Teen Pregnancy in Ireland: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
Teen pregnancy remains a significant public health concern in Ireland, with rates consistently higher than the European average. This issue has far-reaching implications for both the young mothers and their children, as well as society as a whole. This article provides a comprehensive overview of teen pregnancy in Ireland, exploring its causes, consequences, and potential solutions.
Prevalence and Trends
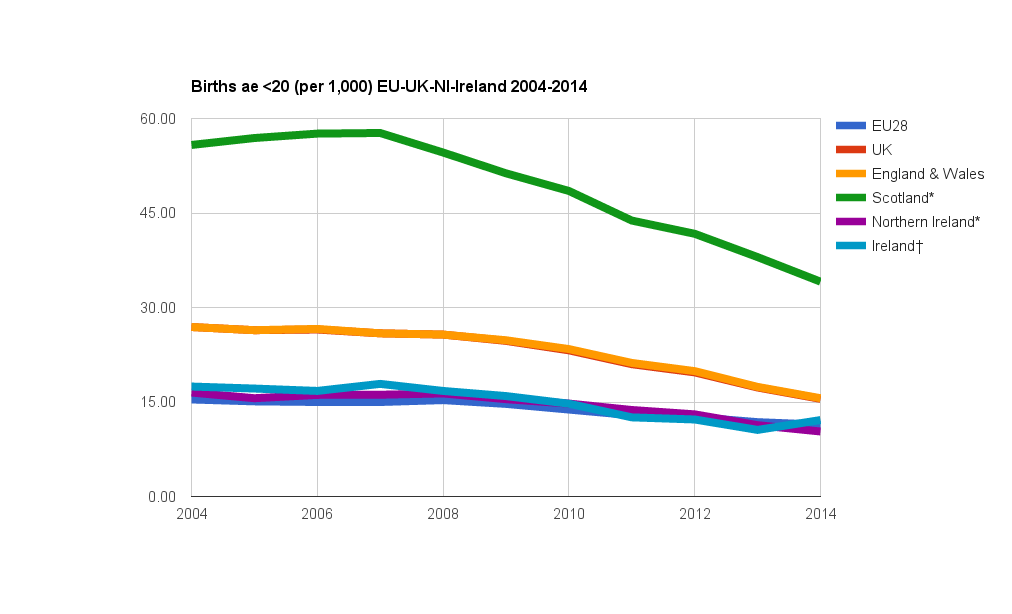
According to the Central Statistics Office (CSO), in 2021, there were 5,075 births to mothers under the age of 20 in Ireland. This represents a rate of 13.5 per 1,000 women aged 15-19, which is higher than the EU average of 9.6 per 1,000.
Over the past decade, teen pregnancy rates in Ireland have shown a slight decline. However, they remain significantly higher than in many other developed countries. For example, in 2021, the teen pregnancy rate in the United States was 19.4 per 1,000, while in the United Kingdom it was 11.3 per 1,000.
Causes of Teen Pregnancy
The causes of teen pregnancy are complex and multifaceted. Some of the key factors identified include:
- Socioeconomic disadvantage: Teen mothers are more likely to come from low-income families, with limited access to education, employment, and healthcare.
- Lack of comprehensive sex education: Many young people in Ireland do not receive adequate sex education, which can lead to a lack of knowledge about contraception and sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
- Peer pressure and social norms: Teenagers who have friends who are pregnant or have children are more likely to become pregnant themselves.
- Mental health issues: Young people who experience mental health problems, such as depression or anxiety, are at increased risk of teen pregnancy.
- Abuse and exploitation: Teenagers who have been subjected to abuse or exploitation are more likely to become pregnant.
Consequences of Teen Pregnancy
Teen pregnancy has a range of negative consequences for both the young mothers and their children. These include:
- Health risks: Teen mothers are at increased risk of pregnancy complications, such as premature birth, low birth weight, and postpartum depression. Their children are also more likely to have health problems.
- Educational attainment: Teen mothers are less likely to complete their education, which can limit their future employment opportunities.
- Economic hardship: Teen mothers are more likely to experience poverty and unemployment.
- Social stigma: Teen mothers often face social stigma and discrimination, which can make it difficult for them to access services and support.
Children of Teen Mothers
Children of teen mothers also face a range of challenges. They are more likely to:
- Have health problems: Children of teen mothers are more likely to be born prematurely, have low birth weight, and experience developmental delays.
- Live in poverty: Children of teen mothers are more likely to live in poverty, which can have a negative impact on their health, education, and well-being.
- Experience educational difficulties: Children of teen mothers are more likely to have difficulties in school, including lower academic achievement and higher dropout rates.
- Be involved in crime: Children of teen mothers are more likely to be involved in crime and violence.
Solutions and Interventions
Addressing teen pregnancy requires a multi-pronged approach that involves both prevention and support services. Some of the key solutions and interventions include:
- Comprehensive sex education: Providing young people with comprehensive sex education is essential for reducing teen pregnancy rates. This education should include information about contraception, STIs, and healthy relationships.
- Access to contraception: Ensuring that young people have access to affordable and effective contraception is crucial for preventing teen pregnancy. This includes providing free or low-cost contraception through school-based clinics and other community health centers.
- Support for young mothers: Providing support for young mothers is essential for improving their health and well-being, as well as the well-being of their children. This support should include access to healthcare, education, and employment services.
- Addressing socioeconomic disadvantage: Addressing the socioeconomic factors that contribute to teen pregnancy is essential for reducing rates. This includes providing support for low-income families, improving access to education and employment, and reducing poverty.
- Community engagement: Engaging with communities to raise awareness about teen pregnancy and its consequences is important for changing social norms and attitudes. This can involve working with schools, youth groups, and community organizations.
Conclusion
Teen pregnancy remains a significant public health concern in Ireland. It has far-reaching consequences for both the young mothers and their children, as well as society as a whole. Addressing this issue requires a multi-pronged approach that involves both prevention and support services. By implementing evidence-based solutions and interventions, Ireland can reduce teen pregnancy rates and improve the health and well-being of young people and their children.