Teen Pregnancy Statistics: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
Teen pregnancy remains a prevalent issue in the United States, with significant implications for both the young mothers and their children. Understanding the statistics surrounding teen pregnancy is crucial for developing effective prevention and support strategies. This article provides a comprehensive overview of teen pregnancy statistics in the United States, examining trends, risk factors, and the impact on individuals and society.
Prevalence and Trends
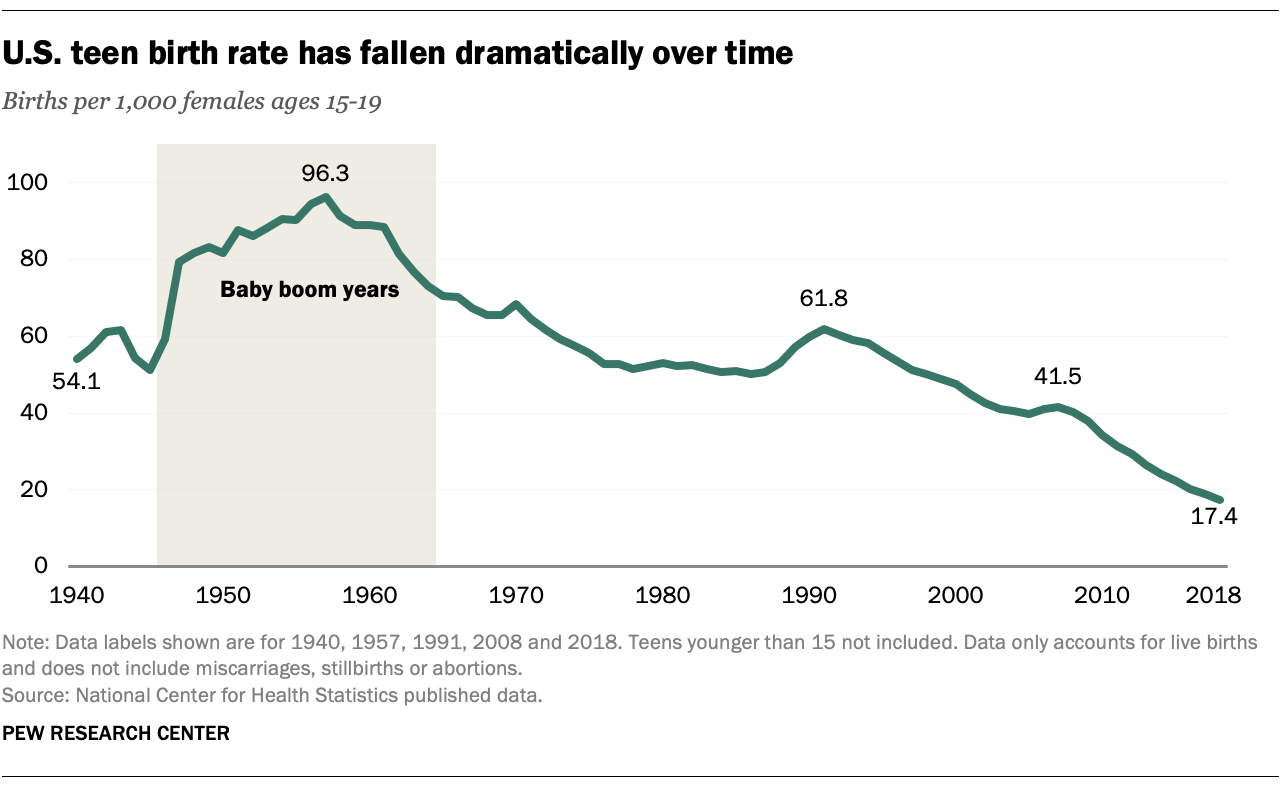
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), in 2020, the birth rate among teenagers aged 15-19 was 17.4 births per 1,000 females. While this rate has declined significantly since its peak in 1991, it remains higher than in many other developed countries.
Teen pregnancy rates vary widely by race and ethnicity. In 2020, the birth rate among Hispanic teenagers was 25.8 per 1,000, while the rate among non-Hispanic Black teenagers was 22.3 per 1,000. Non-Hispanic White teenagers had the lowest birth rate at 10.2 per 1,000.
Risk Factors
Numerous factors contribute to teen pregnancy, including:
- Socioeconomic status: Teenagers from low-income families are more likely to become pregnant than those from higher-income families.
- Education: Teenagers who drop out of school are at an increased risk of pregnancy.
- Peer pressure: Teenagers who have friends who are pregnant are more likely to become pregnant themselves.
- Lack of access to contraception: Teenagers who do not have access to reliable contraception are more likely to become pregnant.
- Sexual abuse: Teenagers who have been sexually abused are at an increased risk of pregnancy.
Consequences for Young Mothers
Teen pregnancy has significant consequences for young mothers, including:
- Health risks: Teen mothers are more likely to experience health complications during pregnancy and childbirth, such as premature birth and low birth weight.
- Educational attainment: Teen mothers are less likely to complete high school and pursue higher education.
- Economic instability: Teen mothers are more likely to live in poverty and experience unemployment.
- Mental health issues: Teen mothers are more likely to experience depression and anxiety.
Consequences for Children
Children born to teen mothers also face challenges, including:
- Health problems: Children born to teen mothers are more likely to have health problems, such as premature birth, low birth weight, and developmental delays.
- Educational difficulties: Children born to teen mothers are more likely to struggle in school and have lower educational attainment.
- Social and behavioral problems: Children born to teen mothers are more likely to experience social and behavioral problems, such as delinquency and substance abuse.
Societal Impact
Teen pregnancy has a significant impact on society as a whole, including:
- Increased healthcare costs: Teen pregnancy contributes to increased healthcare costs for both the young mothers and their children.
- Lost productivity: Teen pregnancy leads to lost productivity in the workforce as young mothers are less likely to be employed and more likely to experience unemployment.
- Increased crime: Children born to teen mothers are more likely to engage in criminal activity.
Prevention and Support
Preventing teen pregnancy requires a comprehensive approach that includes:
- Education: Providing teenagers with comprehensive sex education and access to contraception.
- Support services: Offering support services to teenagers who are at risk of pregnancy, such as counseling and mentoring.
- Community involvement: Engaging communities in efforts to prevent teen pregnancy, such as after-school programs and youth development initiatives.
Supporting teen mothers is also crucial for improving their outcomes and the well-being of their children. Support services for teen mothers include:
- Prenatal care: Providing access to prenatal care and support services for teen mothers.
- Education and job training: Offering education and job training programs to help teen mothers complete their education and secure employment.
- Housing and childcare assistance: Providing housing and childcare assistance to teen mothers to help them provide a stable environment for their children.
Conclusion
Teen pregnancy remains a serious issue in the United States, with significant consequences for both the young mothers and their children. Understanding the statistics surrounding teen pregnancy is essential for developing effective prevention and support strategies. By addressing the risk factors, providing comprehensive education and support services, and engaging communities, we can work towards reducing teen pregnancy rates and improving the outcomes for young mothers and their children.