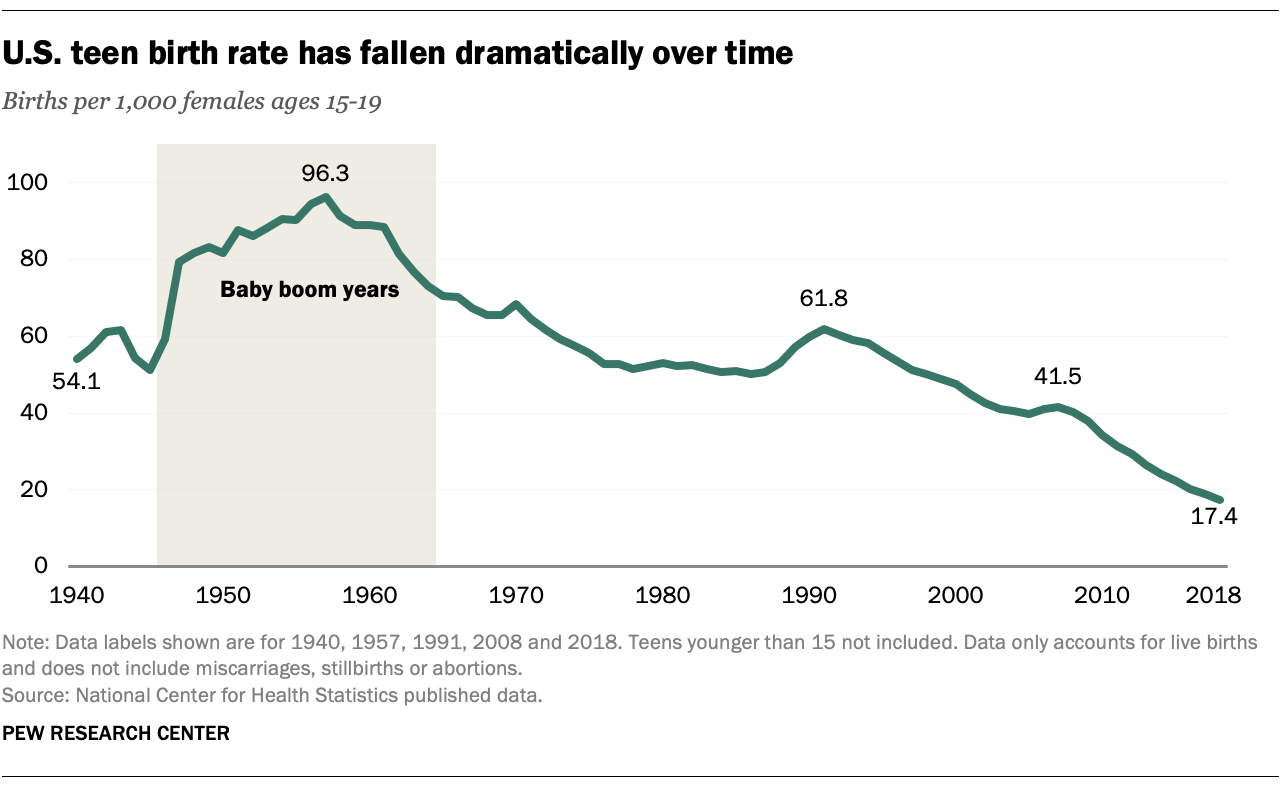
Teen Pregnancy: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
Teen pregnancy, defined as pregnancy in individuals between the ages of 13 and 19, remains a prevalent issue worldwide, posing significant health, social, and economic challenges. This article delves into the multifaceted nature of teen pregnancy, exploring its causes, consequences, and effective prevention strategies. By shedding light on this complex topic, we aim to empower young people, parents, educators, and policymakers to address this issue effectively and promote the well-being of our communities.
Causes of Teen Pregnancy
The etiology of teen pregnancy is multifaceted, influenced by a combination of biological, social, and economic factors.
-
Biological Factors: Early onset of puberty, particularly in girls, can increase the risk of teen pregnancy. Hormonal changes and the development of secondary sexual characteristics can lead to increased sexual activity and a heightened desire for intimacy.
-
Social Factors: Lack of comprehensive sex education, peer pressure, and exposure to media messages that normalize teen pregnancy can contribute to the likelihood of engaging in sexual activity without adequate knowledge or protection. Additionally, poverty, family instability, and lack of parental support can create an environment that increases the risk of teen pregnancy.
-
Economic Factors: Limited access to education and employment opportunities can perpetuate a cycle of poverty and increase the likelihood of teen pregnancy. Young people who face economic hardship may engage in sexual activity as a means of gaining financial support or stability.
Consequences of Teen Pregnancy
Teen pregnancy has far-reaching consequences for both the young mother and her child.
-
Health Risks: Teen mothers are at increased risk for pregnancy complications, such as preeclampsia, premature birth, and low birth weight infants. They are also more likely to experience postpartum depression and other mental health issues.
-
Educational and Economic Challenges: Teen pregnancy often disrupts education, making it difficult for young mothers to complete high school or pursue higher education. This can limit their future earning potential and job opportunities, perpetuating a cycle of poverty.
-
Social Stigma: Teen pregnancy can lead to social isolation, judgment, and discrimination, which can further exacerbate the challenges faced by young mothers.
-
Child Outcomes: Children born to teen mothers are more likely to experience developmental delays, health problems, and academic difficulties. They are also at increased risk for teen pregnancy themselves, perpetuating an intergenerational cycle.
Prevention Strategies
Addressing teen pregnancy requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses education, access to healthcare, and social support.
-
Comprehensive Sex Education: Evidence-based sex education programs that provide accurate information about reproductive health, contraception, and decision-making skills are essential for preventing teen pregnancy. These programs should be age-appropriate, culturally sensitive, and accessible to all young people.
-
Access to Contraception: Ensuring access to affordable and confidential contraception is crucial for preventing unplanned pregnancies. This includes providing a range of contraceptive options, such as condoms, birth control pills, and long-acting reversible contraceptives (LARCs).
-
Social Support: Providing young people with supportive environments that foster healthy decision-making and encourage responsible sexual behavior is essential. This includes strong family relationships, positive peer groups, and access to youth-friendly healthcare services.
-
Economic Empowerment: Addressing the economic factors that contribute to teen pregnancy, such as poverty and lack of education, is essential for long-term prevention. This includes investing in education, job training, and programs that support young families.
Conclusion
Teen pregnancy is a complex issue with far-reaching consequences for both the young mother and her child. By understanding the causes and consequences of teen pregnancy, we can develop effective prevention strategies that address the underlying factors that contribute to this issue. Comprehensive sex education, access to contraception, social support, and economic empowerment are essential components of a holistic approach to preventing teen pregnancy and promoting the well-being of our communities. By working together, we can create a society where all young people have the knowledge, resources, and support they need to make informed decisions about their sexual health and future.