Teen Pregnancy Rates in 2001: A Comprehensive Analysis
Introduction
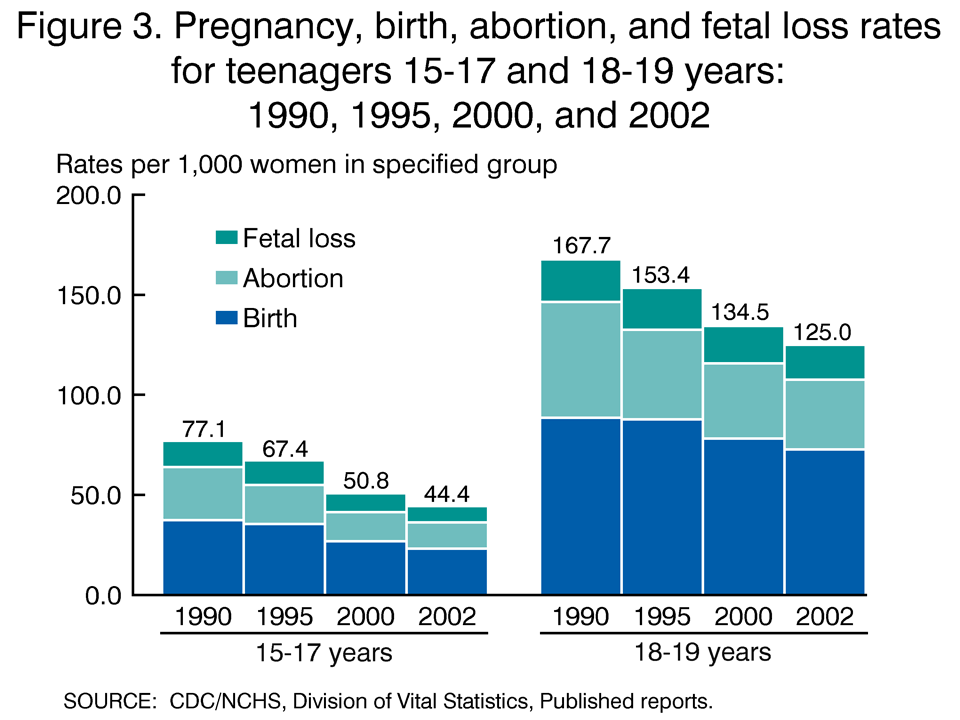
Teen pregnancy has been a persistent issue in the United States, with significant implications for the health and well-being of young women and their children. In 2001, the teen pregnancy rate in the United States stood at 45.3 per 1,000 females aged 15-19, a concerning statistic that highlighted the need for comprehensive interventions to address this issue. This article aims to provide an in-depth analysis of teen pregnancy rates in 2001, examining the contributing factors, disparities among different population groups, and the effectiveness of prevention strategies.
Contributing Factors
Numerous factors contribute to teen pregnancy, including:
- Early sexual initiation: Adolescents who engage in sexual activity at a young age are at an increased risk of pregnancy.
- Lack of comprehensive sex education: Inadequate knowledge about reproductive health and contraception can lead to unintended pregnancies.
- Socioeconomic disadvantage: Poverty, lack of access to healthcare, and limited educational opportunities can increase the likelihood of teen pregnancy.
- Peer pressure and social norms: Adolescents who are surrounded by peers who engage in sexual activity or who hold positive attitudes towards teen pregnancy may be more likely to become pregnant themselves.
- Mental health issues: Depression, anxiety, and other mental health conditions can impair judgment and increase the risk of risky sexual behaviors.
Disparities Among Population Groups
Teen pregnancy rates vary significantly among different population groups in the United States. In 2001, the rate was highest among Native American/Alaska Native adolescents (92.1 per 1,000), followed by African American adolescents (68.3 per 1,000), Hispanic adolescents (53.4 per 1,000), and White adolescents (29.8 per 1,000). These disparities are attributed to a complex interplay of socioeconomic, cultural, and historical factors.
Effectiveness of Prevention Strategies
A variety of prevention strategies have been implemented to address teen pregnancy, including:
- Comprehensive sex education: Programs that provide accurate and age-appropriate information about reproductive health and contraception have been shown to reduce teen pregnancy rates.
- Abstinence-only education: While abstinence-only programs may delay sexual initiation, they have not been found to be effective in reducing teen pregnancy rates.
- Access to contraception: Ensuring that adolescents have access to affordable and confidential contraception is crucial for preventing unintended pregnancies.
- Parent-child communication: Open and honest communication between parents and adolescents about sexual health can help reduce the risk of teen pregnancy.
- Community-based interventions: Programs that engage the entire community, including schools, healthcare providers, and community organizations, can create a supportive environment that promotes healthy sexual behaviors.
Evaluation of Prevention Strategies
Evaluating the effectiveness of teen pregnancy prevention strategies is essential to ensure that resources are being allocated to the most effective interventions. Studies have shown that comprehensive sex education programs that include information about both abstinence and contraception are the most effective in reducing teen pregnancy rates. Abstinence-only programs have not been found to be as effective, and may even increase the risk of teen pregnancy by delaying sexual initiation without providing adequate information about contraception.
Policy Recommendations
Based on the evidence, the following policy recommendations can be made to reduce teen pregnancy rates:
- Increase funding for comprehensive sex education programs: Ensure that all adolescents have access to accurate and age-appropriate information about reproductive health and contraception.
- Expand access to contraception: Make contraception affordable and confidential for all adolescents.
- Promote parent-child communication: Encourage open and honest communication between parents and adolescents about sexual health.
- Support community-based interventions: Invest in programs that engage the entire community in promoting healthy sexual behaviors.
- Address socioeconomic disparities: Implement policies that address the underlying socioeconomic factors that contribute to teen pregnancy.
Conclusion
Teen pregnancy remains a significant public health concern in the United States. In 2001, the teen pregnancy rate stood at 45.3 per 1,000 females aged 15-19, with significant disparities among different population groups. A comprehensive understanding of the contributing factors and effective prevention strategies is essential to reducing teen pregnancy rates and improving the health and well-being of young women and their children. By implementing evidence-based policies and programs, we can create a society where all adolescents have the knowledge, resources, and support they need to make healthy choices about their sexual health.