Teen Pregnancy in the United States: A Comprehensive Analysis
Introduction
Teen pregnancy, defined as pregnancy in individuals under the age of 20, remains a significant public health concern in the United States. Despite decades of efforts to reduce its prevalence, teen pregnancy rates have remained stubbornly high, with the United States having one of the highest rates among developed nations. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of teen pregnancy in the United States, examining its causes, consequences, and potential solutions.
Causes of Teen Pregnancy
The causes of teen pregnancy are complex and multifaceted, involving a combination of individual, social, and economic factors.
- Individual Factors: Teenagers who engage in risky sexual behaviors, such as unprotected intercourse or multiple partners, are at increased risk of pregnancy. Factors contributing to these behaviors include lack of knowledge about contraception, peer pressure, and substance abuse.
- Social Factors: Teenagers who live in poverty, have low educational attainment, or come from single-parent households are more likely to become pregnant. These factors often lead to limited access to healthcare, education, and support systems.
- Economic Factors: Economic hardship can increase the likelihood of teen pregnancy by limiting access to contraception, education, and healthcare. Teenagers who live in poverty may also engage in risky sexual behaviors as a means of coping with their circumstances.
Consequences of Teen Pregnancy
Teen pregnancy has numerous negative consequences for both the mother and the child.
- Maternal Health: Teen mothers are at increased risk for pregnancy complications, such as preeclampsia, preterm labor, and low birth weight. They are also more likely to experience postpartum depression and other mental health issues.
- Child Health: Children born to teen mothers are more likely to have health problems, such as low birth weight, developmental delays, and chronic diseases. They are also at increased risk for poverty and educational difficulties.
- Social and Economic Consequences: Teen pregnancy can disrupt a teenager’s education and career prospects. It can also lead to poverty, homelessness, and involvement in the criminal justice system.
Solutions to Teen Pregnancy
Addressing teen pregnancy requires a comprehensive approach that involves multiple stakeholders.
- Education and Prevention: Comprehensive sex education programs that provide accurate information about contraception, sexually transmitted infections, and healthy relationships are essential for reducing teen pregnancy.
- Access to Contraception: Ensuring that teenagers have access to affordable and effective contraception is crucial. This includes providing free or low-cost contraception through clinics, schools, and community organizations.
- Support Services: Teenagers who are pregnant or parenting need access to support services, such as prenatal care, parenting classes, and housing assistance. These services can help them navigate the challenges of teen pregnancy and provide a stable environment for their children.
- Economic Empowerment: Addressing the economic factors that contribute to teen pregnancy is essential. This includes providing job training, educational opportunities, and affordable housing for teenagers and their families.
Progress and Challenges
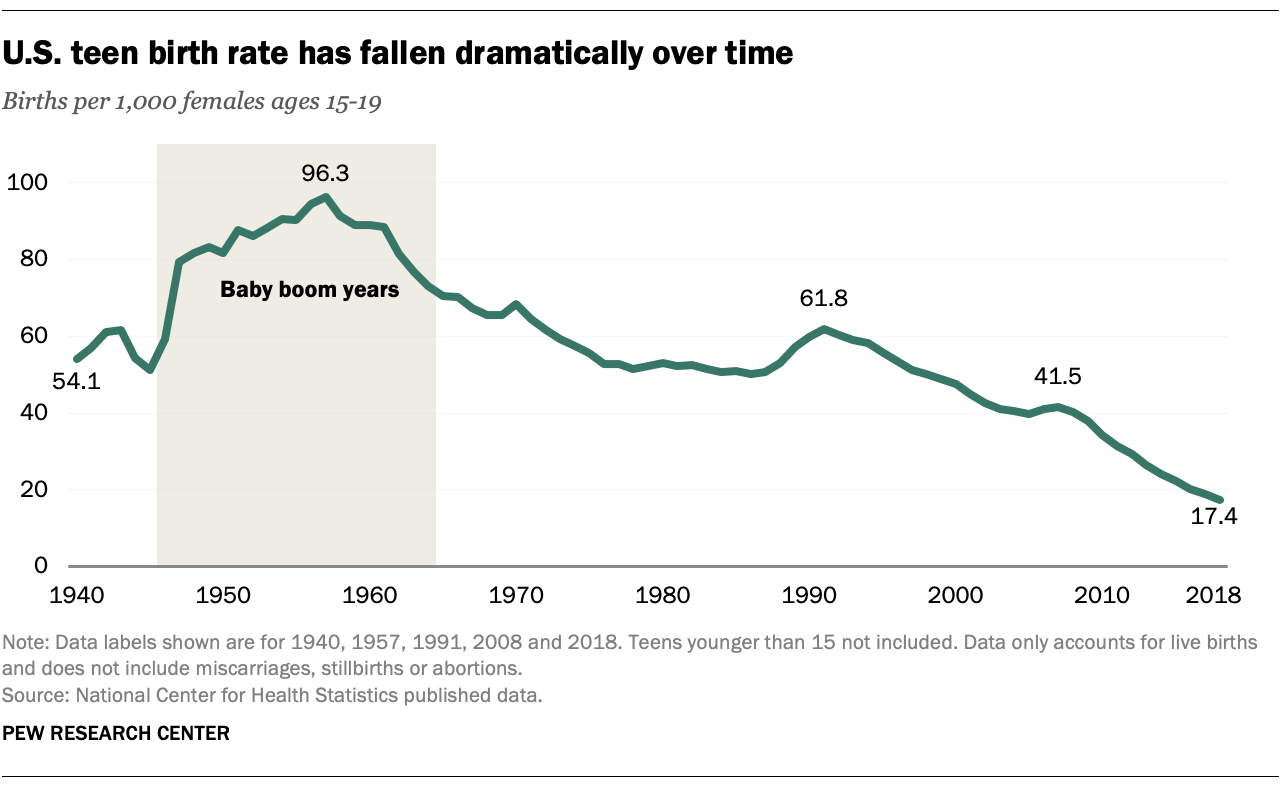
In recent decades, there has been a significant decline in teen pregnancy rates in the United States. This decline is attributed to increased access to contraception, improved sex education, and a shift in social norms. However, disparities in teen pregnancy rates persist across racial, ethnic, and socioeconomic lines.
- Racial and Ethnic Disparities: Teen pregnancy rates are disproportionately high among African American and Hispanic teenagers. These disparities are due to a combination of factors, including poverty, lack of access to healthcare, and cultural norms.
- Socioeconomic Disparities: Teenagers from low-income families are more likely to become pregnant than their more affluent peers. This is due to the challenges they face in accessing healthcare, education, and support services.
Conclusion
Teen pregnancy remains a significant public health concern in the United States. It has negative consequences for both the mother and the child, and it contributes to poverty and inequality. Addressing teen pregnancy requires a comprehensive approach that involves education, prevention, support services, and economic empowerment. By working together, we can create a society where all teenagers have the knowledge, resources, and opportunities they need to make healthy choices about their sexual and reproductive health.