Teen Pregnancy: A Statistical Overview
Introduction
Teen pregnancy remains a prevalent issue in the United States, with significant implications for both individuals and society. This article delves into the latest statistics on teen pregnancy, exploring its prevalence, trends, and associated risk factors. By understanding these statistics, we can better develop and implement effective strategies to address this complex problem.
Prevalence of Teen Pregnancy
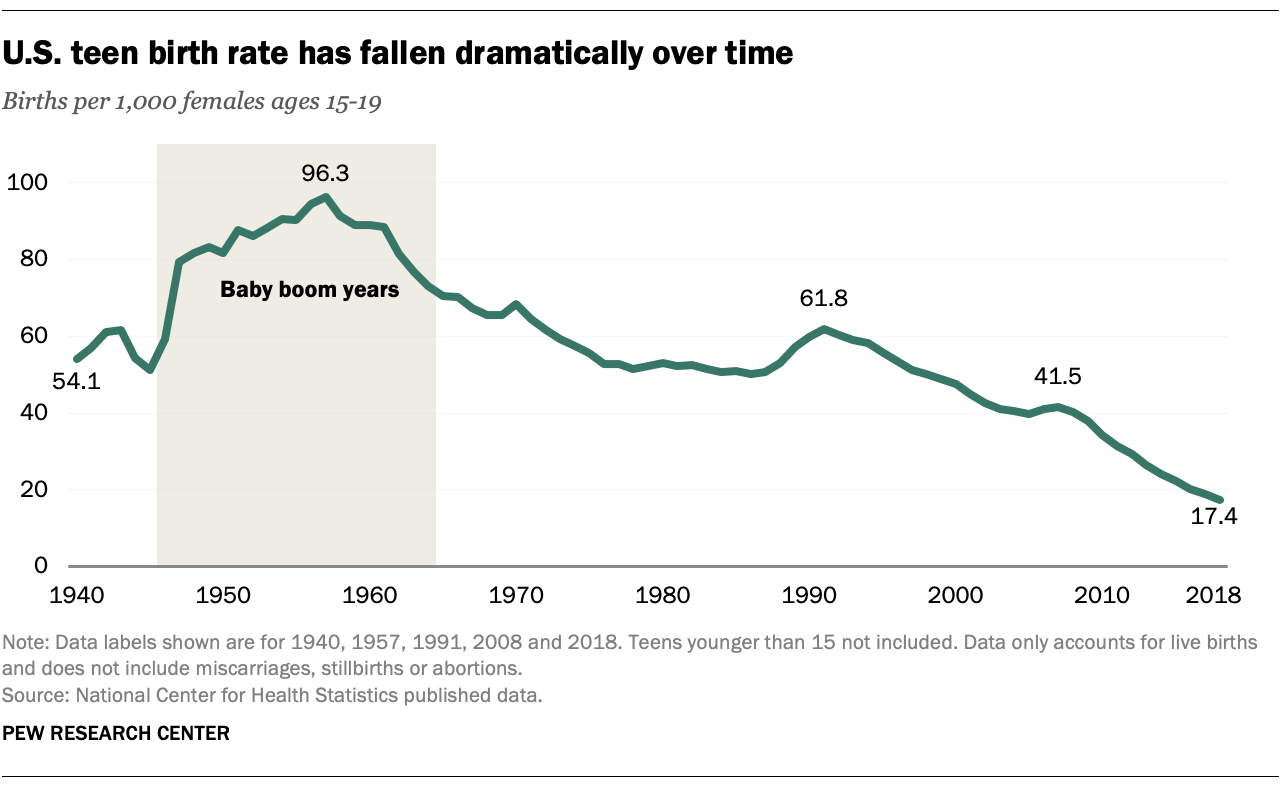
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), in 2020, the birth rate among females aged 15-19 was 17.4 per 1,000, a decline from 27.3 per 1,000 in 2010. While this decline is encouraging, teen pregnancy remains a significant public health concern.
Racial and Ethnic Disparities
Teen pregnancy rates vary significantly by race and ethnicity. In 2020, the birth rate among Black teenagers was 26.5 per 1,000, compared to 14.9 per 1,000 among Hispanic teenagers and 10.3 per 1,000 among White teenagers. These disparities highlight the need for targeted interventions to address the specific challenges faced by minority youth.
Geographical Variations
Teen pregnancy rates also vary geographically. In 2020, the highest birth rates among teenagers were observed in the South (20.6 per 1,000) and the Midwest (19.5 per 1,000), while the lowest rates were in the Northeast (13.2 per 1,000) and the West (12.6 per 1,000). These variations suggest that local factors, such as access to healthcare and education, play a role in teen pregnancy rates.
Trends in Teen Pregnancy
The teen pregnancy rate in the United States has been declining steadily over the past several decades. This decline is attributed to a number of factors, including increased access to contraception, improved sex education, and changes in social norms. However, the decline has slowed in recent years, and some experts are concerned that it may plateau or even reverse.
Consequences of Teen Pregnancy
Teen pregnancy has significant consequences for both the mother and the child. Teen mothers are more likely to experience health problems during pregnancy and childbirth, and their children are more likely to be born prematurely or with low birth weight. Teen mothers are also more likely to drop out of school, have lower incomes, and live in poverty.
Risk Factors for Teen Pregnancy
A number of factors increase the risk of teen pregnancy, including:
- Poverty: Teenagers who live in poverty are more likely to have children than those who live in more affluent households.
- Lack of education: Teenagers who do not attend school or who have low educational attainment are more likely to become pregnant.
- Peer pressure: Teenagers who have friends who are pregnant are more likely to become pregnant themselves.
- Sexual abuse: Teenagers who have been sexually abused are more likely to become pregnant.
- Mental health problems: Teenagers who have mental health problems are more likely to become pregnant.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing teen pregnancy requires a comprehensive approach that addresses the underlying risk factors. Effective prevention strategies include:
- Comprehensive sex education: Sex education programs that provide accurate information about contraception and sexually transmitted infections (STIs) can help teenagers make informed decisions about their sexual behavior.
- Access to contraception: Teenagers should have access to a wide range of contraceptive methods, including condoms, birth control pills, and intrauterine devices (IUDs).
- Support for teen parents: Teen parents need support to stay in school, find employment, and provide a stable home for their children.
- Community involvement: Communities can play a role in preventing teen pregnancy by providing after-school programs, mentoring, and other support services for teenagers.
Conclusion
Teen pregnancy remains a significant public health issue in the United States, with serious consequences for both individuals and society. By understanding the statistics on teen pregnancy, we can better develop and implement effective prevention strategies. These strategies should focus on addressing the underlying risk factors, providing comprehensive sex education, ensuring access to contraception, supporting teen parents, and involving communities in prevention efforts. By working together, we can create a society where all teenagers have the opportunity to reach their full potential.