Teen Pregnancy in the United States: A Statistical Overview
Introduction
Teen pregnancy remains a significant public health concern in the United States, despite decades of efforts to reduce its prevalence. Teen mothers and their children face numerous challenges, including increased risks of health complications, lower educational attainment, and economic hardship. Understanding the trends and patterns of teen pregnancy is crucial for developing effective prevention and intervention strategies. This article presents a comprehensive statistical overview of teen pregnancy in the United States, examining data from various sources to provide a detailed picture of the issue.
National Trends
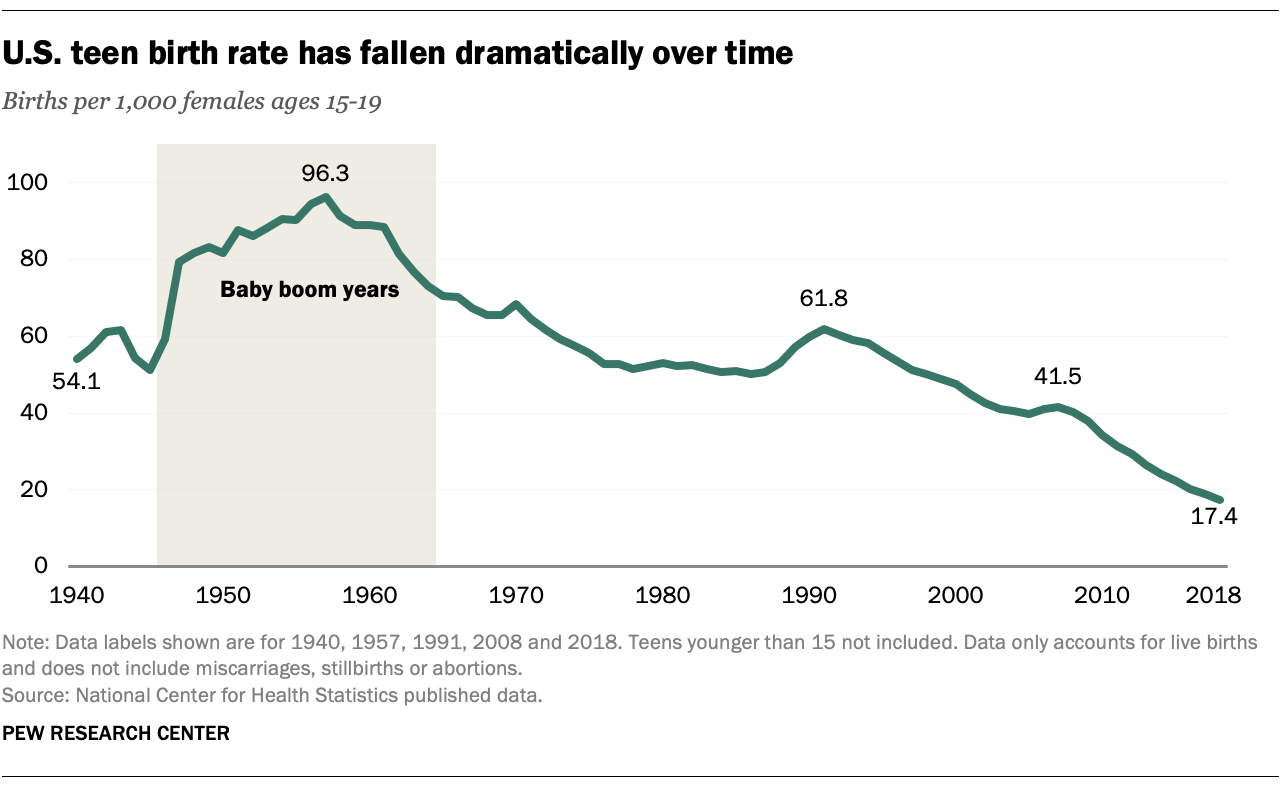
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the teen birth rate in the United States has declined significantly in recent decades. In 1991, the teen birth rate was 61.8 births per 1,000 females aged 15-19. By 2020, it had dropped to 18.8 births per 1,000 females, representing a decline of over 70%. This decline has been attributed to increased access to contraception, improved sex education, and delayed sexual initiation among teenagers.
However, despite the overall decline, disparities in teen birth rates persist across racial and ethnic groups. In 2020, the teen birth rate among Hispanic females was 25.9 births per 1,000 females, compared to 14.3 births per 1,000 females among non-Hispanic white females and 21.5 births per 1,000 females among non-Hispanic black females. These disparities highlight the need for targeted interventions to address the specific needs of these populations.
State-Level Variations
The teen birth rate varies considerably across states in the United States. In 2020, the highest teen birth rates were observed in Mississippi (31.2 births per 1,000 females), Arkansas (28.9 births per 1,000 females), and Oklahoma (28.7 births per 1,000 females). The lowest teen birth rates were observed in Massachusetts (4.9 births per 1,000 females), New Hampshire (5.2 births per 1,000 females), and Connecticut (5.3 births per 1,000 females).
These state-level variations may be influenced by a combination of factors, including access to healthcare, socioeconomic conditions, and cultural norms. States with higher teen birth rates tend to have lower levels of educational attainment, higher rates of poverty, and less access to comprehensive sex education.
Age-Specific Trends
The teen birth rate is not evenly distributed across all age groups. In 2020, the highest teen birth rate was observed among females aged 18-19 (24.6 births per 1,000 females). The teen birth rate was lower among females aged 15-17 (12.4 births per 1,000 females) and females aged 14 and under (1.8 births per 1,000 females).
This age distribution suggests that older teenagers are more likely to engage in sexual activity and become pregnant. However, it is important to note that even younger teenagers are at risk of pregnancy, and early pregnancy can have particularly severe consequences for their health and well-being.
Risk Factors
Numerous risk factors are associated with teen pregnancy, including:
- Poverty: Teenagers from low-income families are more likely to become pregnant than those from higher-income families.
- Lack of education: Teenagers who do not attend school or who drop out are more likely to become pregnant.
- Limited access to healthcare: Teenagers who do not have access to comprehensive sex education and contraception are more likely to become pregnant.
- Peer pressure: Teenagers who have friends who are pregnant or who engage in sexual activity are more likely to become pregnant themselves.
- Abuse and neglect: Teenagers who have experienced abuse or neglect are more likely to become pregnant.
Consequences
Teen pregnancy has numerous consequences for both the mother and the child.
Maternal Consequences:
- Increased risk of health complications: Teen mothers are more likely to experience premature birth, low birth weight, and other pregnancy-related complications.
- Lower educational attainment: Teen mothers are more likely to drop out of school and have lower levels of educational attainment.
- Economic hardship: Teen mothers are more likely to live in poverty and experience economic hardship.
Child Consequences:
- Increased risk of health problems: Children of teen mothers are more likely to have health problems, such as low birth weight, developmental delays, and chronic diseases.
- Lower educational attainment: Children of teen mothers are more likely to drop out of school and have lower levels of educational attainment.
- Increased risk of poverty: Children of teen mothers are more likely to live in poverty.
Prevention and Intervention
Preventing teen pregnancy requires a comprehensive approach that addresses the underlying risk factors. Effective prevention strategies include:
- Comprehensive sex education: Providing teenagers with accurate and age-appropriate information about sexual health and reproduction.
- Access to contraception: Ensuring that teenagers have access to a wide range of contraceptive methods.
- Support for teen parents: Providing teen parents with support services, such as prenatal care, parenting education, and job training.
- Addressing social and economic factors: Addressing the social and economic factors that contribute to teen pregnancy, such as poverty, lack of education, and abuse and neglect.
Conclusion
Teen pregnancy remains a significant public health concern in the United States, despite the progress that has been made in reducing its prevalence. Disparities in teen birth rates across racial and ethnic groups and across states highlight the need for targeted interventions to address the specific needs of these populations. Understanding the trends and patterns of teen pregnancy is crucial for developing effective prevention and intervention strategies that can improve the health and well-being of teenagers and their children.