Teen Pregnancy Statistics for 2000: A Comprehensive Analysis
Teen pregnancy remains a pressing public health concern in the United States, with significant implications for both the young mothers and their children. Understanding the prevalence, trends, and factors associated with teen pregnancy is crucial for developing effective prevention and intervention strategies. This article presents a comprehensive analysis of teen pregnancy statistics for the year 2000, providing insights into the magnitude and characteristics of this issue.
Prevalence and Trends
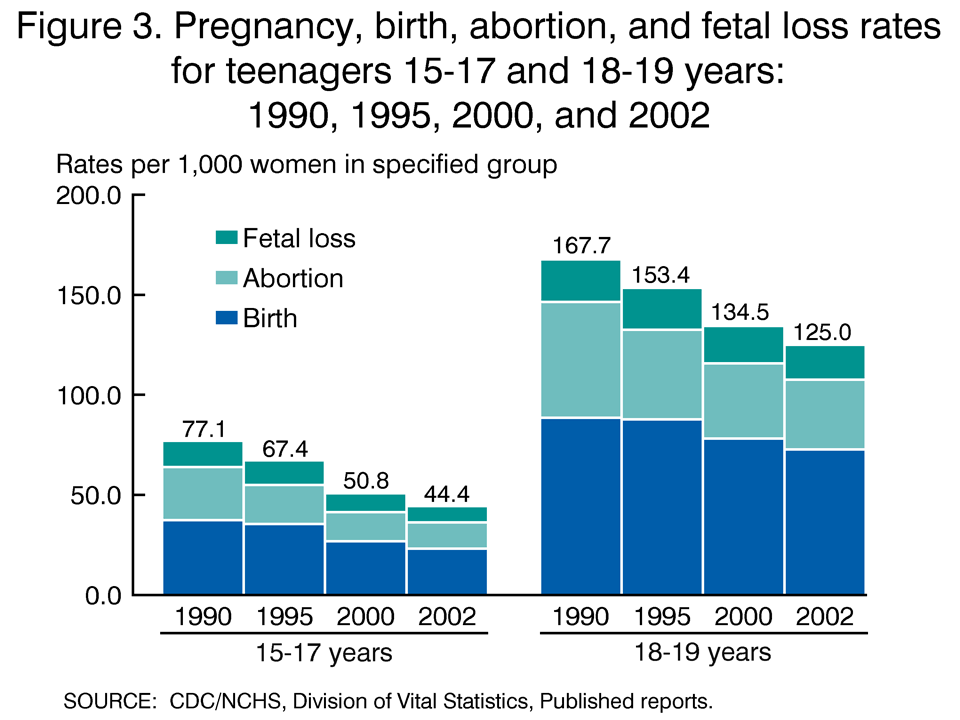
In 2000, an estimated 751,000 teenagers between the ages of 15 and 19 became pregnant in the United States. This translates to a pregnancy rate of 96.3 per 1,000 females in this age group. The pregnancy rate among teens has declined significantly over the past few decades, with a 27% decrease from 1990 to 2000. However, the rate remains higher than in many other developed countries.
Racial and Ethnic Disparities
Teen pregnancy rates vary significantly across racial and ethnic groups. In 2000, the pregnancy rate among non-Hispanic black teenagers was 168.2 per 1,000, more than twice the rate among non-Hispanic white teenagers (75.4 per 1,000). Hispanic teenagers also had a higher pregnancy rate (106.5 per 1,000) compared to non-Hispanic white teenagers. These disparities highlight the need for targeted interventions to address the unique challenges faced by minority youth.
Socioeconomic Factors
Socioeconomic factors play a significant role in teen pregnancy. Teenagers from low-income families are more likely to become pregnant than those from higher-income families. In 2000, the pregnancy rate among teenagers living below the poverty level was 129.3 per 1,000, compared to 63.3 per 1,000 among teenagers living above the poverty level.
Educational Attainment
Teenagers who drop out of school are at a higher risk of becoming pregnant. In 2000, the pregnancy rate among high school dropouts was 212.4 per 1,000, compared to 72.6 per 1,000 among high school graduates. This association between educational attainment and teen pregnancy underscores the importance of promoting educational success as a protective factor.
Consequences for Teen Mothers
Teen pregnancy has a profound impact on the lives of young mothers. Teen mothers are more likely to experience poverty, unemployment, and health problems. They are also more likely to have children with low birth weight and other health complications.
Consequences for Children
Children born to teen mothers face a range of challenges. They are more likely to be born prematurely, have low birth weight, and experience developmental delays. They are also more likely to live in poverty and have difficulty succeeding in school.
Prevention and Intervention Strategies
Preventing teen pregnancy requires a multifaceted approach that addresses the underlying factors that contribute to this issue. Effective strategies include:
- Comprehensive sex education: Providing teenagers with accurate and age-appropriate information about sexual health and contraception is essential for preventing unplanned pregnancies.
- Access to contraception: Ensuring that teenagers have access to a range of contraceptive methods, including condoms, birth control pills, and long-acting reversible contraceptives (LARCs), is crucial for reducing pregnancy rates.
- Economic support: Providing financial assistance to low-income families can help reduce the risk of teen pregnancy by improving access to education, healthcare, and other essential resources.
- Mentoring and support programs: Providing teenagers with mentors and support programs can help them develop positive relationships, build self-esteem, and make healthy choices.
Conclusion
Teen pregnancy remains a significant public health concern in the United States. While the pregnancy rate has declined over the past few decades, it remains higher than in many other developed countries. Racial and ethnic disparities, socioeconomic factors, and educational attainment all play a role in teen pregnancy. Effective prevention and intervention strategies are essential for reducing the number of teen pregnancies and improving the lives of young mothers and their children.