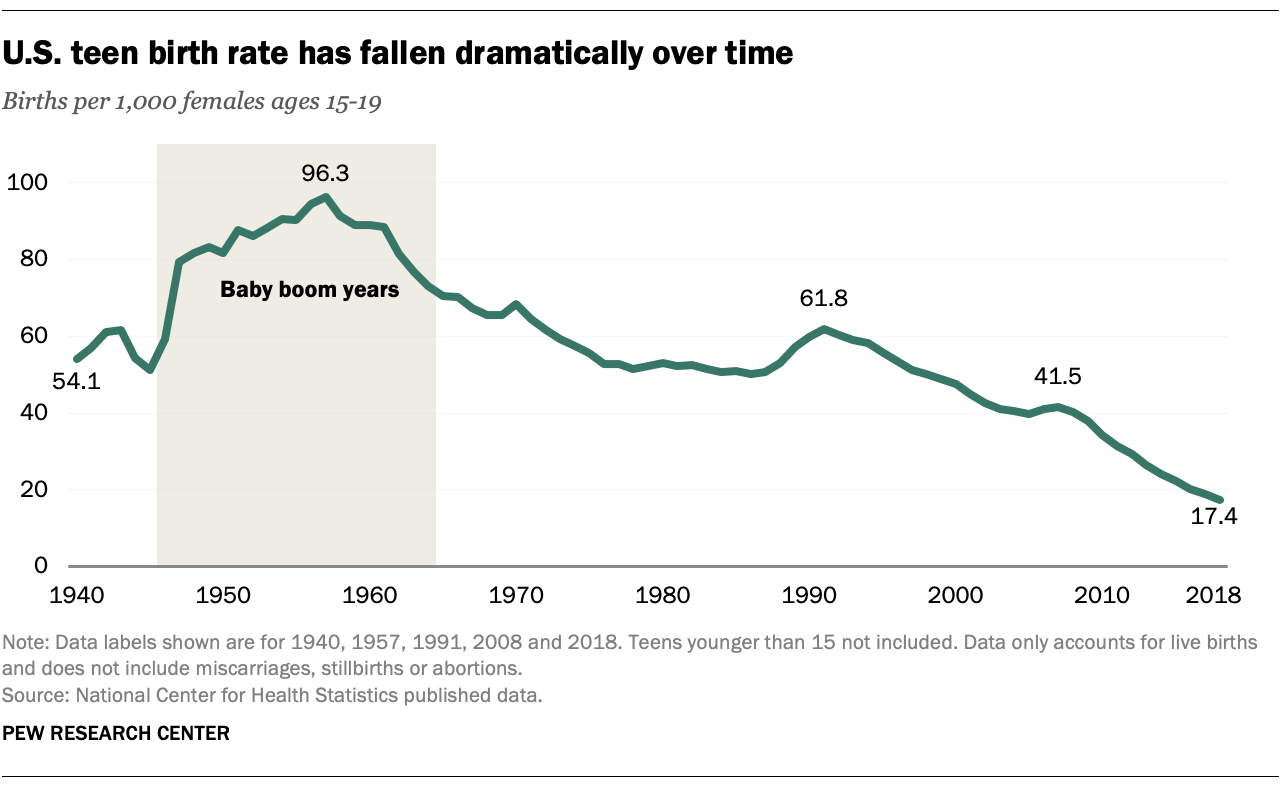
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the teen birth rate in the United States has declined significantly in recent decades. In 2020, the birth rate among 15-19-year-olds was 18.8 per 1,000, a 75% decrease from its peak in 1991. However, the rate remains higher than in many other developed countries.
The decline in teen pregnancy rates is attributed to several factors, including increased access to contraception, improved sex education, and a shift in social norms. Despite the progress, disparities persist among different racial and socioeconomic groups.
Risk Factors
Teenagers who experience certain risk factors are more likely to become pregnant. These include:
- Poverty: Teenagers living in poverty are more likely to face challenges that increase their risk of pregnancy, such as lack of access to healthcare, education, and support services.
- Low educational attainment: Teenagers who drop out of school or have low academic achievement are more likely to become pregnant.
- Substance abuse: Teenagers who use alcohol or drugs are more likely to engage in risky sexual behaviors, including unprotected sex.
- Mental health issues: Teenagers with mental health problems, such as depression or anxiety, are more likely to experience unplanned pregnancies.
- Peer pressure: Teenagers who have friends who are pregnant or who engage in risky sexual behaviors are more likely to do the same.
Consequences
Teenage pregnancy has significant consequences for both the young mothers and their children.
For the Mothers:
- Health risks: Teen mothers are more likely to experience pregnancy complications, such as premature birth and low birth weight. They are also more likely to have chronic health conditions, such as diabetes and heart disease.
- Educational attainment: Teen mothers are more likely to drop out of school and have lower educational attainment than their peers.
- Economic challenges: Teen mothers are more likely to live in poverty and experience financial instability.
For the Children:
- Health risks: Children born to teen mothers are more likely to have low birth weight, developmental delays, and health problems.
- Educational attainment: Children of teen mothers are more likely to have lower educational attainment and higher dropout rates.
- Social and emotional problems: Children of teen mothers are more likely to experience social and emotional problems, such as behavioral issues and mental health problems.
Impact on Society
Teenage pregnancy has a significant impact on society as a whole. It contributes to:
- Increased healthcare costs: Teenage pregnancy and its associated health complications result in increased healthcare costs for the government and society.
- Lost productivity: Teen mothers are more likely to have lower educational attainment and economic instability, which can lead to lost productivity and lower tax revenue.
- Increased crime: Children of teen mothers are more likely to engage in criminal activity, contributing to higher crime rates and social instability.
Prevention and Intervention
Preventing teen pregnancy requires a comprehensive approach that addresses the underlying risk factors and provides support to young people. Effective prevention strategies include:
- Comprehensive sex education: Providing young people with accurate and age-appropriate information about sexual health and contraception is essential for reducing teen pregnancy rates.
- Access to contraception: Ensuring that young people have access to affordable and reliable contraception is crucial for preventing unplanned pregnancies.
- Support services: Providing young people with support services, such as counseling, mentoring, and after-school programs, can help them overcome challenges and make healthy decisions.
- Community engagement: Engaging community organizations, schools, and parents in teen pregnancy prevention efforts can create a supportive environment for young people.
Conclusion
Teenage pregnancy remains a complex and challenging issue with significant consequences for both the young mothers and their children. By understanding the statistics, risk factors, and impact of teen pregnancy, we can develop effective prevention and intervention strategies to reduce its prevalence and improve the lives of young people.