Teenage Pregnancy in Australia: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
Teenage pregnancy, defined as pregnancy occurring in individuals between the ages of 13 and 19, remains a significant public health concern in Australia. Despite a gradual decline in rates over the past few decades, Australia still has one of the highest teenage pregnancy rates among developed nations. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of teenage pregnancy in Australia, exploring its causes, consequences, and the multifaceted strategies employed to address this issue.
Prevalence and Trends
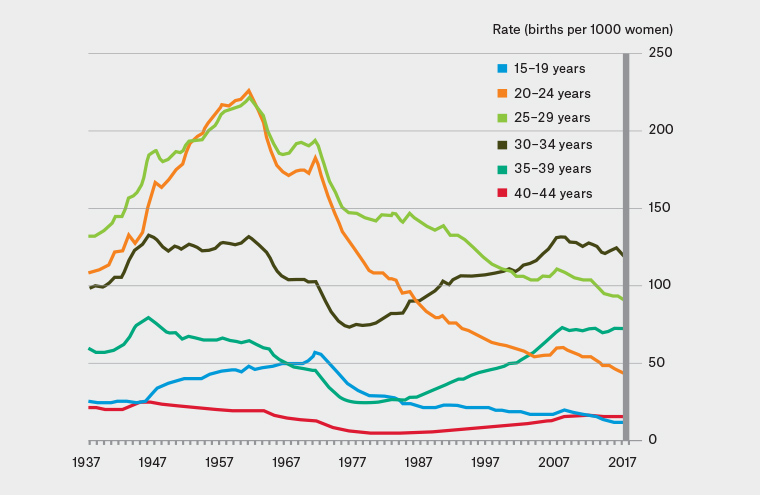
According to the Australian Institute of Health and Welfare (AIHW), in 2020, the teenage pregnancy rate in Australia was 16.4 per 1,000 women aged 15-19. This rate has declined by 23% since 2010, but it is still higher than the average rate of 12.5 per 1,000 among OECD countries.
The decline in teenage pregnancy rates has been attributed to several factors, including increased access to comprehensive sex education, improved contraceptive use, and a shift in societal attitudes towards teenage pregnancy. However, disparities persist across different population groups, with Indigenous Australian teenagers and those living in disadvantaged areas experiencing disproportionately higher rates.
Causes
The causes of teenage pregnancy are complex and multifaceted. They include:
- Lack of knowledge and education: Many teenagers lack comprehensive information about sexual health, contraception, and the consequences of unprotected sex.
- Peer pressure and social norms: Teenagers may feel pressured to engage in sexual activity to conform to peer expectations or to gain acceptance.
- Socioeconomic factors: Poverty, unemployment, and lack of access to healthcare and education can increase the risk of teenage pregnancy.
- Family dynamics: Unstable family environments, lack of parental support, and exposure to abuse or neglect can contribute to teenage pregnancy.
- Biological factors: Early puberty and certain hormonal imbalances can increase the likelihood of pregnancy.
Consequences
Teenage pregnancy can have significant consequences for both the young mother and her child. These include:
- Health risks: Teenage mothers are at increased risk of pregnancy complications, such as pre-eclampsia, premature birth, and low birth weight. Their babies are also more likely to have health problems.
- Educational attainment: Teenage mothers are more likely to drop out of school, which can limit their future employment opportunities.
- Economic challenges: Teenage mothers often face financial difficulties due to the costs of raising a child and the challenges of balancing work and family responsibilities.
- Social stigma: Teenage pregnancy can lead to social isolation and discrimination, which can further compound the challenges faced by young mothers.
Strategies to Address Teenage Pregnancy
Australia has implemented a range of strategies to address teenage pregnancy, including:
- Comprehensive sex education: Schools and community organizations provide comprehensive sex education programs that cover topics such as anatomy, reproduction, contraception, and healthy relationships.
- Access to contraception: Free or low-cost contraception is available through a variety of channels, including youth health clinics, pharmacies, and schools.
- Support services: Support services for pregnant and parenting teenagers are available through government agencies, non-profit organizations, and community groups. These services provide prenatal care, counseling, and assistance with housing, education, and employment.
- Targeted interventions: Targeted interventions are designed to address the specific needs of high-risk groups, such as Indigenous Australian teenagers and those living in disadvantaged areas. These interventions may include mentoring programs, culturally appropriate health services, and community outreach initiatives.
Conclusion
Teenage pregnancy remains a significant public health issue in Australia, but progress has been made in reducing rates over the past few decades. The multifaceted strategies employed to address this issue, including comprehensive sex education, access to contraception, support services, and targeted interventions, have contributed to this decline.
However, ongoing efforts are needed to further reduce teenage pregnancy rates and mitigate its consequences. This includes addressing the underlying causes of teenage pregnancy, such as lack of knowledge, peer pressure, and socioeconomic factors. By investing in comprehensive prevention and support programs, Australia can empower young people to make informed choices about their sexual health and future.